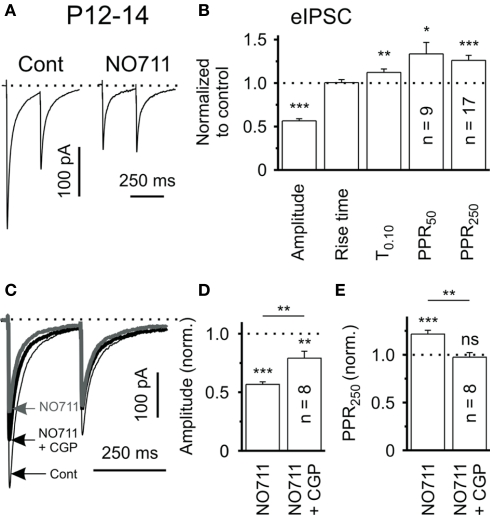
Figure 1.
Tonic activation of presynaptic GABABRs induced by GAT-1 blockade in rat brain slices. (A) eIPSCs in response to paired-pulse stimulation (ISI 250 ms) in control solution and in the presence of the GAT-1 blocker, NO-711 (10 μm), in slices of P12-14 rats. Traces represent averages of 20 responses. (B) Quantification of results for NO-711 effects on the mean eIPSC amplitude, PPR (PPR50: ISI 50 ms, PPR250: ISI 250 ms), rise time (20–80%) and decay (T0.10) of striatal eIPSC. Data from 17 striatal output neurons (SONs), except PPR50. (C) Evoked IPSCs in response to paired-pulse stimulation (ISI 250 ms) in control solution and in the presence of either NO-711 or NO-711 plus the GABAB-receptor antagonist CGP55845 (1 μm). Traces represent averages of 20 responses. (D,E) CGP55845 partially restored the NO-711-induced reduction in eIPSC amplitude and completely reversed the NO-711-induced increase in PPR (ISI 250 ms). ns – not significant, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. Reprinted from Kirmse et al. (2008) with permission from John Wiley and Sons.