Fig 2.
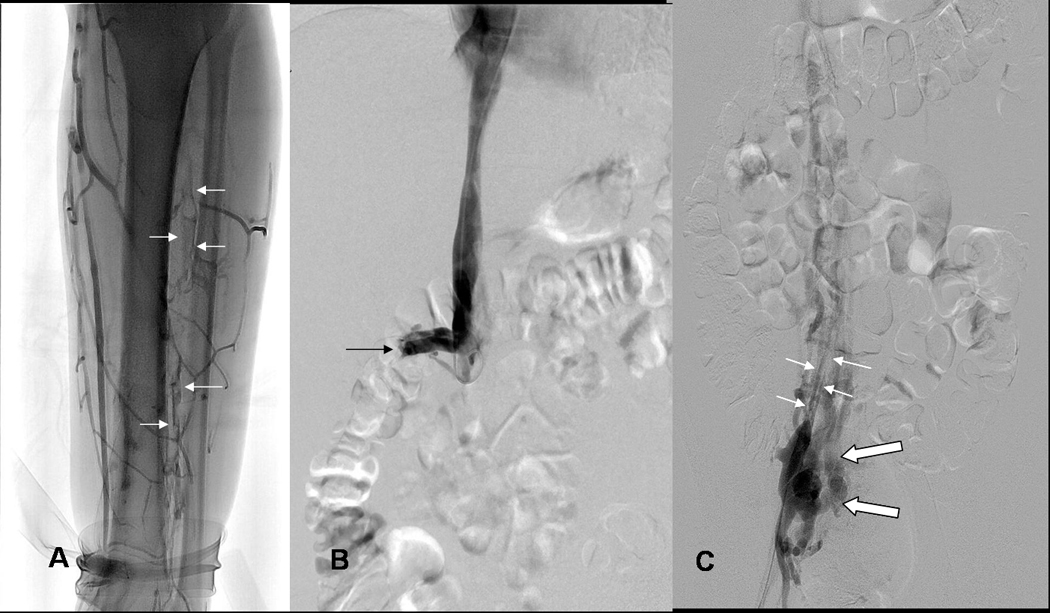
ABC: 19yo WM (patient 20) with Factor V-Leiden (FV-L) referred for acute DVT left leg.
A) Lower end of thrombosis: Left leg venogram shows thrombosis of peroneal veins (arrows) down to ankle; posterior tibial veins do not opacify due to occlusive thrombosis at mid calf level.
B) Upper end of thrombosis: IVCgram shows IVC occluded by thrombosis below renal veins (arrows, right renal vein), unsuspected because initial diagnosis was made by ultrasound examination only.
C) Asymptomatic right leg: Chronic thrombosis of right common iliac vein demonstrated by right femoral venogram shows narrow recanalized right common iliac vein (small white arrows) and collateral venous drainage from internal iliac vein to paravertebral collateral veins bypassing obstructed IVC (large open white arrows).
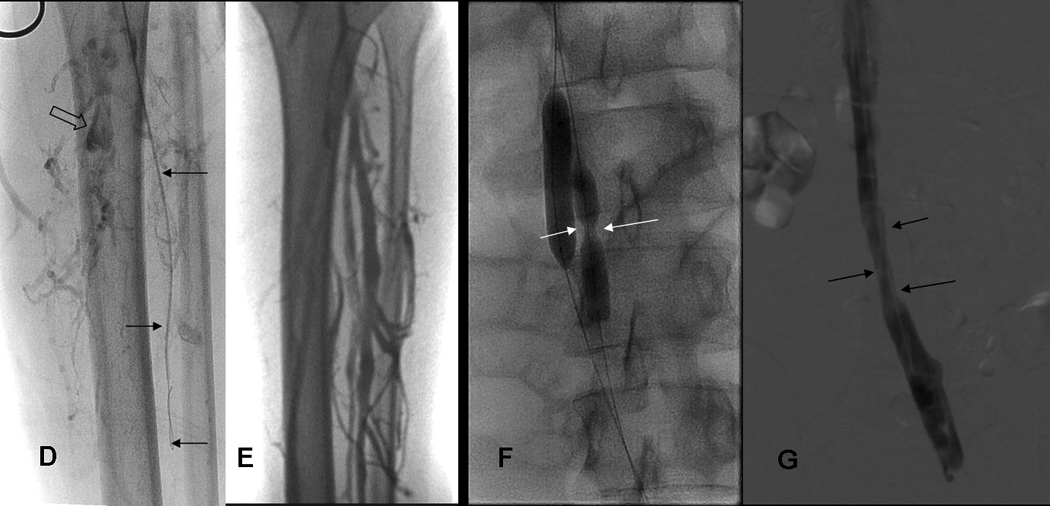
DEFG: 19yo WM with FV-L: Acute DVT left leg/IVC thrombosis received 3 treatments (10mg/10mg/8mg tPA).
D) Using retrograde femoral vein access, guidewire and 4 french glidecatheter (arrows) was passed down into clotted peroneal veins to allow intraclot injection of tPA. Note, thrombosis of proximal posterior tibial vein (open arrow).
E) Follow up leg venogram at 1 month shows patency of calf veins; patency also recovered in left popliteal, femoral and iliac veins (not shown).
F) IVC occlusion treated with pulse spray injections of tPA and double balloon dilatation (10 mm balloon introduced via right jugular vein, and 8 mm balloon from left femoral vein) of partially organized thrombus. Note presence of stricture in IVC (white arrows, 8mm balloon catheter).
G) Brisk flow restored in left external, left common iliac vein (mildly narrowed, arrows), and small IVC at 1 month.
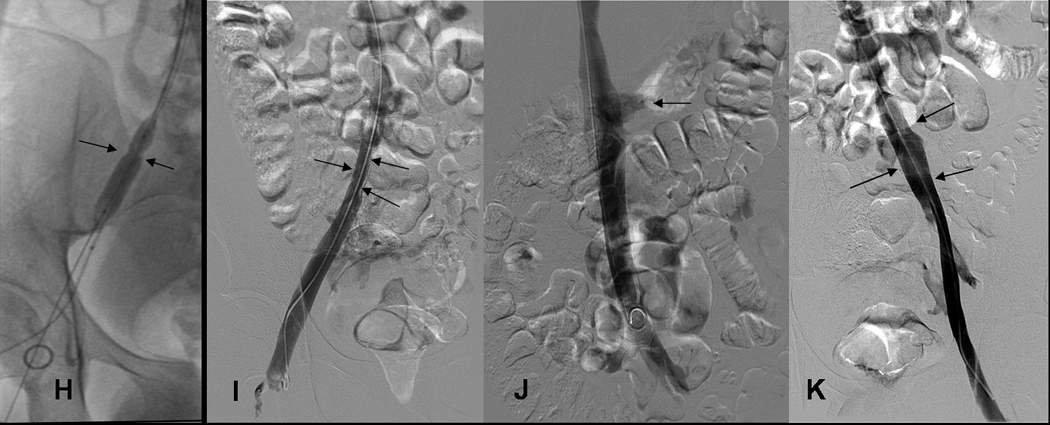
HIJK: 19 yo WM with FV-L: treatment chronic DVT right iliac vein and 6 month venograms.
H) Narrowed right common iliac vein (arrows) was dilated with 10 mm balloon 1 month after treatment of acute DVT left leg and received 2 (6mg/ 6mg) treatments with tPA.
I) At 6 month follow up, despite mild narrowing (arrows), right common iliac vein is again the dominant pathway for venous return.
J) IVC patent (arrows, transient reflux into left renal vein) at 6 months.
K) Left femoral, external iliac and common iliac vein at 6 months. Left Common iliac vein (arrows) caliber has improved since 1 month study (see Fig. 2G).
