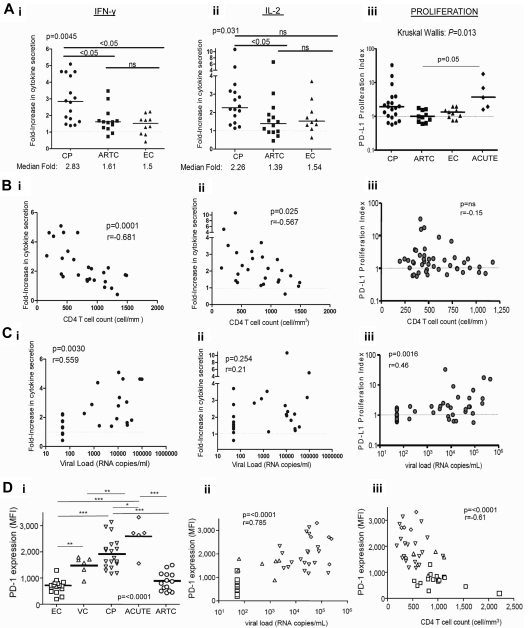
Figure 2.
Capacity of PD-L1 blockade to restore HIV-specific CD4 T-cell functions correlates with HIV disease stage. (Ai-iii) Statistical comparison of impact of PD-L1 blockade on IFN-γ (i) and IL-2 (ii) secretion and HIV-specific CD4 T-cell proliferation (iii) in subjects with different disease status; horizontal bars represent the median fold increase; statistical analysis was performed with the Kruskall Wallis test, followed by Dunn post-test for paired comparisons. (B-C) Correlation of the effect of PD-L1 blockade on IFN-γ (i), IL-2 (ii), and proliferation (iii), from untreated subjects (CP and EC), with the VL and CD4 count, respectively. Statistical analysis used the Spearman rank-sum test. (Di) PD-1 expression on HIV-specific CD4 T cells from CP (n = 18), ARTC (n = 14), VC (n = 6), EC (n = 15), and acutely infected subjects (ACUTE; n = 5; Kruskall Wallis test, followed by Dunn post-test for paired comparisons). (Dii-iii) Statistical analysis of the correlation of the PD-1 mean fluorescence intensity on the HIV-specific CD4 T cells with the VL and CD4 count. Statistical analysis used the Spearman rank sum test. Symbols for values: *P < .0; **P < .01; ***P < .001.