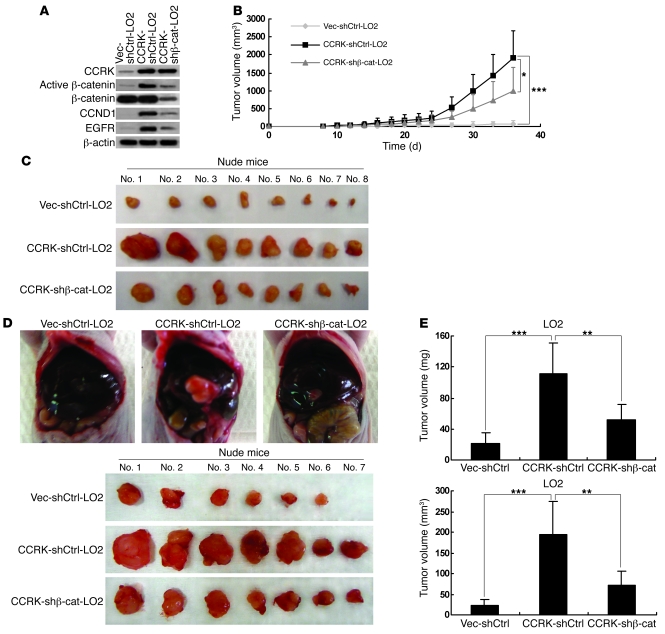
Figure 8. Silencing β-catenin expression reduces CCRK-induced tumorigenicity in nude mice.
(A) Expression of CCRK, CCND1, EGFR, active, and total β-catenin in Vec-shCtrl-LO2, CCRK-shCtrl-LO2, and CCRK–shβ-catenin–LO2 cells was detected by Western blot. β-actin was used as a loading control. (B) CCRK-shCtrl-LO2 cells displayed highly elevated tumor growth in nude mice when compared with Vec-shCtrl-LO2 cells. However, CCRK-induced tumorigenicity was decreased by β-catenin knockdown, as shown in mice injected with CCRK–shβ-catenin–LO2 cells. (C) Images of the tumors formed in the nude mice injected with the 3 types of cells are shown. (D) Intrahepatic tumorigenicity of Vec-shCtrl-LO2, CCRK-shCtrl-LO2, and CCRK–shβ-catenin–LO2 cells was determined by an orthotopic mouse model. Images of the tumors excised from the livers in each group are shown. (E) Knockdown of β-catenin significantly attenuated the intrahepatic tumorigenicity induced by CCRK. The weight and volume of the excised tumors in the 3 groups were measured. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. Data are presented as mean + SD of 3 independent experiments.