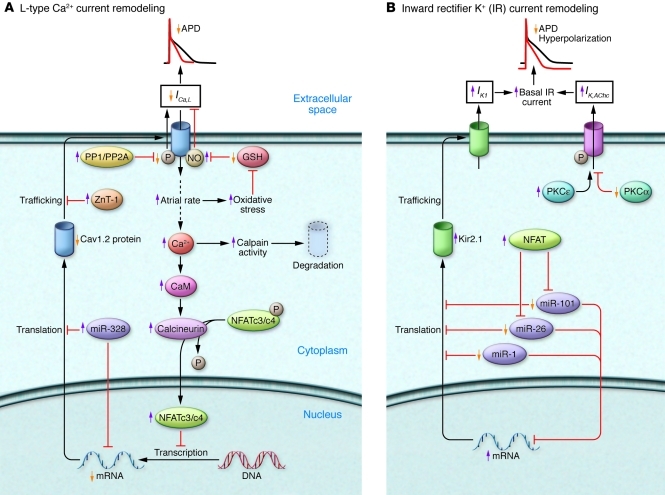
Figure 8. Remodeling of ICa,L and inward-rectifier K+ currents by AF/tachycardia.
(A) The high atrial rate in AF increases intracellular Ca2+ load, activating calcineurin via the Ca2+/calmodulin system. Calcineurin stimulates nuclear translocation of nuclear factor of activated T lymphocytes (NFAT), reducing transcription of the principal ICa,L subunit, Cav1.2. Increased mRNA degradation/impaired protein translation of Cav1.2 and breakdown of Cav1.2 protein by calpains may also contribute. Increased expression of zinc transporter–1 (ZnT-1) impairs membrane trafficking of Cav1.2. Reduced Cav1.2 phosphorylation due to increased protein phosphatase (PP) activity and increased channel nitrosylation may also decrease ICa,L. GSH, glutathione. (B) Increased IK1 density results from upregulation of the principle Kir2.1 subunit, likely due to reduced levels of inhibitory miRNAs (miR-101, miR-26, miR-1). Increased IK,AChc is caused by altered PKC regulation: increased membrane abundance of stimulatory PKCε and reduced expression of inhibitory PKCα.