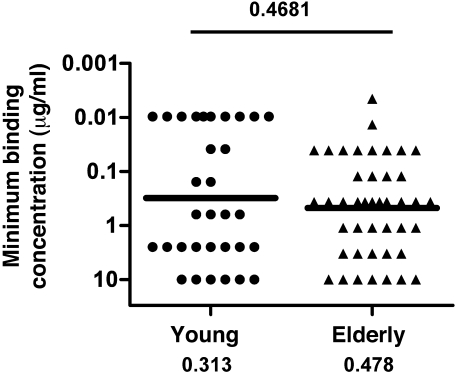
Figure 6. Affinity of influenza vaccine virus-specific re-mAbs derived from young and elderly recipients of seasonal TIV.
Binding affinity was measured by ELISA with microtiter plates coated with individual vaccine component viruses. The binding affinity was defined as the minimum concentration of each re-mAb that resulted in an OD405nm greater than 0.607 in the assay. All re-mAbs (32 from the young group; 43 from the elderly group) with a minimum binding concentration up to 10 μg/ml for 1 of the vaccine component viruses were considered vaccine specific and included for this analysis. The OD405nm threshold of 0.607 was set at a level that would exclude 95% of random control re-mAb as vaccine-specific, based on ELISA results of 48 such re-mAbs derived from individual naive B cells. Geometric means of minimum binding concentrations are shown as bars and numerical values below.