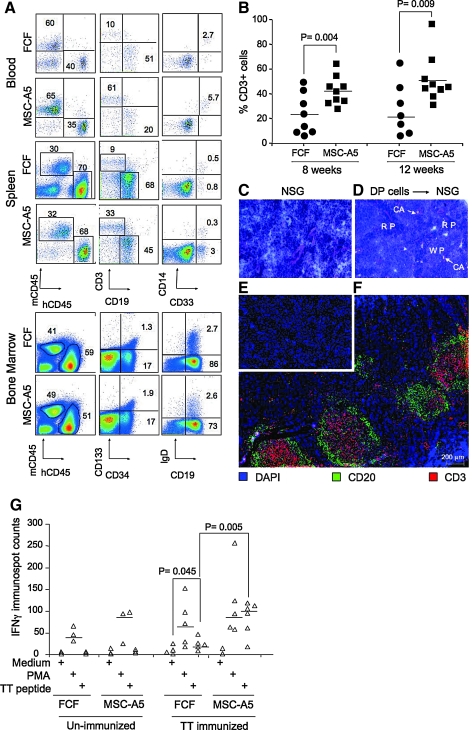
FIG. 5.
Expanded cells are capable of differentiating into multiple lineages of hematopoietic cells in NSG mice. (A) CD34+ CD133+ cells from the same donor were either expanded in the MSC-A5 coculture or the FCF culture for 11 days. Total expanded cells, containing 105 DP cells, were engrafted into sublethally irradiated NSG neonates. Fourteen weeks after injection, the presence of various lineages of human hematopoietic cells in the blood, spleen, and bone marrow were analyzed by flow cytometry. All staining profiles were gated on human CD45+ cells, except for mCD45 versus hCD45 staining profiles, which were gated on total live cells from the individual tissues. The percentage of human CD45+ cells is calculated by [%hCD45+/(%hCD45+ + %mCD45+)] and the percentage of mouse CD45+ cells is calculated by [%mCD45+/(%hCD45+ + %mCD45+)]. Representative dot plots are shown from 1 set of mice reconstituted with cells from the same cord blood. Cord blood from 3 different donors were used. (B) Blood was sampled at 8 and 12 weeks postengraftment and mononuclear cells were stained for human CD45, CD3, and CD19. The percentages of CD3+ cells among CD45+ cells are shown for mice reconstituted with expanded cells from MSC-A5 cocultures or FCF culture. Each symbol represents 1 mouse. The horizontal line indicates the median value. (C–F) Comparison of hematoxylin and eosin, or CD3 and CD20 immunohistochemical staining of spleen sections of NSG mice (C, E) and NSG mice engrafted with expanded cells from MSC-A5 cocultures (D and F, 20 weeks after engraftment). (C, D) Hematoxylin and eosin staining, showing spleen architecture with the red pulp (RP), the white pulp (WP), and the arrows pointing at the central arterioles (CA). Magnification 4 × . (E, F) Anti-CD3 and anti-CD20 staining. Scale bar is 200 μm. (G) T-cell responses in mice engrafted with coculture-expanded cells. Mice with similar human leukocyte reconstitution were immunized with TT thrice with 3 weeks' interval. Two weeks after the third immunization, the percentages of human T cells from the spleen were determined by flow cytometry. For ELISPOT assay, the same number (5 × 105) of human T cells from different samples were seeded into wells coated with anti-human IFN-γ antibody and cultured for 48 h under 3 conditions: medium alone (control), in the presence of phorbol myristate acetate, or in the presence of a TT-specific peptide. A comparison of the numbers of IFN-γ immunospots among different samples is shown. Each symbol represents 1 mouse. Data shown are from 1 of 2 independent experiments. IFN-γ, interferon gamma; TT, tetanus toxoid.