Figure 3.
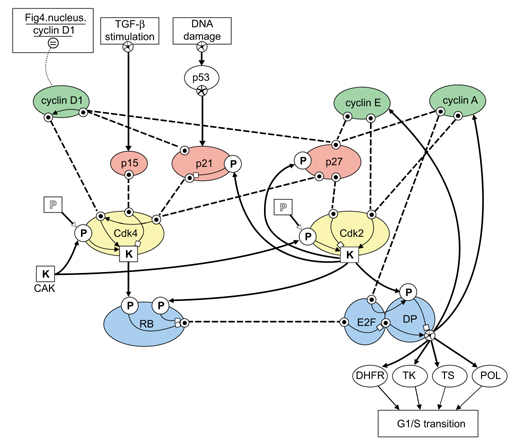
A BioD model of structures and functional elements controlling the G1/S transition of the cell cycle [6,10,11,12,13,14]. Key molecular players are represented by binding sites, phosphorylation sites and kinase sites whose occupancies and activities interact to control the cell cycle. The critical synthesis and degradation kinetics of cyclin D1 are represented by an 'identity' link to the nuclear cyclin D1 icon in the 'process' modeled in Figure 4. Additional inputs to the model (TGF-β stimulation and DNA damage) and outputs (G1/S transition) are included as unmodeled processes. CAK, cyclin-activating kinase; DP, DRTF1-polypeptide; DRTF, differentiation-regulated transcription factor; E2F, E2F transcription factor; TK, thymidine kinase; TS,thymidylate synthetase; POL, DNA polymerase.
