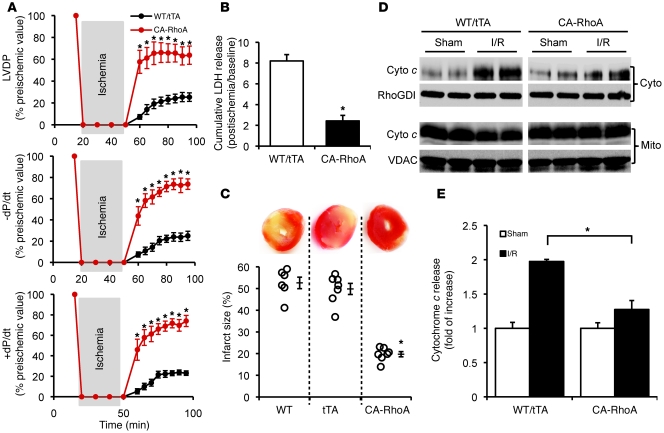
Figure 3. RhoA activation protects against I/R injury in the isolated perfused heart.
WT, tTA, and CA-RhoA mice (8 weeks off Dox) were subjected to global I/R. (A) Time course recovery of contractility following ischemia measured by LVDP, +dP/dt, and –dP/d. *P < 0.001 versus WT/tTA (n = 7). (B) LDH release to the coronary effluent following 45 minutes reperfusion. WT and tTA were not significantly different, and data were pooled together as WT/tTA. *P < 0.001 versus WT/tTA (n = 6). (C) Representative TTC-stained heart sections (top) and quantitative analysis of infarct size (bottom). *P < 0.001 versus WT or tTA (n = 6–7). (D and E) The LV of the WT/tTA and CA-RhoA hearts were fractioned following 30 minutes I/30 minutes R, and cytosolic (cyto) and mitochondrial (mito) cytochrome c (cyto c) were analyzed by Western blots. (D) Representative blots showing cyto (top) and mito (bottom) cytochrome c level. (RhoGDI and VDAC were used as cytosolic and mitochondrial loading control, respectively. VDAC was not detected in the cytosol fraction and RhoGDI was not detected in the mitochondrial fraction.) (E) Quantification of cytochrome c release in the cytosolic fraction. *P < 0.05 (n = 4). Data are shown as mean ± SEM.