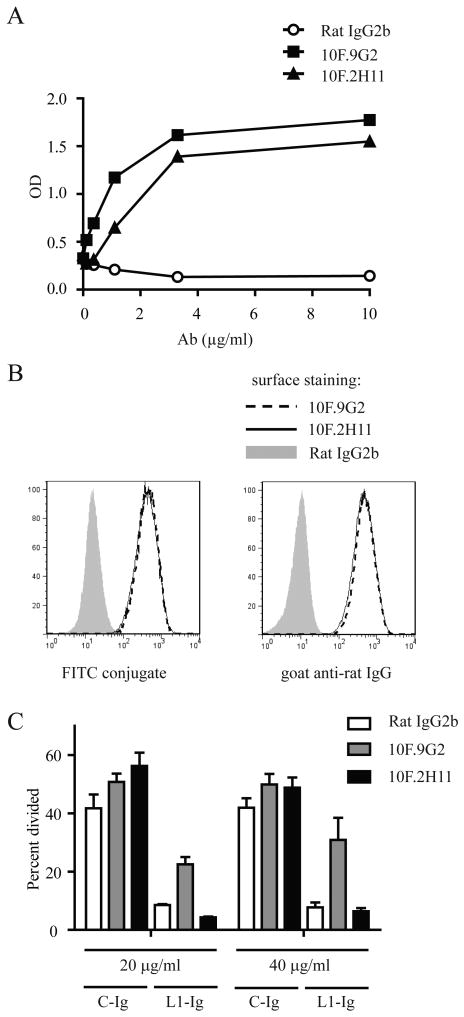
Figure 1. Anti-PD-L1 mAb 10F.2H11 does not interfere with functional PD-L1:PD-1 signaling, whereas 10F.9G2 does.
A, Binding of 10F.9G2, 10F.2H11 and Rat IgG2b isotype control mAb to PD-L1-Ig fusion protein was compared by ELISA. B, Binding of 10F.9G2 or 10F.2H11 to PD-L1-transfected 300.19 cells assessed by flow cytometry. Directly conjugated mAb (left panel) or fluorescently conjugated anti-rat IgG secondary (right panel) were used. C, Functional engagement of PD-1 is inhibited by 10F.9G2, but not 10F.2H11. PD-1-overexpressing transgenic T cells were cultured on plates coated with anti-CD3 and either PD-L1-Ig fusion protein (L1-Ig) or control protein (C-Ig). After coating, plates were incubated with the indicated concentrations of anti-PD-L1 Abs or control Ab, washed and then T cells were added. Proliferation was measured by CFSE dilution of 7-AAD-negative T cells by flow cytometry. Data are representative of at least two independent experiments.