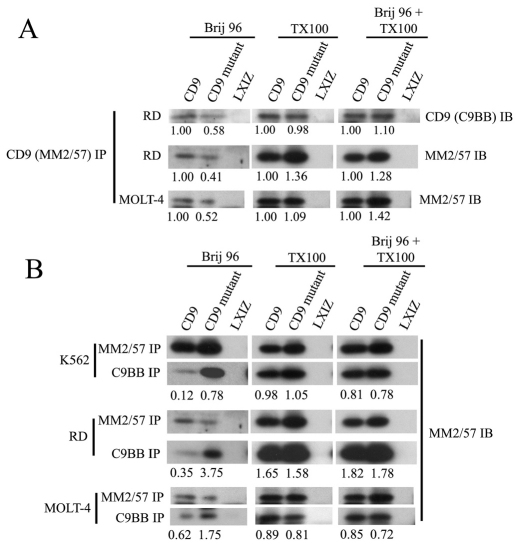
Fig. 6.
CD9 mutation affects recovery of CD9 complexes in Brij 96 detergent. (A) RD and MOLT-4 cells were lysed in 1% Brij 96, 1% Triton X-100, or 1% Brij 96 subsequently supplemented to also contain 1% Triton X-100. After immunoprecipitation (IP) using anti-CD9 mAb MM2/57 and SDS-PAGE resolution, CD9 was detected by immunoblotting using mAb C9BB or MM2/57. Numbers indicate recovery of mutant CD9 relative to that of wild-type CD9. Note that the six lower panels are used again in B for a different purpose. (B) After detergent lysis as in A, immunoprecipitations were carried out using anti-CD9 mAb MM2/57 or C9BB as indicated. CD9 was then detected by immunoblotting using mAb MM2/57. Numbers indicate recovery of CD9 (wild type or mutant) using mAb C9BB relative to mAb MM2/57. Note that the third and fifth panel rows are identical to images used in the second and third rows of A.