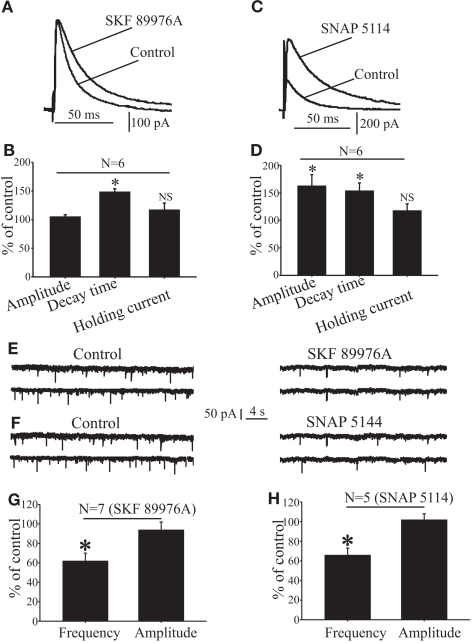
Figure 5.
Effects of GAT-1 and GAT-3 blockade on GABAergic and glutamatergic synaptic transmission in the rat GP. (A) Application of SKF 89976A increases the decay time, but not the amplitude of IPSCs evoked in GP neurons after striatal stimulation. (B) Bar graph showing that SKF 89976A increases the decay time, but has no effect on the amplitude and base line holding currents of eIPSCs expressed as percent of control ± SEM (*P < 0.005). (C) Application of SNAP 5114 increases the amplitude and decay time of IPSCs evoked in GP neuron by striatal stimulation. (D) Bar graph summarizing the effects of SNAP 5114 on eIPSCs amplitude, decay time, and holding current expressed as percent of control ± SEM (*P < 0.005). (E,F). Sample traces showing mEPSCs recorded in control condition and during SKF 89976A or SNAP 5114 application. (G,H) The summary bar graphs show that SKF 89976A or SNAP 5114 significantly reduce the frequency, but not amplitude of mEPSCs. * P < 0.01. For more details see Jin et al. (2009, 2011).