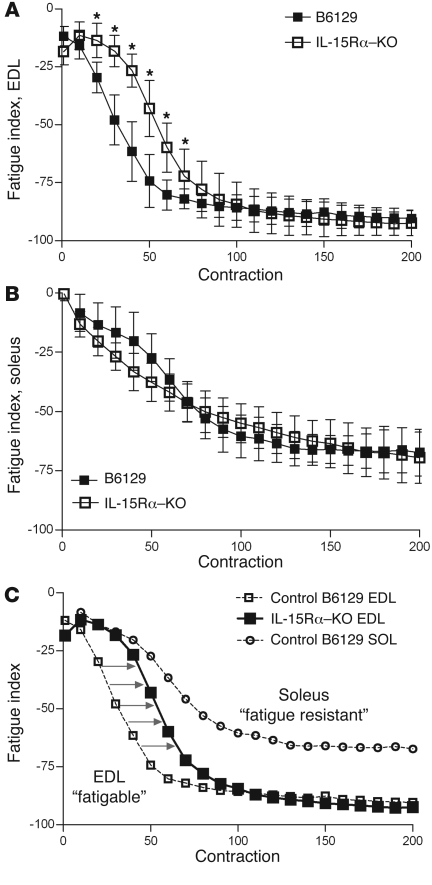
Figure 1. Fast EDL muscles from IL-15Rα–KO mice adopt a more oxidative, fatigue-resistant phenotype.
A repeated stimulation protocol was performed to determine the fatigue characteristics of isolated EDL muscles. Muscles were stimulated for 330 ms every second for 6 minutes, and the fatigue index was calculated as the percent difference in tetanic force between the first contraction and each subsequent contraction. (A) The fatigue curve of EDL muscles from IL-15Rα–KO mice (n = 8 muscles) was shifted to the right compared with EDL muscles from B6129 control mice (n = 8 muscles), indicating a resistance to repeated stimulation–induced fatigue. (B) No differences were observed in the fatigue index of soleus muscles from IL-15Rα–KO (n = 8 muscles) and B6129 control mice (n = 8 muscles). (C) The fatigue curve for EDL muscles from IL-15Rα–KO mice is plotted with fatigue curves of EDL and soleus muscles from B6129 control mice. The fatigue curve from IL-15Rα–KO EDL muscles lies between the curves for the fatigable EDL muscle and the fatigue-resistant soleus muscle, highlighting the oxidative characteristics of EDL muscles deficient in IL-15Rα. 350 total contractions were analyzed per muscle, with data presented as mean ± SD. *P < 0.05.