Table 2.
Scope and selectivity in nickel-catalyzed coupling of alkenes and isocyanates.
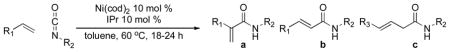 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| entrya | R1 | R2 | R3 | product(s) | yield a;b;c (%)b |
| 1 | n-hexyl | Cy | - | 6a, 6b | 79; 14; 0 |
| 2 | n-hexyl | t-Bu | - | 7a, 7b | 74; 17; 0 |
| 3 |
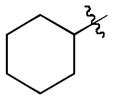
|
t-Bu | - | 8a | 91; 0; 0 |
| 4c |
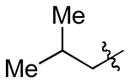
|
Cy | - | 9a, 9b | 74; 5; 0 |
| 5c | PhCH2 | Cy | Ph | 10a, 10b, 10c | 65; 8; 22 |
| 6c | PhCH2 | t-Bu | Ph | 11a, 11b, 11c | 83; 1d; 5d |
| 7c |
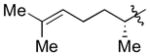
|
Cy | - | 12a | 86; 0; 0; |
| 8 |
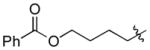
|
Cy | - | 13a, 13b | 74; 13; 0 |
| 9 |
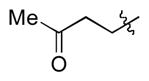
|
t-Bu | - | 14a, 14b | 70; 2; 0 |
| 10 |
|
t-Bu | - | 15a, 15b | 65; 9; 0 |
Standard conditions: Reactions were run with 0.5 mmol of 1-octene, 1.0 mmol of isocyanate, 0.05 mmol of Ni(cod)2, and 0.05 mmol of IPr in 0.5 mL toluene under Ar(g) in a sealed tube at 60 ºC for 18–24 h.
Isolated yields.
Reaction was run using 2 mL of toluene.
Isolated as a mixture of 10b and 10c, with relative ratios determined by 1H NMR.
