Figure 5.
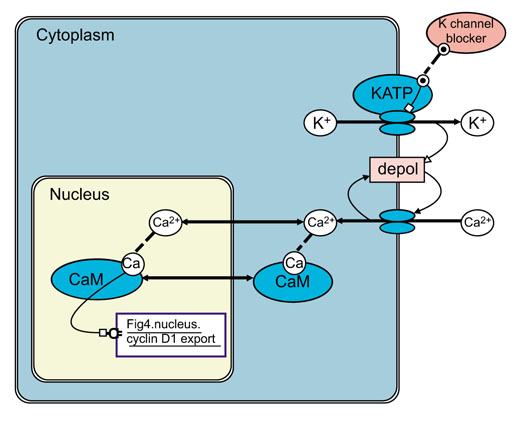
A model of the activation of calmodulin (CaM) by calcium influx in which K-channel blockers [46,47,48] inhibit ATP-sensitive potassium channels (KATP) and thus cause membrane depolarization (depol). Membrane depolarization activates voltage-dependent calcium 'ion channel' transporters and Ca2+ influx which have the dual effects of increasing intracellular Ca2+ concentration and further increasing depolarization. The action of Ca2+-activated CaM is linked via an action link (Fig 4.nucleus.cyclinD1.export) to the inhibition of cyclin D1 export in Figure 4.
