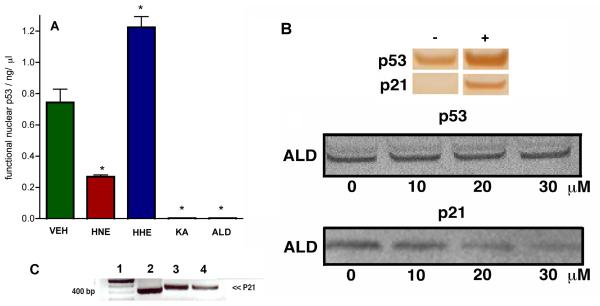
Figure 3. Lipid Aldehydes Affect Wild-type p53 DNA Binding and p21 Activation in Cells.
A Bar chart representing level of DNA binding nuclear p53 extracted from A-427 cells incubated at 37 °C for 24 h with either VEH (0.1 % ethanol), HNE, HHE, KA or ALD (each at 40 μM) after receiving a dose of γ-radiation (5000 rads). After the incubation, nuclear extracts were taken, total protein (BCA), p53 (Western blot) and functional p53 (ELISA) were measured. Data are reported as the mean ± SEM of triplicate determinations. Data was analyzed using a student two-tail t test and was considered significantly different from VEH (*) if P<0.05. B Upper Western blot analysis of p53 and p21 in nuclear protein extracts from A-427 cells before (−) and after (+) receiving γ-radiation (5000 rads). Lower Western blot analysis of p53 and p21 in nuclear protein extracts from A-427 cells. Cells incubated at 37 °C for 24 h with ALD (0-30 μM) after receiving a dose of γ-radiation (5000 rads). After the incubation, nuclear extracts were taken, total protein (BCA), p53 and p21 (Western blot) were measured. C Agarose gel analysis of p21 PCR DNA derived from p53 immunoprecipitation (IP) of A-427 genomic DNA. Lane 1, 100 bp ladder; Lane 2, A-427 genomic DNA with p53 IP (after irradiation); Lane 3, A-427 genomic DNA with p53 IP (after irradiation and incubated with VEH for 20 h); Lane 4, A-427 genomic DNA with p53 IP (after irradiation, ALD, 30 μM for 20 h).