Abstract
We describe here the design, synthesis, molecular modeling, and biological evaluation of a series of small molecule, nonpeptide inhibitors of SARS-CoV PLpro. Our initial lead compound was identified via high-throughput screening of a diverse chemical library. We subsequently carried out structure-activity relationship studies, and optimized the lead structure to potent inhibitors that have shown antiviral activity against SARS-CoV infected Vero E6 cells. Based upon the X-ray crystal structure of one of the potent inhibitors 24-bound to SARS-CoV PLpro, a drug-design template was created. Our structure-based modification led to the design of a more potent inhibitor, 2 (enzyme IC50 = 0.46 μM; antiviral EC50 = 12.5 μM). Interestingly, its methylamine derivative 49 displayed good enzyme inhibitory potency (IC50 = 1.3 μM) and most potent SARS antiviral activity (EC50 = 2.5 μM) in the series. We have carried out computational docking studies and generated a predictive 3D-QSAR model for SARS-CoV PLpro inhibitors.
Introduction
Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS), a contagious and fatal respiratory illness, was first reported in Guangdong province, China, in November 2002.1 It rapidly spread to other Asian countries, North America, and Europe, creating panic to both the public and the World Health Organization (WHO). The emergence of SARS affected more than 8000 individuals and caused 774 deaths within a few months.6 Quite remarkably, the spread of SARS-CoV was effectively halted within months after the initial outbreaks through public health measures. Through a concerted effort monitored by the WHO, scientists determined that SARS is caused by a novel coronavirus, SARS-CoV.2,3,3b The more recent isolation of strains from zoonotic origins thought to be the reservoir for SARS-CoV, emphasizes the possibility of a reemergence.4,5 It is quite alarming just how rapidly a contagious illness can spread in the more mobile and highly interconnected world of the 21st century. While there are no new reports of SARS cases, there is no guarantee that this outbreak will not strike again. Therefore, development of antivirals effective against SARS-CoV is important for future outbreaks.
The identification of biochemical events critical to the coronaviral lifecycle has provided a number of significant targets for halting viral replication. One of the early and essential processes is the cleavage of a multidomain, viral polyprotein into 16 individual components termed non-structural proteins, or nsps. These proteins assemble into complexes to execute viral RNA synthesis.7 Two cysteine proteases, a papain-like protease (PLpro) and a 3C-like protease (3CLpro), reside within the polyprotein. They catalyze their own release and that of the other nsps from the polyprotein and initiate virus-mediated RNA replication. Since 2003, numerous biochemical, structural and inhibitor development studies have been directed at the 3CLpro enzyme8, which cleaves eleven sites within the polyprotein. Recently, we reported potent inhibitors of 3CLpro that have shown antiviral activity against SARS-CoV.9
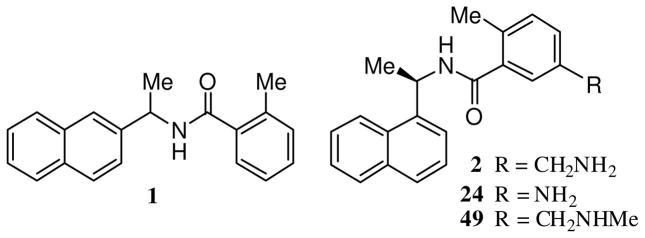
Recent structural and functional studies directed at PLpro have suggested potential roles for this protease beyond viral peptide cleavage, including deubiquitination, deISGylation, and involvement in virus evasion of the innate immune response.10,11 Furthermore, studies have shown that the homologous enzyme, PLP2, from the human coronavirus 229E, is essential for 229E viral replication.12 Therefore, PLpro has emerged as a significant drug development target. Our screening of a structurally diverse library of 50,080 compounds led to the discovery of a noncovalent lead inhibitor 1 (7724772, Figure 1), with an IC50 value of 20 μM as a racemic mixture.13 Subsequent SAR studies and lead optimization provided potent inhibitor 24 (IC50 = 600 nM) which also inhibits SARS-CoV viral replication in Vero cells with an EC50 value of 15 μM.13 In these studies, we also reported the X-ray crystal structure of SARS-CoV PLpro bound to inhibitor 24, which revealed important molecular insight into the ligand-binding site interactions. We now describe the full details of our significantly extended studies that include the design, synthesis, molecular modeling, and biological evaluation of a series of inhibitors of SARS-CoV PLpro.
Figure 1.
Structure of inhibitors 1, 2, 24 and 4
Chemistry
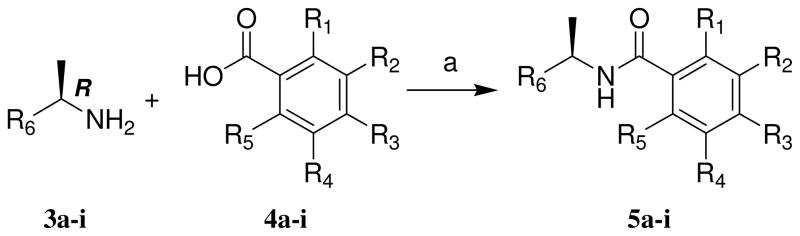
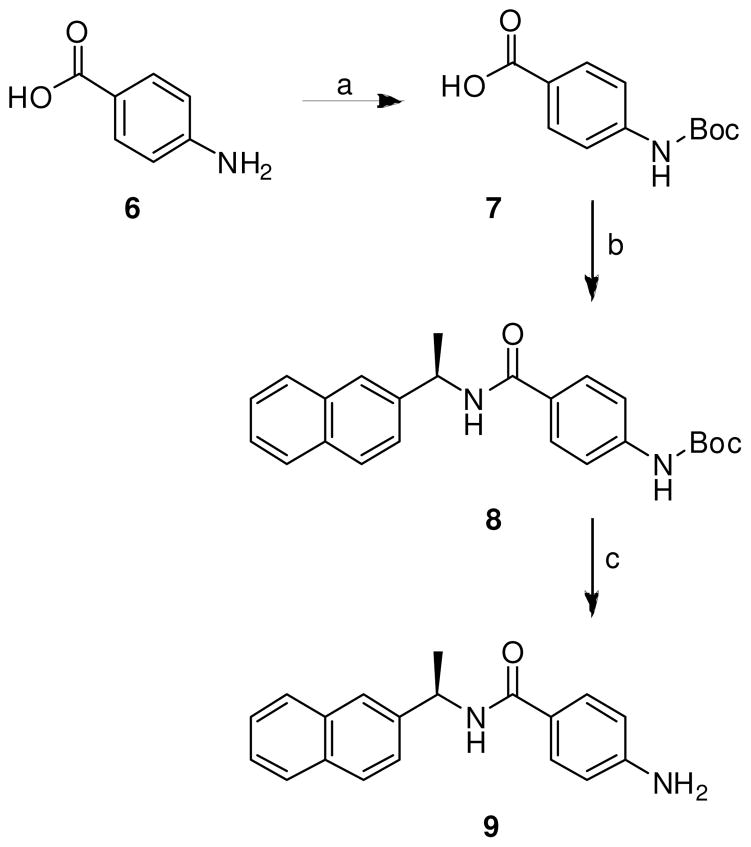
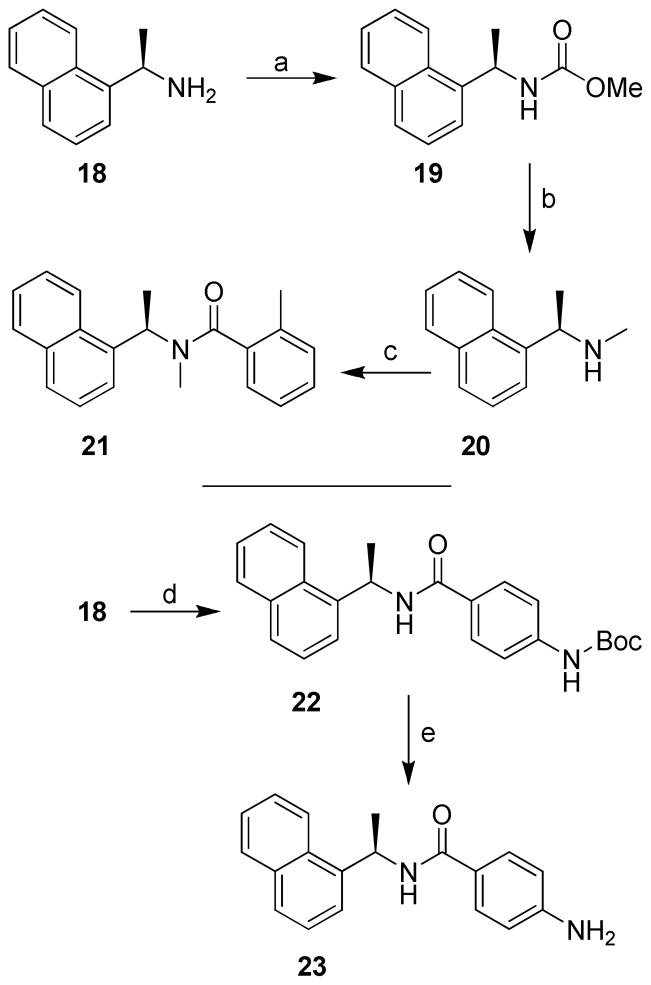
As shown in Scheme 1, coupling of (R)-(+)-1-(2-naphthyl)ethylamine or (R)-(+)-1-(1-naphthyl)ethylamine with benzoic acid derivatives utilizing N-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-N′-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride (EDCI), 1-hydroxybenzotriazole hydrate (HOBT) in the presence of diisopropylethylamine in CH2Cl2 at 23 ºC gave the corresponding inhibitor in excellent yield. Inhibitors 8 and 9 were synthesized by general method with N-Boc protected benzoic acid derivative followed by deprotection of the Boc group as shown in Scheme 2. Protection of p-aminobenzoic acid 6 with di-t-butyl dicarbonate in the presence of triethylamine in a mixture (2:1) of dioxane and water at 23 ºC for 16 h gave the corresponding t-Bu carbamate 7.14 A coupling reaction utilizing EDCI and HOBt provided inhibitor 8. Removal of the Boc group with trifluoroacetic acid in CH2Cl2 at 23 ºC for 2 h afforded inhibitor 9.
Scheme 1.
Reagents and conditions: (a) EDCI, HOBT, DIPEA, 23 ºC, 16 h.
| compounds | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | R5 | R6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5a | H | Me | H | H | H | 2-naphthyl |
| 5b | H | H | Me | H | H | 2-naphthyl |
| 5c | OMe | H | H | H | H | 2-naphthyl |
| 5d | H | OMe | H | H | H | 2-naphthyl |
| 5e | H | H | OMe | H | H | 2-naphthyl |
| 5f | Me | H | H | H | Me | 2-naphthyl a |
| 5g | OH | H | H | H | H | 2-naphthyl |
| 5h | Me | H | H | H | H | 1-naphthyl |
| 5i | Me | H | H | NO2 | H | 1-naphthyl |
Scheme 2.
Reagents and conditions: (a) Boc2O, Et3N, dioxane/H2O (2:1), 23 ºC, 16 h; (b) (R)-(+)-1-(2-naphthyl)ethylamine, EDCI, HOBT, DIPEA, CH2Cl2, 23 ºC, 16 h; (c) TFA, CH2Cl2, 23 ºC, 2 h.
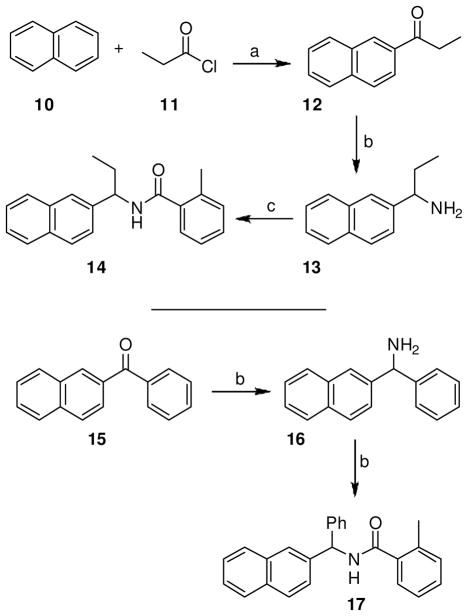
Inhibitors 14 and 17 were racemic compounds (Scheme 3). A Friedel-Crafts reaction of naphthalene 10 with propionyl chloride 11 in the presence of aluminum chloride in 1,2-dichloroethane at 35 ºC for 4 h gave ethyl naphthyl ketone 12.15 Reductive amination16 with ammonium acetate and sodium cyanoborohydride in methanol at 23 ºC for 24 h generated amine 13. Coupling of this amine with o-toluic acid provided inhibitor 14. Reductive amination of naphthyl phenyl ketone 15 by using similar conditions as the amine 13 gave amine 16. Coupling of 16 with o-toluic acid furnished inhibitor 17.
Scheme 3.
Reagent and conditions: (a) AlCl3, 1,2-dichloroethane, 35 ºC, 4 h; (b) NH4OAc, NaBH3CN, MeOH, 23 ºC, 24 h; (c) o-toluic acid, EDCI, HOBT, DIPEA, DMF, 23 ºC, 16 h; (d) o-toluic acid, EDCI, HOBT, DIPEA, CH2Cl2, 23 ºC, 16 h.
Inhibitor 21 with N-methyl amide was prepared as shown in Scheme 4. Protection of (R)-(+)-1-(1-naphthyl)ethylamine 18 with methyl chloroformate in the presence of potassium carbonate in a mixture (1:1) of dioxane and water at 0 ºC for 1 h afforded carbamate 19. Reduction of 19 with lithium aluminum hydride in THF at reflux for 1 h gave methylamine 20. A coupling reaction utilizing general methods provided inhibitor 21. Inhibitor 23 was prepared by coupling of optically active amine 18 with acid 7 as shown.
Scheme 4.
Reagents and conditions: (a) ClCO2Me, K2CO3, dioxane/H2O (1:1), 0 ºC, 1 h; (b) LiAlH4, THF, reflux, 1 h; (c) o-toluic acid, EDCI, HOBT, DIPEA, DMF, 23 ºC, 16 h; (d) 7, EDCI, HOBT, DIPEA, DMF, 23 ºC, 16 h; (e) TFA, CH2Cl2, 23 ºC, 2 h.
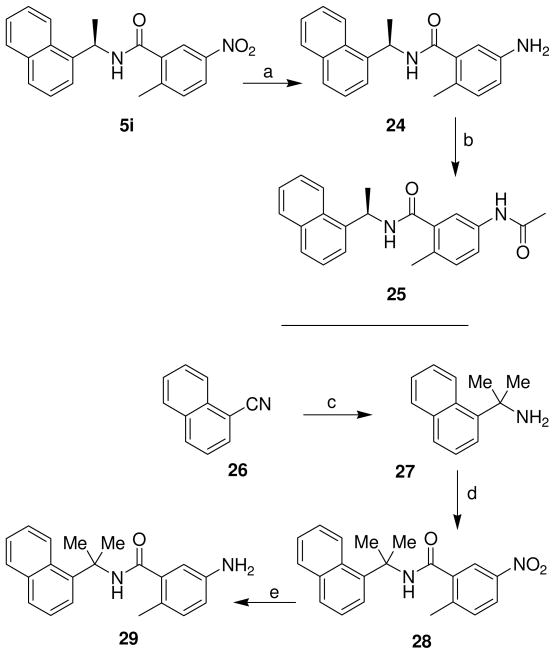
Inhibitor 24 and 25 containing 2-methyl-5-amino derivatives were synthesized as outlined in Scheme 5. Reduction of the nitro group in 5i by catalytic hydrogenation in the presence of 5% Pd-C in a mixture (1:1) of ethyl acetate and methanol at 23 ºC for 15 h provided inhibitor 24. Acetylation of 24 with acetic anhydride and triethylamine in CH2Cl2 at 23 ºC for 18 h generated inhibitor 25. The synthesis of inhibitor 29 with a gem dimethyl group in the α-naphthyl side chain was carried out by dimethylation of 1-cyanonaphthalene 26 with methyl lithium in the presence of cerium(III) chloride in tetrahydrofuran at 23 ºC for 2 h to provide amine 27.17 A coupling reaction using the general method described above provided 28, and hydrogenation in the presence of 5% Pd-C in a mixture (1:1) ethyl acetate and methanol at 23 ºC for 15 h provided inhibitor 29.
Scheme 5.
Reagents and conditions: (a) H2, Pd-C, EtOAc/MeOH (1:1), 23 ºC, 15 h; (b) Ac2O, Et3N, CH2Cl2, 23 ºC, 18 h; (c) MeLi, CeCl3, THF, 23 ºC, 2 h; (d) 2-Methyl-5-nitrobenzoic acid, EDCI, HOBT, DIPEA, CH2Cl2, 23 ºC, 16 h; (e) H2, Pd-C, EtOAc/MeOH (1:1), 23 ºC, 15 h.
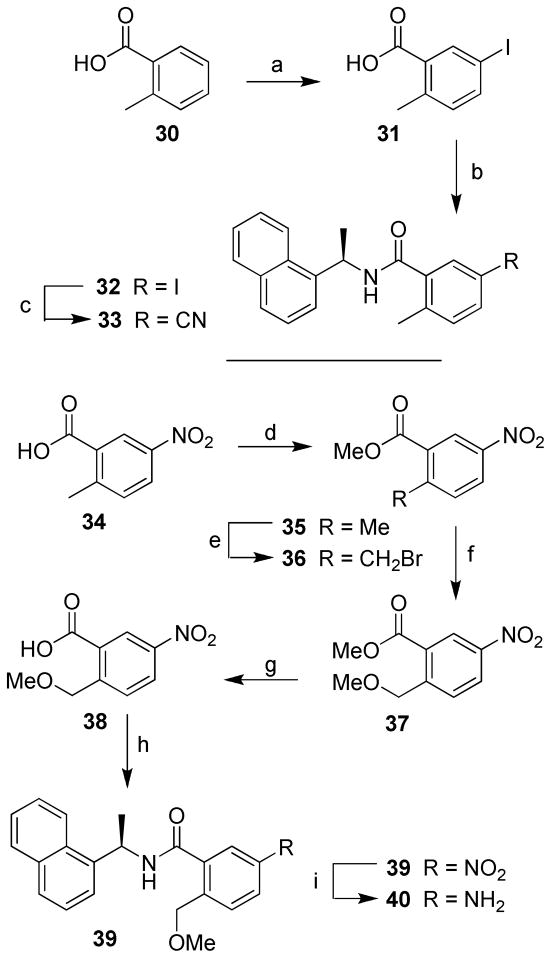
The synthesis of 32 with 2-methyl-5-iodide and 33 with 2-methyl-5-cyanide substituents on the benzamide moiety is outlined in Scheme 6. Iodination of o-toluic acid 30 with sodium perchlorite and potassium iodide in concentrated sulfuric acid at 25–30 ºC for 2 h afforded iodide 31.18 The coupling reaction following the general method provided inhibitor 32 and cyanation with copper cyanide and sodium cyanide in DMF at 130 ºC for 16 h furnished inhibitor 33. Inhibitor 40 was synthesized by esterification of 34 in the presence of thionyl chloride in methanol at reflux for 4 h to provide ester 35. Bromination of 35 with N-bromosuccinimide and benzoyl peroxide in carbon tetrachloride at reflux for 24 h generated bromide 36.19 Reaction of 36 with sodium hydride and sodium methoxide in methanol at 50 ºC for 16 h provided 37.20 Hydrolysis of 37 with lithium hydroxide monohydrate in a mixture (5:1) of tetrahydrofuran and water at 23 ºC for 16 h afforded acid 38. Coupling reaction with general method gave 39 and hydrogenation in the presence of 5% Pd-C in ethyl acetate at 23 ºC for 10 h provided inhibitor 40.
Scheme 6.
Reagents and conditions: (a) KI, NaIO4, conc. H2SO4, 25–30 ºC, 2 h; (b) (R)-(+)-1-(1-naphthyl)ethylamine 18, EDCI, HOBT, DIPEA, DMF/CH2Cl2 (1:1), 23 ºC, 48 h; (c) CuCN, KCN, DMF, 130 ºC, 16 h; (d) SOCl2, MeOH, reflux, 4 h; (e) NBS, Bz2O2, CCl4, reflux, 24 h; (f) NaH, NaOMe, MeOH, 50 ºC, 4 h; (g) LiOH·H2O, THF/H2O (5:1), 23 ºC, 1.5 h; (h) (R)-(+)-1-(1-naphthyl)ethylamine 18, EDCI, HOBT, DIPEA, DMF/CH2Cl2 (1:1), 23 ºC, 16 h; (i) H2, Pd-C, EtOAc, 23 ºC, 10 h.
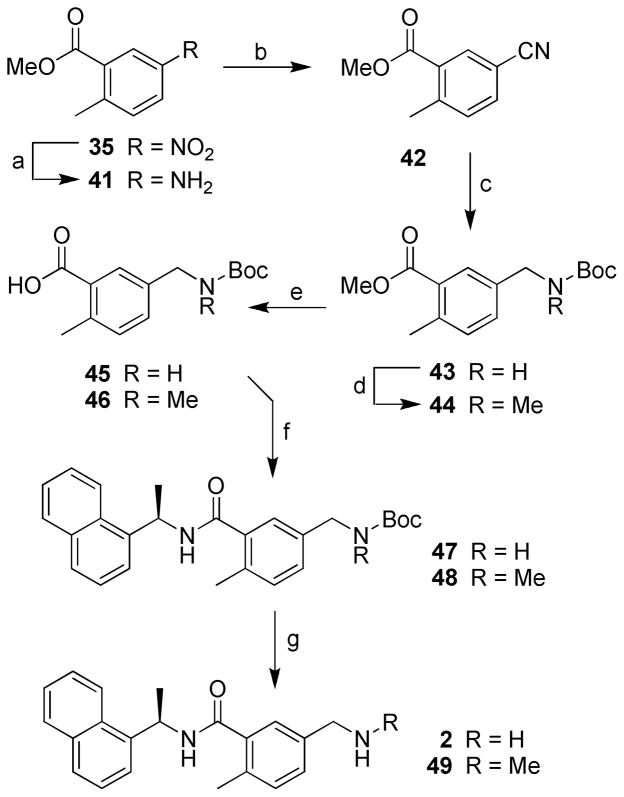
Inhibitors 47, 49 and 2 have been synthesized as shown in Scheme 7. Reduction of nitro group in 35 by catalytic hydrogenation in the presence of 5% Pd-C in ethyl acetate at 23 ºC for 15 h provided amine 41. Reaction of 41 with sodium nitrite, copper cyanide and sodium cyanide in acidic condition at 23 ºC for 3 h afforded corresponding benzonitrile 42.21 Reduction and subsequent N-Boc protection with di-t-butyl dicarbonate and sodium borohydride in the presence of nickel (II) chloride hexahydrate in methanol at 23 ºC for 2 h provided N-Boc-benzylamine 43.22 N-Methylation with methyl iodide and potassium bis(trimethylsilyl)amide in tetrahydrofuran at 23 ºC for 16 h afforded methylamine 44. Hydrolysis of 43 with lithium hydroxide monohydrate in a mixture (9:1) of tetrahydrofuran and water at 23 ºC for 16 h generated acid 45. Coupling reaction of 45 with amine 18 using conditions described above provided inhibitor 47. Removal of Boc-group with trifluoroacetic acid in dichloromethane at 23 ºC for 2 h gave inhibitor 2. Inhibitor 49 was prepared from benzylamine 44. Ester hydrolysis, coupling of the resulting acid with amine 18 and subsequent removal of Boc-group as described for 2, afforded inhibitor 49.
Scheme 7.
Reagents and conditions: (a) H2, Pd-C, EtOAc, 23 ºC, 16 h; (b) NaNO2, conc. HCl, CuCN, NaCN, H2O, 23 ºC, 3 h; (c) Boc2O, NiCl2·6H2O, NaBH4, MeOH, 23 ºC, 2 h; (d) MeI, KHMDS, THF, 23 ºC, 16 h; (e) LiOH·H2O, THF/H2O (9:1), 23 ºC, 16 h; (f) (R)-(+)-1-(1-naphthyl)ethylamine 18, EDCI, HOBT, DIPEA, CH2Cl2, 23 ºC, 16 h; (g) TFA, CH2Cl2, 23 ºC, 2 h.
Results and discussion
As described previously, screening of a library of 50,080 diverse compounds identified 1 as an inhibitor of PLpro activity.13 Since 1 is a racemic mix, we synthesized the corresponding chiral compounds to evaluate the stereospecific recognition of these compounds by PLpro. Compound, with the R-configuration, was found to be twice as potent as the racemic compound 1 (R-configuration compound, IC50 = 8.7 μM; compound 1, IC50 = 20.1 μM). We therefore selected R-configuration compound for further optimization as lead compound.
As shown in Table 1, we modified the substituent on the benzamide ring with methyl and methoxy groups. Compounds 5a–5e turned out to be less potent than lead compound. Thus, a methyl group at the ortho position in lead compound displayed the most potent activity (IC50 = 8.7 μM). A methoxy group at the ortho position resulted in a 10-fold reduction in potency compared to lead compound. A methoxy group in the meta position (compound 5f, IC50 = 13.5 μM) is the most potent analog among the methoxy substituted derivatives.
Table 1.
Structure and activity of substituted benzamide derivatives
 | ||
|---|---|---|
| compound | R | IC50 (μM) |
| lead | 2-Me | 8.7 ± 0.7 |
| 5a | 3-Me | 14.8 ± 5.0 |
| 5b | 4-Me | 29.1 ± 3.8 |
| 5c | 2-OMe | 90 ± 26 |
| 5d | 3-OMe | 13.5 ± 6.8 |
| 5e | 4-OMe | 149 ± 43 |
(IC50 = enzyme inhibitory activity)
We next attempted further modification of the substituent on the benzamide as well as on the naphthyl rings, and the results are summarized in Table 2. As shown, a 2,6-dimethyl derivative, 5f, led to an increase in the IC50 value compared to lead compound (compound 5f, IC50 = 12.1 μM). Bulky substituents at the ortho and para positions of the benzamide ring and α-naphthyl position also resulted in increased IC50 values.
Table 2.
Structure and activity of naphthyl and benzamide derivatives
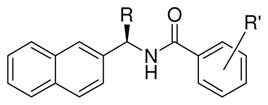 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| compound | R | R′ | IC50 (μM) |
| lead | Me | 2-Me | 8.7 ± 0.7 |
| 5f | Me | 2,6-diMe | 12.1 ± 0.7 |
| 5g | Me | 2-OH | N/A |
| 9 | Me | 4-NH2 | 46.1 ± 13.0 |
| 8 | Me | 4-Boc-NH | N/A |
| 14 | Et (racemic) | 2-Me | N/A |
| 17 | Ph (racemic) | 2-Me | N/A |
(IC50 = enzyme inhibitory activity)
In an attempt to further improve the potency of PLpro inhibitors, we then examined 1-naphthalene derivatives and also explored polar functionalities on the benzamide ring based upon modeling studies. The results are shown in Table 3. Compound 5h, with an R-1-naphthylethylamide derivative, shows improvement in potency compared to lead compound (compound 5h, IC50 = 2.3 μM). The importance of an amide NH is demonstrated as the N-methyl derivative has significantly attenuated potency (compound 21, IC50 = 22.6 μM; compound 5h, IC50 = 2.3 μM). 5-Amino group resulted in an even more potent inhibitor 24 with an IC50 value of 0.56 μM. However, incorporation of a polar acetamide derivative afforded a less potent derivative (compound 25, IC50 = 2.6 μM).
Table 3.
Structure and activity of 1-, 2-naphthalene and benzamides
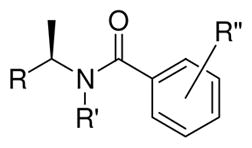 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| compound | R | R′ | R″ | IC50 (μM) |
| Lead | 2-Naphthyl | H | 2-Me | 8.7 ± 0.7 |
| 5h | 1-Naphthyl | H | 2-Me | 2.3 ± 0.1 |
| 21 | 1-Naphthyl | Me | 2-Me | 22.6 ± 6.9 |
| 23 | 1-Naphthyl | H | 4-NH2 | 24.8 ± 1.0 |
| 24 | 1-Naphthyl | H | 2-Me and 5-AcNH | 0.56 ± 0.03 |
| 25 | 1-Naphthyl | H | 2-Me and 5-NH2 | 2.64 ± 0.04 |
(IC50 = enzyme inhibitory activity)
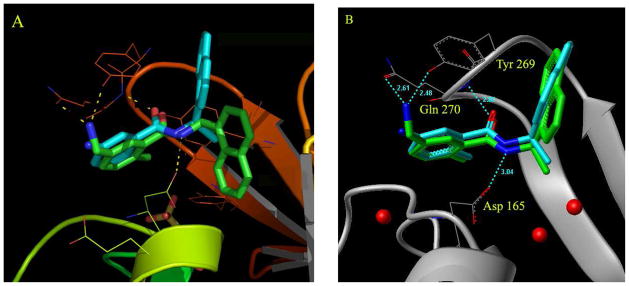
To obtain molecular insights into the ligand-binding site interactions responsible for the inhibitory potency of compound 24, the X-ray structure of PLpro complexed with 24 was determined previously to 2.5Å resolution.13, 23 Comparison of the apoenzyme SARS-CoV PLpro structure to the inhibitor 24-complexed structure reveals significant conformational differences between these structures. 23 Based upon this molecular insight, we further modified the substituents on the benzamide ring. Particularly interesting is the fact that the amine group in 24 is positioned at the opening of the cleft where it appears to come within hydrogen bonding distance to the hydroxyl of Tyr269. Furthermore, there are a number of water molecules present (see Figure 2) that occupy the pocket accommodating the (R)-methyl substituent of 24. This suggested the potential for extending the methyl branch further into the pocket through the addition of polar substituents. As shown in Table 4, we incorporated a dimethyl group in place of the (R)-methyl substituent, however the corresponding inhibitor showed a reduction in potency for SARS PLpro (compound 29, IC50 = 11.1 μM). Based upon the X-ray structure, we then incorporated 5-methylamine substituents on the benzamide ring. The resulting compound 2 showed a slight improvement in inhibitory potency (compound 2, IC50 = 0.46 μM) and antiviral activity (EC50 = 12.5 μM) as shown in Table 5. The addition of a methyl group to the amine group of 2, provided compound 49 which showed slightly decreased enzyme activity (IC50 = 1.3 μM) but significantly improved antiviral potency (EC50 = 2.5 μM). These results illustrate the importance of testing compounds not only for their ability to inhibit the purified protein, but also to assess their effects on cell viability and inhibition of viral replication in a cell-based assay.
Figure 2.
Docking in the presence of conserved water molecules is critical for replicating the binding conformation of inhibitors in the active site of the bound form of SARS-CoV PLpro. (A) Docking of compound 2 in the absence of water molecules in the active site of the inhibitor-bound form of SARS-CoV PLpro causes the naphthyl rings to flip down into a pocket, as shown by the docked conformation of compound 2 (in green) when compared to the crystal structure conformation of compound 24 (in cyan). In the x-ray structure of compound 24, the naphthyl rings are flipped up in the opposite direction, holding the flexible loop in place. The yellow dotted lines show the possible interactions of the docked compound 2 with residues Tyr269, Gln270 and Asp165 (catalytic domain residue numbering). (B) The three conserved water molecules are marked; two of them are buried deep in the pocket (P5) whereas the third one lies in a groove between residues Lys158 and Glu168. The position of these water molecules is integral to structure-based inhibitor design efforts. The crystal structure conformation of compound 24 is shown in cyan whereas the docked conformation of compound 2 in the presence of water molecules (red dots) is shown in green.
Table 4.
Structure and activity of substituted benzamide derivatives And an α-disubstituted naphthyl derivative
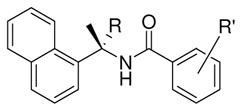 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| compound | R | R′ | IC50 (μM) |
| 24 | H | 2-Me and 5-NH2 | 0.56 ± 0.03 |
| 29 | Me | 2-Me and 5-NH2 | 11.1 ± 1.3 |
| 33 | H | 2-Me and 5-CN | 5.2 ± 0.5 |
| 40 | H | 2-CH2OMe and 5-NH2 | 2.7 ± 0.1 |
| 32 | H | 2-Me and 5-I | 1.4 ± 0.3 |
| 47 | H | 2-Me and 5-CH2NHBoc | 4.8 ± 0.4 |
| 49 | H | 2-Me and 5-CH2NHMe | 1.3 ± 0.1 |
| 2 | H | 2-Me and 5-CH2NH2 | 0.46 ± 0.03 |
(IC50 = enzyme inhibitory activity)
Table 5.
Evaluation of compounds as inhibitors of SARS-CoV replication in a cell-based assay.
| Compound | IC50 (μM) | EC50 (μM) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 20.1 ± 1.1 | NI* |
| 2 | 0.46 ± 0.03 | 6.0 ± 0.1 |
| lead | 8.7 ± 0.7 | NI |
| 5a | 14.8 ± 5.0 | NI |
| 24 | 0.56 ± 0.03 | 14.5 ± 0.8 |
| 25 | 2.64 ± 0.04 | 13.1 ± 0.7 |
| 29 | 11.1 ± 1.3 | NI |
| 47 | 4.8 ± 0.4 | NI |
| 49 | 1.3 ± 0.1 | 5.2 ± 0.3 |
(IC50 = enzyme inhibitory activity; EC50 = antiviral activity; NI = no inhibition)
To obtain molecular insights into the active site interactions leading to improved inhibitory potency, we created an energy-minimized model of 2 in the 24-inhibited SARS-CoV PLpro active site (Figure 2B). The model reveals that the 5-methylamine substituent of inhibitor 2 may be involved in hydrogen bonding with the side chain of residues Gln270 and Tyr269. Similar to the crystal structure conformation of compound 24, compound 2 appears to be anchored in the site by two effective hydrogen bonds made between the carboxamide group and residue Asp165 and Gln 270. The three conserved water molecules found in both the complex crystal structure of compound 24-bound protein and the crystal structure of the apo enzyme are retained for modelling studies and are shown as red dots in the P5 binding pocket (see Figure 2B). In docking studies, these water molecules are necessary for obtaining the crystal bound orientation of these compounds which positions the naphthyl ring of the inhibitor to be flipped upwards holding the loop (shown in cyan, Figure 2A). In the absence of these three waters, the naphthyl ring tends to occupy the P5 pocket, shown in green, Figure 2A.
To better quantitate and understand the contributions of the inhibitor substituents to the inhibitory potency, we also conducted an extensive Quantitative Structural Activity Relationship (QSAR) analysis. QSAR studies are often employed as a standard method to determine valuable information for designing novel and potent inhibitors. An alternative approach to labor-intensive chemical synthesis is to develop a theory that quantitatively relates variations in biological activity to changes in molecular descriptors for each compound. The goal of our computational study was to develop a robust QSAR model that can predict and differentiate inhibition values of this series of inhibitors against SARS-CoV PLpro. Partial least squares (PLS) methodology was used for the 3D-QSAR analyses. The CoMSIA descriptors were used as independent variables and percent inhibition values at 100 μM were used as dependent variables in PLS regression analyses to derive the models. The predictive value of the models were evaluated by leave-one-out (LOO) cross-validation. To assist ligand-based structure design efforts, we used docking in conjugation with 3D-QSAR (CoMSIA) to investigate the SAR of 46 inhibitors with considerable structural diversity and a wide range of bioactivity against the SARS-CoV PLpro.
The crystal structures of the apo protein (PDB id: 2fe8)11 and the inhibitor 24-bound form (PDB id: 3e9s)13 were carefully studied, and it was determined that three water molecules are conserved in the active sites of both the structures; two are buried deep in the P5 pocket and one between residues Lys158 and Glu168. Apart from these three conserved water molecules, two additional water molecules are located at the ridge by the P5 pocket in the inhibitor-bound form of the protein. As previously mentioned, by conducting extensive analyses both with and without water molecules bound to the structures, we determined that retaining the three conserved water molecules made a substantial difference in replicating the crystal structure binding geometry of compound 24 in docking studies. When docking was performed in the absence of water molecules in the P5 pocket, the study suggested that the naphthyl rings prefer to flip downward and probably find lower energy conformations in this pocket as shown in Figure 2A. In the inhibitor 24-bound crystal structure, two of the conserved water molecules hinder placement of the naphthyl rings in the P5 pocket and thereby flip the rings upwards. This position of the naphthyl rings fits nicely in the hydrophobic pocket and forms favorable interactions with the flexible loop residues. The five water molecules mentioned above are clearly shown in Figure 2B and were retained for the docking procedure prior to CoMSIA24 model generation. In Figure 2B, the superimposition of the naphthyl rings of modeled compound 2 (green) and x-ray structure bound orientation of compound 24 (cyan) is clearly shown as obtained in the presence of the conserved water molecules.
Using the binding conformation of inhibitor 24 from the crystal structure as a template, 45 other inhibitors were docked. The docked geometry of these 45 inhibitors aligned very well with the binding geometry of compound 24 in the crystal structure. A predictive 3D-QSAR model was derived from the alignment of the docked conformations of the inhibitors as extracted directly from the 3D coordinates of the docked complexes. A successful CoMSIA model was built with a cross-validated q2 of 0.678 and bootstrap R2 of 0.984. It is imperative to mention here that without the inclusion of at least the three conserved water molecules, the docking geometry of the inhibitors does not align with the crystal structure (as shown in Figure 2A). In the absence of these water molecules, the wrong ligand conformation is generated where the naphthyl ring is flipped into the P5 pocket, consequently resulting in an SAR with no correlation.
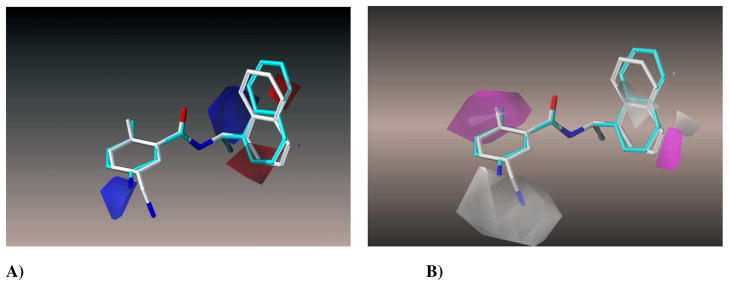
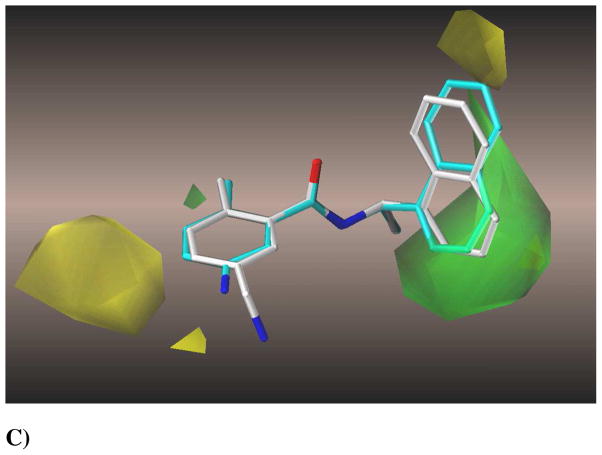
The CoMSIA model at six components gave a cross-validated q2 of 0.678, r2 of 0.984, F of 302.2 and a mean standard error estimate of 4.72. The high r2 of 0.984 illustrates that the physicochemical descriptors chosen were appropriate to describe the binding interactions mode of the various inhibitors with the PLpro active site. The plot shown in Figure 3 shows the correlation between the experimental percent inhibition values of 41 compounds and the inhibition percentages predicted by the CoMSIA model. The contour maps generated, shown in Figures 4A–C, were mapped back to the topology of the active site to reveal that electrostatic, hydrophobic, and steric fields were in accordance with the distribution of the binding site residues. These contour maps should prove to be helpful in determining the incorporation of functional groups for the inhibitors that can extensively interact with specific binding pocket residues. We conclude that this robust 3D-QSAR model built using CoMSIA can be used as a reliable guide for future structure-based drug design efforts.
Figure 3.
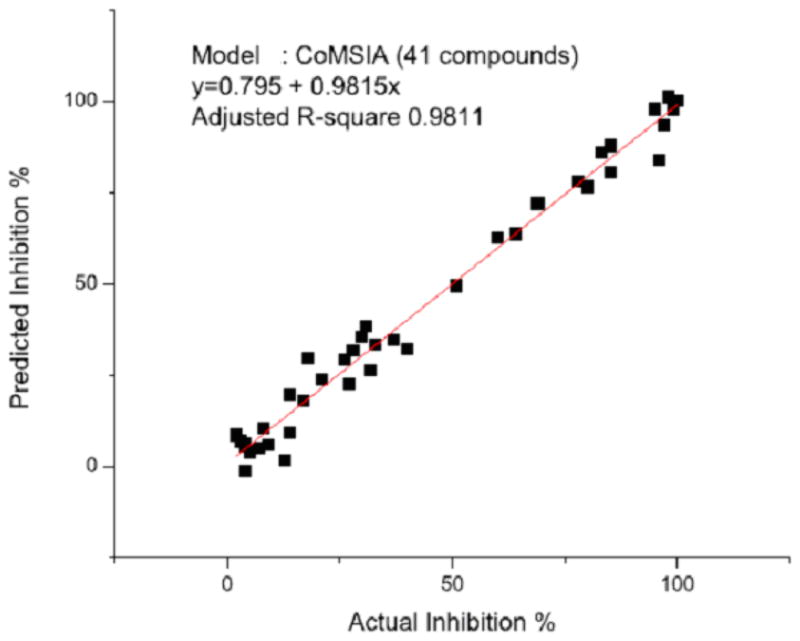
Correlation plot between the predicted percent inhibition of 41 compounds and the actual experimental percent inhibition values obtained at 100 μM.
Figure 4.
Compound 24 is shown in cyan in its bound conformation as in the crystal structure aligned with the docked conformation of the most active compound 2, in white, when docked in the presence of 3 conserved water molecules. A) The electrostatic contour map for this series of SARS-CoV PLpro inhibitors. Blue is the region of unfavorable negative charge and red is of favorable negative charge. B) The hydrophobic contour map, where white is the region of unfavorable lipophilic interactions and magenta is of favorable lipophilicity. C) A steric contour map, with green denoting the region of favorable steric interactions and yellow denoting unfavorable regions.
Conclusion
In summary, a series of novel inhibitors of SARS-CoV PLpro has been designed, synthesized and evaluated in enzyme inhibitory and antiviral assay. Initial lead compound 1 was discovered via high-throughput screening. This racemic compound has shown enzyme IC50 value of 20 μM. The stereochemical preference for the R-isomer was established through synthesis and evaluation of optically pure inhibitors, and kinetic studies showed that the optically pure lead inhibitor is a reversible inhibitor of SARS-CoV-PLpro enzyme. In the absence of any structural information, initially our structure-activity-relationship studies and systematic modification guided by molecular modeling studies provided potent inhibitor 24. This inhibitor displayed enzyme inhibitory activity of 560 nM and antiviral EC50 value of 14.5 μM in SARS-CoV infected Vero E6 cells. A protein-ligand X-ray structure of 24-bound SARS-CoV PLpro provided detailed molecular interaction in the active site of PLpro enzyme. Based upon the X-ray structural information, our structure-based design led to identification of potent inhibitors 2 and 49. Inhibitor 2 has shown potent enzyme inhibitor activity of 460 nM and antiviral EC50 value of 12.5 μM against SARS. Interestingly, the corresponding methylamine derivative 49 (enzyme IC50 = 1.3 μM) has shown most potent antiviral activity against SARS (EC50 = 2.5 μM). To obtain molecular insight into the binding properties of 2 and its derivative, we have created active model based upon the X-ray structure of 24-bound SARS PLpro. It appears that the methylamine functionality is within proximity to hydrogen bond with the side chain residues of Gln270 and Tyr269. We have also carried out computational docking studies and generated predictive 3D-QSAR model for SARS-CoV PLpro. Further design of reversible SARS-CoV PLpro inhibitors is currently underway in our laboratory.
Experimental Section
Chemistry
1H-NMR and 13C-NMR spectra were recorded on Varian Oxford 300 and Bruker Avance 400 spectrometers. Optical rotations were recorded on Perkin-Elmer 341 polarimeter. Anhydrous solvent was obtained as follows: dichloromethane by distillation from CaH2, THF by distillation from Na and benzophenone. All other solvents were reagent grade. Column chromatography was performed with Whatman 240–400 mesh silica gel under low pressure of 3–5 psi. TLC was carried out with E. Merck silica gel 60-F-254 plates. Purity of all test compounds was determined by HRMS and HPLC analysis on an Agilent 1100 unit in two different solvent systems. All test compounds showed ≥95% purity.
General procedure for coupling reaction of naphthylethylamine and benzoic acid derivative
2-Methyl-N-[(R)-1-(1-naphthyl)ethyl]benzamide (5h)
To a solution of o-toluic acid (16.2 mg, 0.12 mmol), N-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-N′-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride (EDCI) (29.1 mg, 0.15 mmol) and 1-hydroxybenzotriazole hydrate (HOBT) (20.5 mg, 0.15 mmol) in dry-CH2Cl2 was added a solution of (R)-(+)-1-(1-naphthyl)ethylamine 18 (20 mg, 0.12 mmol) and diisopropylethylamine (81.4 μL, 0.47 mmol) in dry-CH2Cl2 at 0 °C under argon atmosphere and it was allowed to stir for 15 h at 23 °C. The reaction mixture was quenched with water and extracted with CH2Cl2. The organic layers were dried over Na2SO4 and concentrated under reduced pressure. The residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography to furnish compound 5l (33 mg, 98%) as a white solid, Rf = 0.34 (hexane: EtOAc = 3:1), [α]20D −50.0 (c=1, CHCl3); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.24 (d, 1H, J = 8.5 Hz), 7.89 (d, 1H, J = 8.0 Hz), 7.82 (d, 1H, J = 8.0 Hz), 7.60–7.51 (m, 3H), 7.46 (dd, 1H, J = 7.6 and 7.7 Hz), 7.27-7.24 (m, 2H), 7.17 (d, 1H, J = 7.7 Hz), 7.11 (dd, 1H, J = 7.6 and 8.0 Hz), 6.15-6.07 (m, 2H), 2.44 (s, 3H), 1.79 (d, 3H, J = 6.4 Hz); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 168.9, 137.9, 136.3, 136.0, 133.9, 131.1, 130.9, 129.7, 128.7, 128.4, 126.5, 126.5, 129.5, 125.6, 125.1, 123.5, 122.5, 44.8, 20.5, 19.7. MS (EI): m/z 289.20 [M]+; HRMS (EI), calcd for C20H19NO 289.1467, found [M]+ 289.1468.
3-Methyl-N-[(R)-1-(2-naphthyl)ethyl]benzamide (5a)
The title compound was obtained as described in the general procedure in 92% yield (white solid). Rf = 0.35 (hexane: EtOAc = 3:1), [α]20D +39.5 (c=1, CHCl3); 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.83-7.79 (m, 4H), 7.60-7.44 (m, 5H), 7.27 (d, 2H, J = 5.4 Hz), 6.51 (d, 1H, J = 6.9 Hz), 5.53-5.44 (m, 1H), 2.35 (s, 3H), 1.67 (d, 3H, J = 6.6 Hz); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): δ 166.8, 140.5, 138.3, 134.5, 133.3, 132.7, 132.2, 128.5, 128.4, 127.9, 127.6, 127.6, 126.2, 125.8, 124.8, 124.6, 123.9, 49.1, 21.5, 21.3. MS (EI): m/z 289.15 [M]+; HRMS (EI), calcd for C20H19NO 289.1467, found [M]+ 289.1468.
4-Methyl-N-[(R)-1-(2-naphthyl)ethyl]benzamide (5b)
The title compound was obtained as described in the general procedure in >99% yield (white solid). Rf = 0.32 (hexane: EtOAc = 3:1), [α]20D +19.7 (c=1, CHCl3); 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.82-7.79 (m, 4H), 7.68 (d, 2H, J = 8.1 Hz), 7.50-7.42 (m, 3H), 7.17 (d, 2H, J = 7.5 Hz), 6.59 (d, 1H, J = 6.9 Hz), 5.52-5.42 (m, 1H), 2.36 (s, 3H), 1.64 (d, 3H, J = 6.9 Hz); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): δ 166.5, 141.8, 140.6, 133.3, 132.7, 131.6, 129.1, 128.5, 127.9, 127.6, 126.9, 126.2, 125.8, 124.8, 124.6, 49.1, 21.6, 21.4. MS (EI): m/z 289.10 [M]+; HRMS (EI), calcd for C20H19NO 289.1467, found [M]+ 289.1469.
2-Methoxy-N-[(R)-1-(2-naphthyl)ethyl]benzamide (5c)
The title compound was obtained as described in the general procedure in >99% yield (white solid). Rf = 0.23 (hexane: EtOAc = 3:1), [α]20D −30.7 (c=1, CHCl3); 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.28 (d, 1H, J = 7.8 Hz), 8.22 (dd, 1H, J = 1.8 and 8.1 Hz), 7.52 (dd, 1H, J = 1.8 and 8.7 Hz), 7.49-7.40 (m, 3H), 7.07 (t, 1H, J = 7.7 Hz), 6.95 (d, 1H, J = 9.0 Hz), 5.57-5.47 (m, 1H), 3.92 (s, 3H), 1.67 (d, 3H, J = 6.3 Hz); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): δ 164.4, 157.5, 141.2, 133.4, 132.7, 132.6, 132.3, 128.4, 127.8, 127.6, 126.1, 125.7, 124.7, 124.4, 121.6, 121.3, 111.3, 55.9, 49.1, 22.3. MS (EI): m/z 305.15 [M]+; HRMS (EI), calcd for C20H19NO2 305.1416, found [M]+ 305.1414.
3-Methoxy-N-[(R)-1-(2-naphthyl)ethyl]benzamide (5d)
The title compound was obtained as described in the general procedure in >99% yield (white solid). Rf = 0.24 (hexane: EtOAc = 3:1), [α]20D +50.0 (c=1, CHCl3); 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.82-7.79 (m, 4H), 7.50-7.44 (m, 3H), 7.38-7.38 (m, 1H), 7.31-7.27 (m, 2H), 7.03-6.97 (m, 1H), 6.57 (d, 1H, J = 7.8 Hz), 5.51-5.42 (m, 1H), 3.79 (s, 3H), 1.65 (d, 3H, J = 7.2 Hz); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): δ 166.4, 159.8, 140.5, 136.0, 133.3, 132.7, 129.5, 128.5, 127.9, 127.6, 126.2, 125.9, 124.7, 124.6, 118.6, 117.7, 112.4, 55.4, 49.3, 21.5. MS (EI): m/z 305.20 [M]+; HRMS (EI), calcd for C20H19NO2 305.1416, found [M]+ 305.1417.
4-Methoxy-N-[(R)-1-(2-naphthyl)ethyl]benzamide (5e)
The title compound was obtained as described in the general procedure in >99% yield (white solid). Rf = 0.20 (hexane: EtOAc = 3:1), [α]20D +3.0 (c=1, CHCl3); 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.81-7.73 (m, 6H), 7.49-7.41 (m, 3H), 6.85 (d, 2H, J = 8.7 Hz), 6.58 (d, 1H, J = 7.8 Hz), 5.50-5.40 (m, 1H), 3.79 (s, 3H), 1.63 (d, 3H, J = 6.9 Hz); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): δ 166.1, 162.1, 140.7, 133.3, 132.7, 128.7, 128.4, 127.8, 127.5, 126.7, 126.1, 125.8, 124.8, 124.5, 113.6, 55.3, 49.1, 21.6. MS (EI): m/z 305.15 [M]+; HRMS (EI), calcd for C20H19NO2 305.1416, found [M]+ 305.1419.
2,6-dimethyl-N-[(R)-1-(2-naphthyl)ethyl]benzamide (5f)
The title compound was obtained as described in the general procedure in 94% yield (white solid). Rf = 0.26 (hexane: EtOAc = 3:1), [α]20D +32.9 (c=1, CHCl3); 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.82-7.77 (m, 4H), 7.49-7.43 (m, 3H), 7.13 (dd, 1H, J = 7.2 and 8.1 Hz), 6.98 (d, 2H, J = 7.5 Hz), 6.17 (d, 1H, J = 8.1 Hz), 5.56-5.46 (m, 1H), 2.27 (s, 3H), 1.64 (d, 3H, J = 6.3 Hz); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): δ 169.3, 140.1, 137.5, 134.1, 133.2, 132.7, 128.6, 128.4, 127.8, 127.5, 127.4, 126.2, 125.9, 124.8, 124.6, 48.6, 21.4, 19.0. MS (EI): m/z 303.05 [M]+; HRMS (EI), calcd for C21H21NO 303.1623, found [M]+ 303.1624.
2-Hydroxy-N-[(R)-1-(2-naphthyl)ethyl]benzamide (5g)
The title compound was obtained as described in the general procedure in 97% yield (white solid). Rf = 0.49 (hexane: EtOAc = 3:1), [α]20D +68.3 (c=1, CHCl3); 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ 12.39 (s, 1H), 7.85-7.80 (m, 4H), 7.51-7.33 (m, 5H), 6.97 (d, 1H, J = 8.1 Hz), 6.81-6.76 (m, 2H), 5.49-5.39 (m, 1H), 1.67 (d, 3H, J = 7.2 Hz); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): δ 169.2, 161.5, 139.8, 134.2, 133.2, 132.7, 128.6, 127.8, 127.6, 126.3, 126.0, 125.4, 124.5, 124.5, 118.6, 118.5, 114.1, 49.1, 21.5. MS (EI): m/z 291.10 [M]+; HRMS (EI), calcd for C19H17NO2 291.1259, found [M]+ 291.1261.
2-Methyl-5-nitro-N-[(R)-1-(1-naphthyl)ethyl]benzamide (5i)
The title compound was obtained as described in the general procedure in 95% yield (white solid). Rf = 0.24 (hexane: EtOAc = 3:1), [α]20D −53.0 (c=1, CHCl3); 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.18 (d, 1H, J = 8.1 Hz), 8.11-8.06 (m, 2H), 7.87 (d, 1H, J = 8.0 Hz), 7.81 (d, 1H, J = 8.0 Hz), 7.60-7.43 (m, 4H), 7.32 (d, 1H, J = 8.4 Hz), 6.13-6.10 (bm, 2H), 2.49 (s, 3H), 1.80 (d, 3H, J = 6.3 Hz); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): δ 166.5, 144.3, 137.8, 137.3, 133.8, 131.9, 131.1, 128.9, 128.8, 126.7, 126.1, 125.2, 124.4, 123.2, 122.7, 122.6, 121.6, 45.2, 20.5, 20.0. MS (EI): m/z 334.20 [M]+; HRMS (EI), calcd for C20H18N2O3 334.1317, found [M]+ 334.1323.
4-N-TERT-Butoxycarbonylaminobenzoic acid (7)
To a solution of 4-aminobenzoic acid 6 (520 mg, 3.8 mmol) in dioxane/H2O (2:1) (13 mL) was added triethylamine (0.79 mL, 5.7 mmol) and Boc2O (1.31 mL, 5.7 mmol) at 23 °C and it was allowed to stir for 48 h at same temperature. The solvent was removed under reduced pressure, and 3M HCl (5 mL) was added dropwise to the residue at 0 °C. A precipitate was obtained, collected, washed with water, and dried to give corresponding acid 7 (836 mg, 93%) as slightly yellow solid, Rf = 0.78 (CH2Cl2: MeOH = 9:1), 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 9.25 (brs, 1H), 7.91 (d, 2H, J = 8.7 Hz), 7.50 (d, 2H, J = 8.7 Hz), 1.51 (s, 9H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 169.7, 154.8, 131.8, 125.3, 118.6, 118.5, 81.3, 28.6. MS (EI): m/z 237.10 [M]+; HRMS (EI), calcd for C12H15NO4 237.1001, found [M]+ 237.1004.
4-N′-TERT-Butoxycarbonylamino-N-[(R)-1-(2-naphthyl)ethyl]benzamide (8)
The title compound was obtained as described in the general procedure in 60% yield (white solid). Rf = 0.76 (CH2Cl2: MeOH = 9:1), [α]20D −91.6 (c=1, CHCl3: MeOH = 1:1); 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.77-7.72 (m, 6H), 7.48-7.37 (m, 5H), 5.40-5.33 (m, 1H), 1.60 (d, 3H, J = 6.9 Hz), 1.47 (s, 9H). MS (EI): m/z 390.05 [M]+; HRMS (EI), calcd for C24H26N2O3 390.1943, found [M]+ 390.1942.
4-amino-N-[(R)-1-(2-naphthyl)ethyl]benzamide (9)
To a solution of Boc 8 (60 mg, 0.15 mmol) in CH2Cl2 (4 mL) was added dropwise trifluoroacetic acid (0.6 mL) at 23 °C and it was allowed to stir for 2 h at same temperature. The reaction was concentrated under reduced pressure and the residue was treated with saturated NaHCO3 solution. The mixture was extracted with CH2Cl2. The organic layers were dried over Na2SO4 and concentrated under reduced pressure. The residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography to give compound 9 (44 mg, 99%) as a white solid, Rf = 0.60 (CH2Cl2: MeOH = 9:1), [α]20D −58.0 (c=1, CHCl3: MeOH = 4:1); 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.82-7.80 (m, 4H), 7.60 (d, 2H, J = 8.1 Hz), 7.50-7.41 (m, 3H), 6.63 (d, 2H, J = 8.7 Hz), 6.23 (d, 1H, J = 6.9 Hz), 5.52-5.42 (m, 1H), 1.66 (d, 3H, J = 7.2 Hz). MS (EI): m/z 290.15 [M]+; HRMS (EI), calcd for C19H18N2O 290.1419, found [M]+ 290.1424.
1-(2-Naphthyl)propanone (12)
To a solution of propionyl chloride 11 (5.1 g, 55 mmol) and aluminium chloride (7.7 g, 58 mmol) in 1,2-dichloroethane (16 mL) was added dropwise a solution of naphthalene 10 (7.9 g, 62 mmol) in 1,2-dichloroethane (16 mL) over 3 h at 35 °C and it was allowed to stir for 1 h. The reaction was added 3M HCl solution at 0 °C and then separate a white solid. The filtrate was washed with water. The organic layer was dried over Na2SO4 and concentrated under reduced pressure. The residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography to furnish compound 12 (9.9 g, 98%) as a colorless oil, Rf = 0.56 (hexane: EtOAc = 9:1), 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.58 (d, 1H, J = 8.7 Hz), 7.94 (d, 1H, J = 8.1 Hz), 7.86-7.80 (m, 2H), 7.59-7.42 (m, 3H), 3.04 (q, 2H, J = 6.9 Hz), 1.27 (t, 3H, J = 6.9 Hz); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): δ 205.2, 136.0, 133.8, 132.2, 130.0, 128.3, 127.7, 127.1, 126.3, 125.7, 124.3, 35.2, 8.56. MS (EI): m/z 184.15 [M]+; HRMS (EI), calcd for C13H12O 184.0888, found [M]+ 184.0890.
2-Methyl-N-[1-(2-naphthyl)propyl]benzamide (14)
To a solution of ketone 12 (2.1 g, 11.4 mmol) in MeOH (50 mL) was added ammonium acetate (8.8 g, 0.11 mol) and NaBH3CN (528 mg, 8.0 mmol) at 23 °C and was stirred for 24 h. Conc. HCl was added until pH <2, and the solvent was removed under reduced pressure. The residue was taken up in water (15 mL) and extracted once with Et2O. The aqueous layer was brought to pH >12 with solid KOH and extracted with CH2Cl2. The organic layers were dried over Na2SO4 and concentrated under reduced pressure to give amine 13 as crude compound, MS (EI): m/z 185.20 [M]+; HRMS (EI), calcd for C13H15N 185.1204, found [M]+ 185.1206. Coupling reaction was used general procedure with amine 13 (50 mg, mmol) and o-toluic acid (37.5 mg, mmol) to give inhibitor 14 (21 mg, 2 steps 26%) as a white solid, Rf = 0.25 (hexane: EtOAc = 3:1), 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.84-7.78 (m, 4H), 7.49-7.44 (m, 3H), 7.35-7.26 (m, 2H), 7.20-7.14 (m, 2H), 6.12 (d, 1H, J = 8.4 Hz), 5.28-5.20 (m, 1H), 2.39 (s, 3H), 2.04-1.95 (m, 2H), 0.99 (t, 3H, J = 7.2 Hz); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): δ 169.4, 139.4, 136.6, 136.0, 133.3, 132.7, 130.9, 129.8, 128.5, 127.8, 127.6, 126.5, 126.2, 125.8, 125.7, 125.3, 124.7, 55.2, 29.1, 19.7, 10.9. MS (EI): m/z 303.25 [M]+; HRMS (EI), calcd for C21H21NO 303.1623, found [M]+ 303.1624.
1-(2-Naphthyl)benzylamine (16)
To a solution of naphthylphenylketone 15 (600 mg, 2.6 mmol) in MeOH (15 mL) was added ammonium acetate (2 g, 25.9 mmol) and NaBH3CN (120 mg, 1.9 mmol) at 23 °C and it was allowed to stir for 24 h. Conc. HCl was added until pH <2, and the solvent was removed under reduced pressure. The residue was taken up in water (4 mL) and extracted once with Et2O. The aqueous layer was brought to pH >12 with solid KOH and extracted with CH2Cl2. The organic layers were dried over Na2SO4 and concentrated under reduced pressure to give amine 16 (48 mg, 8%) as crude compound, Rf = 0.53 (CH2Cl2: MeOH = 4:1), 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.74-7.53 (m, 5H), 7.28-7.18 (m, 4H), 7.13-7.01 (m, 3H), 5.14 (s, 1H), 1.89 (bs, 1H); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): δ 145.2, 142.8, 133.3, 132.5, 130.0, 128.5, 128.2, 127.9, 127.6, 127.0, 126.0, 125.7, 125.6, 124.9, 59.7. MS (EI): m/z 233.30 [M]+; HRMS (EI), calcd for C17H15N 233.1204, found [M]+ 233.1205.
2-Methyl-N-[1-(2-naphthyl)benzyl]benzamide (17)
The title compound was obtained as described in the general procedure in 72% yield (white solid). Rf = 0.39 (hexane: EtOAc = 3:1), 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.88-7.80 (m, 5H), 7.55-7.34 (m, 9H), 7.29-7.24 (m, 2H), 6.66 (d, 1H, J = 8.4 Hz), 6.57 (d, 1H, J = 8.4 Hz); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): δ 169.1, 141.3, 138.7, 136.3, 136.0, 133.2, 132.7, 131.1, 130.0, 128.7, 128.7, 128.6, 128.0, 127.6, 127.5, 126.6, 126.3, 126.1, 126.0, 125.7, 125.5, 57.3, 19.8. MS (EI): m/z 351.40 [M]+; HRMS (EI), calcd for C25H21NO 351.1623, found [M]+ 351.1618.
N-Methoxycarbonyl-(R)-(+)-1-(2-naphthyl)ethylamine (19)
To a solution of (R)-(+)-1-(2-naphthyl)ethylamine 18 (200 mg, 1.2 mmol) in a mixture (1:1) of dioxane and H2O was added potassium carbonate (323 mg, 2.3 mmol) and methyl chloroformate (0.11 mL, 1.4 mmol) at 0 °C and it was allowed to stir for 1 h at 0 °C. The reaction was quenched with 10% HCl solution and extracted with EtOAc. The organic layers were dried over Na2SO4 and concentrated under reduced pressure. The residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography to furnish compound 19 (268 mg, >99%) as a colorless oil, Rf = 0.36 (hexane: EtOAc = 3:1), [α]20D +96.8 (c=1, CHCl3); 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.82-7.74 (m, 4H), 7.50-7.40 (m, 3H), 5.14 (bm, 1H), 5.00 (bm, 1H), 3.66 (s, 3H), 1.54 (d, 3H, J = 6.9 Hz); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): δ 156.2, 140.9, 133.1, 132.5, 128.1, 127.7, 127.4, 125.9, 125.5, 124.2, 124.1, 51.8, 50.5, 22.0. MS (EI): m/z 229 [M]+; HRMS (EI), calcd for C14H15NO2 229.1103, found [M]+ 229.1103.
N-Methyl-(R)-(+)-1-(2-naphthyl)ethylamine (20)
To a suspension of lithium aluminum hydride (93 mg, 2.4 mmol) in THF (6 mL) was added dropwise a solution of carbamate 19 (268 mg, 1.2 mmol) in THF (1 mL) at 0 °C under argon atmosphere and it was allowed to stir for 1 h at reflux temperature. The reaction was quenched with 1M NaOH solution at 0 °C and the mixture was filtered through celite pad. The filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure and the residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography to give amine 20 (186 mg, 86%) as a colorless oil, Rf = 0.21 (CH2Cl2: MeOH = 9:1), [α]20D +58.0 (c=1, CHCl3); 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.83-7.80 (m, 3H), 7.73 (s, 1H), 7.49-7.40 (m, 3H), 3.81 (q, 1H, J = 6.6 Hz), 2.33 (s, 3H), 1.80 (bs, 1H), 1.43 (d, 3H, J = 6.6 Hz); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): δ 142.4, 133.2, 132.6, 128.0, 127.5, 127.4, 125.7, 125.3, 125.1, 124.6, 60.1, 34.3, 23.7. MS (EI): m/z 185.30 [M]+; HRMS (EI), calcd for C13H15N 185.1204, found [M]+ 185.1205.
2,N-Dimethyl-N-[(R)-1-(2-naphthyl)ethyl]benzamide (21)
The title compound was obtained as described in the general procedure in 87% yield (white solid). Rf = 0.26 (hexane: EtOAc = 3:1), [α]20D +189.1 (c=1, CHCl3); 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.96-7.91 (m, 3.6H), 7.74-7.71 (m, 0.4H), 7.65-7.55 (m, 2.6H), 7.47-7.24 (m, 4.4H), 6.53 (q, 0.6H, J = 7.2 Hz), 5.11-5.08 (m, 0.4H), 3.04 (s, 0.7H), 2.97 (s, 0.4H), 2.54 (s, 2.6H), 2.43 (s, 2.3H), 1.82 (d, 2.1H, J = 7.2 Hz), 1.79-1.72 (m, 0.9H); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): δ 171.5, 137.7, 137.0, 133.6, 133.1, 132.7, 130.3, 128.7, 128.3, 127.9, 127.5, 126.4, 126.2, 126.1, 126.0, 125.6, 125.5, 125.0, 124.6, 56.6, 56.3, 50.0, 30.4, 27.5, 18.9, 18.1, 15.3. MS (EI): m/z 303.30 [M]+; HRMS (EI), calcd for C21H21NO 303.1623, found [M]+ 303.1627.
4-N′-TERT-Butoxycarbonylamino-N-[(R)-1-(1-naphthyl)ethyl]benzamide (22)
The title compound was obtained as described in the general procedure in >99% yield (white solid). Rf = 0.73 (CH2Cl2: MeOH = 9:1), [α]20D −121.7 (c=1, CHCl3: MeOH = 1:1); 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.10 (d, 1H, J = 8.1 Hz), 7.80-7.73 (m, 2H), 7.59 (d, 2H, J = 8.1 Hz), 7.55 (d, 1H, J = 7.5 Hz), 7.49-7.34 (m, 2H), 7.42 (d, 1H, J = 7.5 Hz), 7.31 (d, 2H, J = 8.1 Hz), 7.04 (s, 1H), 6.52 (d, 2H, J = 7.8 Hz), 6.10-6.01 (m, 1H), 1.71 (d, 3H, J = 6.6 Hz), 1.47 (s, 9H); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): δ 165.8, 152.4, 141.5, 138.3, 133.8, 131.1, 128.6, 128.3, 128.3, 127.9, 126.5, 125.7, 125.1, 123.4, 122.6, 117.6, 80.8, 45.1, 28.2, 20.7. MS (EI): m/z 390.25 [M]+; HRMS (EI), calcd for C24H26N2O3 390.1943, found [M]+ 390.1947.
4-Amino-N-[(R)-1-(1-naphthyl)ethyl]benzamide (23)
The title compound was obtained as described in the compound 9 in 95% yield (slightly yellow solid). Rf = 0.65 (CH2Cl2: MeOH = 4:1), [α]20D −137.8 (c=1, CHCl3: MeOH = 4:1); 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.15 (d, 1H, J = 7.5 Hz), 7.86-7.83 (m, 1H), 7.79 (d, 1H, J = 8.1 Hz), 7.58-7.42 (m, 6H), 6.59 (d, 1H, J = 8.1 Hz), 6.17 (d, 2H, J = 7.5 Hz), 6.13-6.03 (m, 1H), 1.74 (d, 3H, J = 6.6 Hz). MS (EI): m/z 290.35 [M]+; HRMS (EI), calcd for C19H18N2O 290.1419, found [M]+ 290.1422.
5-Amino-2-methyl-N-[(R)-1-(1-naphthyl)ethyl]benzamide (24)
To a stirred solution of nitro 5m (37 mg, 0.11 mmol) in EtOAc/MeOH (1:1) (3 mL) was added 5% Pd-C (4 mg) and it was allowed to stir for 15 h at 23 °C under H2 atmosphere. The reaction was filtered through celite pad and the filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure. The residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography to furnish compound 24 (27 mg, 80%) as a white solid, Rf = 0.29 (hexane: EtOAc = 1:1), [α]20D −76.8 (c=1, CHCl3); 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.20 (d, 1H, J = 8.4 Hz), 7.85 (d, 1H, J = 8.0 Hz), 7.78 (d, 1H, J = 8.0 Hz), 7.57-7.40 (m, 4H), 6.89 (d, 1H, J = 8.0 Hz), 6.70 (bd, 2H, J = 13.5 Hz), 6.10-6.07 (bm, 2H), 3.25 (bs, 2H), 2.27 (s, 3H), 1.73 (d, 3H, J = 6.0 Hz); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): δ 169.0, 143.9, 138.0, 136.9, 133.8, 131.7, 131.1, 128.7, 128.3, 127.2, 126.5, 125.8, 125.1, 123.5, 122.5, 116.6, 113.3, 44.7, 20.5, 18.6. MS (EI): m/z 304.30 [M]+.
5-N-Acetylamino-2-methyl-N-[(R)-1-(1-naphthyl)ethyl]benzamide (25)
To a stirred solution of amine 24 (14 mg, 0.05 mmol) in CH2Cl2 (0.5 mL) was added dropwise triethylamine (9.6 μL, 0.07 mmol) and acetic anhydride (5.2 μL, 0.06 mmol) at 0 °C and it was allowed to stir for 18 h at 23 °C. The reaction was quenched with saturated NH4Cl solution and extracted with CH2Cl2. The organic layers were dried over Na2SO4 and concentrated under reduced pressure. The residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography to furnish compound 25 (5.4 mg, 34%) as a white solid, Rf = 0.60 (CH2Cl2: MeOH = 9:1), 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.19 (d, 1H, J = 8.1 Hz), 7.85 (d, 1H, J = 7.5 Hz), 7.77 (d, 1H, J = 8.1 Hz), 7.56-7.39 (m, 4H), 7.35-7.32 (m, 2H), 7.04 (d, 1H, J = 7.5 Hz), 6.22 (d, 1H, J = 8.1 Hz), 6.12-6.03 (m, 1H), 2.33 (s, 3H), 2.05 (s, 3H), 1.74 (d, 3H, J = 6.6 Hz). MS (EI): m/z 346.30 [M]+; HRMS (EI), calcd for C22H22N2O2 346.1681, found [M]+ 346.1682.
1-Methyl-1-(1-naphthyl)ethylamine (27)
CeCl3·7H2O (3.77 g, 10.1 mmol) was dried while stirring at 160 °C under reduced pressure for 3 h. Argon was added slowly, and the flash was cooled in an ice bath. THF (20 mL) was added and the suspension was stirred at 23 °C for 2 h. 1.5M methyl lithium in THF (6.7 mL, 10.1 mmol) was added below −50 °C. The mixture was stirred for 30 min at −78 °C and a solution of 1-cyanonaphthalene 26 (500 mg, 3.3 mmol) in THF (2 mL) was added. Stirring at 23 °C was continued for 2 h. Conc. NH4OH (6.5 mL) was added at −78 °C and the mixture was warmed to 23 °C and filtered with celite pad. The solid was washed with CH2Cl2. The filtrate was extracted with CH2Cl2 and the organic layers were dried over Na2SO4 and concentrated under reduced pressure. The residue was taken up in toluene (10 mL) and stirred with 3% H3PO4 (10 mL) for 15 min. The toluene layer was extracted with water (x 2), and the combined water layers were washed with toluene and made basic with conc. NH4OH solution. The mixture was extracted with CH2Cl2 and the organic layers were dried over Na2SO4 and concentrated under reduced pressure to furnish compound 27 (368 mg, 61%) as a colorless oil, Rf = 0.25 (CH2Cl2: MeOH = 9:1), 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ 9.03 (d, 1H, J = 9.0 Hz), 7.98 (d, 1H, J = 8.1 Hz), 7.86 (d, 1H, J = 8.4 Hz), 7.71 (dd, 1H, J = 1.2 and 7.5 Hz), 7.65-7.48 (m, 3H), 1.89 (s, 6H); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): δ 144.5, 135.0, 131.2, 129.2, 129.0, 128.1, 127.6, 124.9, 124.8, 122.8, 53.9, 33.3.
2-Methyl-5-nitro-N-[1-methyl-1-(1-naphthyl)ethyl]benzamide (28)
The title compound was obtained as described in the general procedure in 91% yield (white solid). Rf = 0.26 (hexane: EtOAc = 3:1), 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.50 (d, 1H, J = 8.1 Hz), 8.07 (d, 1H, J = 2.4 Hz), 7.95 (dd, 1H, J = 2.4 and 8.4 Hz), 7.87 (d, 1H, J = 8.4 Hz), 7.76 (d, 1H, J = 8.1 Hz), 7.59 (d, 1H, J = 7.5 Hz), 7.54-7.39 (m, 3H), 7.17 (d, 1H, J = 8.7 Hz), 6.87 (bs, 1H), 2.24 (s, 3H), 1.95 (s, 6H); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): δ 166.2, 145.3, 143.9, 140.6, 138.0, 134.9, 131.3, 131.4, 129.9, 129.8, 128.7, 125.3, 125.2, 125.1, 123.7, 123.7, 121.4, 57.5, 28.5, 19.5.
5-Amino-2-methyl-N-[1-methyl-1-(1-naphthyl)ethyl]benzamide (29)
The title compound was obtained as described for compound 24 in 75% yield (slightly yellow solid). Rf = 0.18 (hexane: EtOAc = 1:1), 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.56 (d, 1H, J = 8.7 Hz), 7.88 (d, 1H, J = 7.0 Hz), 7.75 (d, 1H, J = 8.1 Hz), 7.65 (d, 1H, J = 7.3 Hz), 7.49-7.42 (m, 3H), 6.90 (d, 1H, J = 8.0 Hz), 6.60 (s, 1H), 6.53 (d, 1H, J = 8.0 Hz), 6.21 (s, 1H), 2.21 (s, 3H), 2.08 (s, 6H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 169.1, 143.9, 141.2, 138.0, 135.0, 131.7, 130.2, 129.7, 128.7, 125.8, 125.2, 125.2, 125.0, 123.7, 116.3, 113.1, 57.5, 28.5, 18.6. MS (EI): m/z 318.45 [M]+; HRMS (EI), calcd for C21H22N2O 318.1732, found [M]+ 318.1729.
5-Iodo-2-methylbenzoic acid (31)
NaIO4 (295 mg, 1.38 mmol) and KI (685 mg, 4.13 mmol) were added over 45 min slowly portionwise to stirred 95% H2SO4 (15 mL). Stirring was continued for 1 h at 25–30 °C to give a dark brown iodinating solution.) at 25–30 °C. To a stirred solution of 2-toluic acid 30 (680 mg, 5 mmol) in 95% H2SO4 (5 mL), the iodinating solution was added dropwise over 45 min, while maintaining the temperature at 25–30 °C. Stirring was continued for 2 h and the iodination reaction was quenched by slowly pouring the final reaction mixture into stirred ice water. The mixture was extracted with AcOEt and dried over anhydrous Na2SO4. The solvent was evaporated under reduced pressure and purification by silica gel flash column chromatography to afford compound 31 in 63% yield. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.38 (d, 1H, J = 1.8 Hz), 7.75 (dd, 1H, J = 8.1, 1.8 Hz), 7.02 (d, 1H, J = 8.1 Hz), 2.59 (s, 3H).
5-Iodo-2-methyl-N-[1-methyl-1-(1-naphthyl)ethyl]benzamide (32)
The title compound was obtained as described in the general procedure using DMF/CH2Cl2 (1:1) as a solvent in 87% yield (white solid). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.20 (d, 1H, J = 8.5 Hz), 7.89 (d, 1H, J = 8.0 Hz), 7.83 (d, 1H, J = 8.1 Hz), 7.64–7.44 (m, 6H), 6.92 (d, 1H, J = 7.8 Hz), 6.12 (m, 1H,), 5.94 (bd, 1H, J = 8.3 Hz), 2.36 (s, 3H), 1.80 (d, 3H, J = 6.7 Hz); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 167.1, 138.6, 138.4, 137.6, 135.6, 135.0, 133.9, 132.7, 131.1, 128.8, 128.6, 126.6, 125.9, 125.1, 123.3, 122.6, 90.0, 44.9, 20.5, 19.3. MS (ESI): m/z 438.0 [M + Na]+; HRMS (ESI), calcd for C20H18INONa 438.0331; found [M + Na]+ 438.0333.
5-Cyano-2-methyl-N-[1-methyl-1-(1-naphthyl)ethyl]benzamide (33)
Compound 32 (29 mg, 0.07 mmol) was dissolved in dry DMF (2 mL). CuCN (62 mg, 0.7 mmol) and a crystal of KCN were added. The mixture was flushed with nitrogen and stirred at 80 °C for 1 h then 130 °C for 10 h. CuCN (62 mg, 0.7 mmol) was added again. The mixture was flushed with nitrogen and stirred at 130 °C for 6 h. After this time, NH4OH solution was poured into reaction mixture, and the mixture was extracted with AcOEt and dried over anhydrous Na2SO4. The solvent was evaporated under reduced pressure and purification by silica gel flash column chromatography to afford compound 33 in 78% yield as a white solid. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.19 (d, 1H, J = 8.4 Hz), 7.87 (d, 1H, J = 8.3 Hz), 7.84 (d, 1H, J = 8.2 Hz), 7.63–7.44 (m, 6H), 7.29 (d, 1H, J = 7.8 Hz), 6.12 (m, 1H), 6.08-5.99 (bs, 1H), 2.48 (s, 3H), 1.81 (d, 3H, J = 6.6 Hz); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 166.6, 141.9, 137.4, 137.2, 133.9, 133.0, 131.8, 131.0, 130.1, 128.9, 128.7, 126.7, 126.0, 125.1, 123.1, 122.6, 118.1, 109.7, 45.0, 20.4, 20.1. MS (EI): m/z 314.10 [M]+; HRMS (EI), calcd for C21H18N2O 314.1419; found [M]+ 314.1424.
2-Methyl-5-nitrobenzoic acid methyl ester (35)
To a stirring MeOH (4 mL) in a roundbottom flask was added dropwise thionyl chloride (0.24 mL, 3.3 mmol) at 0 °C. The mixture was added 2-methyl-5-nitrobenzoic acid 34 (300 mg, 1.7 mmol) at 0 °C and it was allowed to stir for 4 h at reflux temperature. The reaction was concentrated under reduced pressure and the residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography to give corresponding compound 35 (320 mg, 99%) as a colorless oil, Rf = 0.85 (hexane: EtOAc = 1:1), 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.52 (s, 1H), 8.05 (s, 1H), 7.30 (s, 1H), 3.83 (s, 3H), 2.56 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 165.4, 147.6, 145.6, 132.5, 130.1, 125.8, 125.3, 52.1, 21.5. MS (EI): m/z 195 [M]+; HRMS (EI), calcd for C9H9NO4 195.0532, found [M]+ 195.0539.
2-Bromomethyl-5-nitrobenzoic acid methyl ester (36)
Compound 35 (100 mg, 0.53 mmol) was dissolved in CCl4 (4 mL) followed by addition of NBS (100 mg, 0.58 mmol) and a catalytic amount of benzoyl peroxide. The mixture was stirred at reflux for 24 h. Another portion, of dibenzoyl peroxide (40 mg, 0.23 mmol) was added then the mixture was stirred and heated at reflux for another 10 h. The mixture was allowed to cool to 23 °C and was filtered. The filtrate was washed with NaHCO3, dried over Na2SO4 and the solvent evaporated in vacuo. The residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography to afford compound 36 in 89% yield. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.81 (d, 1H, J = 2.5 Hz), 8.33 (dd, 1H, J = 8.5, 2.5 Hz), 7.68 (d, 1 H, 8.5 Hz), 5.00 (s, 2H), 4.01 (s, 3H).
2-Methoxymethyl-5-nitrobenzoic acid methyl ester (37)
NaH (44 mg, 1.1 mmol) was added to a round-bottomed flask containing methanol (2 mL) at 0 °C. The sodium methoxide solution was added to a cold solution of compound 36 (60 mg, 0.22 mmol) in methanol (2 mL) at 0 °C. The resulting solution was stirred at 50 °C for 4 h. After this time, NH4Cl solution was poured into reaction mixture at 0 °C, and the mixture was extracted with AcOEt and dried over anhydrous Na2SO4. The solvent was evaporated under reduced pressure and purification by silica gel flash column chromatography to afford corresponding compound 37 in 72% yield. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.82 (d, 1H, J = 2.4 Hz), 8.38 (dd, 1H, J = 8.7, 2.4 Hz), 7.94 (d, 1 H, 8.7 Hz), 4.94 (s, 2H), 3.96 (s, 3H), 3.53 (s, 3H).
2-Methoxymethyl-5-nitrobenzoic acid (38)
To a stirring solution of compound 37 (36 mg, 0.75 mmol) in THF: H2O mixture (5 mL:1 mL) at 0 °C was added solid LiOH·H2O (120 mg, 5 mmol), and the resulting solution was stirred at ambient temperature for 1.5 h. After this period, the reaction mixture was evaporated until 1 mL and the mixture was extracted with toluene to remove organic impurities. The aqueous layer was cooled to 0 °C, acidified with 25% aqueous citric acid until pH 3–4, extracted with AcOEt, and dried over anhydrous Na2SO4. The solvent was evaporated and purification by silica gel flash column chromatography to furnish compound 37 in 90% yield. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CD3OD and CDCl3): δ 8.73 (d, 1H, J = 2.4 Hz), 8.26 (dd, 1H, J = 8.6, 2.4 Hz), 7.80 (d, 1 H, 8.6 Hz), 4.88 (s, 2H), 3.43 (s, 3H).
2-Methoxymethyl-5-nitro-N-[1-methyl-1-(1-naphthyl)ethyl]benzamide (39)
The title compound was obtained as described in the general procedure using DMF/CH2Cl2 (1:1) as a solvent in 73% yield (white solid). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CD3OD and CDCl3): δ 8.55 (d, 1H, J = 2.4 Hz), 8.22 (d, 1H, J = 8.4 Hz), 8.21 (d, 1 H, 8.4 Hz), 7.90 (d, 1H, J = 7.9 Hz), 7.83 (d, 1H, J = 8.1 Hz), 7.64–7.46 (m, 5H), 7.43 (br d, J = 8.2 Hz), 6.16 (m, 1H), 4.38 and 4.32 (AB, 2H, J = 11.5 Hz), 2.92 (s, 3H), 1.81 (d, 3H, J = 6.8 Hz).
5-Amino-2-methoxymethyl-N-[1-methyl-1-(1-naphthyl)ethyl]benzamide (40)
The title compound was obtained as described for compound 24 in 82% yield (slightly yellow solid). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.24 (d, 1H, J = 8.3 Hz), 7.97 (br d, 1H, J = 7.7 Hz), 7.88 (d, 1H, J = 8.0 Hz), 7.80 (d, 1H, J = 8.1 Hz), 7.60–7.43 (m, 4H), 7.15 (d, 1H, J = 2.5 Hz), 7.00 (d, 1H, J = 8.1 Hz), 6.65 (dd, 1H, J = 8.1, 2.5 Hz), 6.15 (m, 1H), 4.08 and 4.02 (AB, 2H, J = 10.2 Hz), 3.80 (br s, 2H), 2.70 (s, 3H), 1.77 (d, 3H, J = 6.8 Hz); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 167.1, 146.9, 138.5, 138.0, 133.9, 132.8, 131.2, 128.7, 128.2, 126.5, 125.8, 125.2, 123.6, 123.2, 122.6, 116.2, 73.2, 56.8, 44.8, 20.4. MS (EI): m/z 334.20 [M]+; HRMS (EI), calcd for C21H22N2O2 334.1681, found [M]+ 334.1679.
5-Amino-2-methylbenzoic acid methyl ester (41)
To a solution of nitro 35 (635 mg, 3.3 mmol) in EtOAc (10 mL) was added 10% Pd-C (30 mg) and it was allowed to stir for 16 h at 23 °C under H2 atmosphere. The reaction was filtered through celite pad and the filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure. The residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography to furnish compound 41 (536 mg, >99%) as a colorless oil, Rf = 0.57 (hexane: EtOAc = 1:1), 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.21 (d, 1H, J = 2.5 Hz), 6.97 (d, 1H, J = 8.1 Hz), 6.69 (dd, 1H, J = 2.5 and 8.1 Hz), 3.82 (s, 3H), 3.64 (s, 2H), 2.43 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 168.1, 144.1, 132.3, 129.8, 129.5, 118.8, 116.7, 51.6, 20.6. MS (EI): m/z 165.20 [M]+; HRMS (EI), calcd for C9H11NO2 165.0790, found [M]+ 165.0787.
2-Methyl-5-cyanobenzoic acid methyl ester (42)
CuCN (228 mg, 2.5 mmol) was suspended in distilled water (2 mL). NaCN (353 mg, 7.2 mmol) was added with vigorous stirring and the internal temperature was kept below 40 °C until all the CuCN went into solution. A suspension of amine 41 (350 mg, 2.1 mmol), in water (4 mL) and conc. HCl (0.7 mL) was stirred and cooled in an ice bath. When the temperature reach 5 °C, a solution of NaNO2 (190 mg, 2.8 mmol) in water (0.6 mL) was added dropwise at 5 °C. When all the NaNO2 was added, the solution was added dropwise the NaCN/CuCN solution at 0 °C. A few drops of methanol were added to keep the foaming under control. Stirring was continued for 3 h at 23 °C. The suspension was extracted with EtOAc and the organic layers were dried over Na2SO4 and concentrated under reduced pressure. The residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography to give compound 42 (115 mg, 31%) as a colorless oil, Rf = 0.63 (hexane: EtOAc = 1:1), 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.08 (d, 1H, J = 1.7 Hz), 7.56 (dd, 1H, J = 1.7 and 7.9 Hz), 7.28 (d, 1H, J = 7.9 Hz), 3.83 (s, 3H), 2.56 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 165.7, 145.5, 134.4, 134.1, 132.4, 130.3, 117.8, 109.7, 52.1, 21.8.
5-N-TERT-Butoxycarbonylmethylamino-2-methylbenzoic acid methyl ester (43)
To a solution of nitrile 42 (40 mg, 0.23 mmol) in MeOH (1.5 mL) was added Boc2O (0.1 mL, 0.46 mmol) and NiCl2·6H2O (5.4 mg, 0.022 mmol) at 0 °C. NaBH4 (61 mg, 1.6 mmol) was then added in small portions over 15 min. The reaction was allowed to stir for 2 h at 23 °C. At this point, diethylenetriamine (25 μL, 0.23 mmol) was added. The mixture was allowed to stir for 15 min. The solvent was removed and the residue was dissolved with EtOAc. The organic layer was washed with saturated NaHCO3 solution and dried over Na2SO4. The solvent was removed under reduced pressure to give a residue which was purified by silica gel column chromatography to furnish compound 43 (54 mg, 85%) as a colorless oil, Rf = 0.49 (hexane: EtOAc = 3:1), 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.78 (s, 1H), 7.29 (d, 1H, J = 7.8 Hz), 7.17 (d, 1H, J = 7.8 Hz), 4.92 (bs, 1H), 4.26 (d, 2H, J = 5.7 Hz), 3.85 (s, 3H), 2.53 (s, 3H), 1.42 (s, 9H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 167.8, 155.8, 139.2, 136.5, 132.0, 131.3, 129.4, 129.5, 79.5, 51.8, 44.0, 28.3, 21.3. MS (CI): m/z 278.30 [M]+; HRMS (CI), calcd for C15H20NO4 278.1392, found [M - H]+ 278.1398.
5-(N,N-TERT-Butoxycarbonylmethyl)methylamino-2-methylbenzoic acid methyl ester (44)
To a solution of N-Boc amine 43 (60 mg, 0.21 mmol) in THF (3 mL) was added dropwise 0.5M KHMDS in toluene (0.64 mL, 0.32 mmol) at 0 °C under argon atmosphere and it was allowed to stir for 30 min at 0 °C. The mixture was added dropwise MeI (21 μL, 0.34 mmol) at 0 °C and it was allowed to stir for 16 h at 23 °C. The reaction was quenched with saturated NH4Cl solution and extracted with EtOAc. The organic layers were dried over Na2SO4 and concentrated under reduced pressure. The residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography to give compound 44 (52 mg, 83%) as a colorless oil, Rf = 0.60 (hexane: EtOAc = 3:1), 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.75 (s, 1H), 7.24 (bs, 1H), 7.17 (d, 1H, J = 7.8 Hz), 4.36 (bs, 2H), 3.85 (s, 3H), 2.80 and 2.74 (each s, 3H), 2.54 (s, 3H), 1.45 (s, 9H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 167.8, 155.6, 139.1, 135.6, 131.9, 131.2, 130.8, 129.5, 79.8, 51.7, 33.8, 28.3, 21.3.
5-N-TERT-Butoxycarbonylmethylamino-2-methylbenzoic acid (45)
To a solution of ester 43 (54 mg, 0.19 mmol) in a mixture (9:1) of THF and water (2 mL) was added LiOH·H2O (12 mg, 0.29 mmol) at 0 °C and it was allowed to stir for 16 h at 23 °C. The reaction was concentrated under reduced pressure and the residue was diluted with saturated NaHCO3 solution. The mixture was extracted with Et2O and the aqueous layer was acidified with 1M HCl solution to pH 4. The white solid was extracted with EtOAc and the organic layers were dried over Na2SO4, and concentrated under reduced pressure to provide corresponding acid 45 (39 mg, 76%) as a white solid, Rf = 0.51 (CH2Cl2: MeOH = 9:1), 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.78 (s, 1H), 7.27 (d, 1H, J = 7.8 Hz), 7.15 (d, 1H, J = 7.8 Hz), 4.78 (bs, 1H), 4.19 (s, 2H), 2.50 (s, 3H), 1.40 (s, 9H); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): δ 170.8, 158.0, 139.5, 135.3, 132.5, 131.4, 130.2, 129.7, 80.1, 44.2, 28.7, 21.6.
5-N-TERT-Butoxycarbonylmethylamino-2-methyl-N′-[(R)-1-(1-naphthyl)ethyl]benzamide (47)
The title compound was obtained as described in the general procedure in 91% yield (white solid). Rf = 0.20 (hexane: EtOAc = 3:1), 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.20 (d, 1H, J = 8.4 Hz), 7.85 (d, 1H, J = 7.5 Hz), 7.78 (d, 1H, J = 8.4 Hz), 7.58-7.40 (m, 4H), 7.13 (d, 2H, J = 7.5 Hz), 7.08 (d, 1H, J = 7.8 Hz), 6.15-6.06 (bm, 2H), 4.86 (bs, 1H), 4.14 (d, 2H, J = 5.1 Hz), 2.36 (s, 3H), 1.75 (d, 3H, J = 6.0 Hz), 1.39 (s, 9H); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): δ 168.7, 155.8, 137.9, 136.5, 136.5, 134.9, 133.9, 131.1, 128.7, 128.7, 128.4, 127.2, 126.5, 125.9, 125.5, 125.1, 123.5, 122.5, 79.5, 44.8, 43.9, 28.3, 20.6, 19.3. MS (EI): m/z 418.45 [M]+; HRMS (EI), calcd for C26H30N2O3 418.2256, found [M]+ 418.2252.
5-(N,N-TERT-Butoxycarbonylmethyl)methylamino-2-methyl-N′-[(R)-1-(1-naphthyl)ethyl]benzamide (48)
The title compound was obtained as described for compound 45 and general procedure in 98% yield as 2 steps (white solid). Rf = 0.20 (hexane: EtOAc = 3:1), [α]20D −46.3 (c=1, CHCl3); 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.22 (d, 1H, J = 8.1 Hz), 7.85 (d, 1H, J = 7.5 Hz), 7.78 (d, 1H, J = 8.4 Hz), 7.58-7.40 (m, 4H), 7.11 (d, 1H, J = 7.2 Hz), 6.16-6.05 (m, 1H), 6.04 (bs, 1H), 4.28 (s, 2H), 2.71 (s, 3H), 2.38 (s, 3H), 1.76 (d, 3H, J = 6.3 Hz), 1.39 (s, 9H); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): δ 168.8, 155.5, 137.8, 136.6, 135.6, 134.9, 133.0, 131.1, 128.8, 128.7, 128.4, 127.2, 126.5, 125.9, 125.6, 125.1, 123.5, 122.5, 79.6, 51.9, 44.7, 33.8, 28.3, 20.5, 19.4. MS (ESI): m/z 455.99 [M + Na]+; HRMS (ESI), calcd for C27H32N2O3Na 455.2311, found [M + Na]+ 455.2312.
N-methyl-5-methylamino-2-methyl-N′-[(R)-1-(1-naphthyl)ethyl]benzamide (49)
The title compound was obtained as described for compound 9 in 76% yield (white solid). Rf = 0.27 (CH2Cl2: MeOH = 9:1), [α]20D −71.5 (c=1, MeOH); 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3 plus a small amount of CD3OD): δ 8.25 (d, 1H, J = 8.1 Hz), 7.88 (d, 1H, J = 8.4 Hz), 7.79 (d, 1H, J = 8.4 Hz), 7.63 (d, 1H, J = 7.3 Hz), 7.59-7.44 (m, 3H), 7.25 (d, 2H, J = 7.8 Hz), 7.17 (d, 1H, J = 7.8 Hz), 6.05 (q, 1H, J = 6.9 Hz), 3.61 (s, 2H), 2.32 (s, 3H), 2.31 (s, 3H), 1.69 (d, 3H, J = 6.9 Hz); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3 plus a small amount of CD3OD): δ 171.9, 140.3, 138.1, 137.8, 135.7, 135.5, 132.4, 131.8, 130.9, 129.9, 129.0, 128.2, 127.3, 126.7, 126.5, 124.3, 123.8, 55.7, 46.3, 35.5, 21.4, 19.4. MS (EI): m/z 332.30 [M]+; HRMS (EI), calcd for C22H24N2O 332.1889, found [M]+ 332.1891.
5-methylamino-2-methyl-N-[(R)-1-(1-naphthyl)ethyl]benzamide (2)
The title compound was obtained as described for compound 9 in 56% yield (white solid). Rf = 0.11 (CH2Cl2: MeOH = 9:1), 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3 plus a small amount of CD3OD): δ 8.14 (d, 1H, J = 8.5 Hz), 7.78 (d, 1H, J = 8.0 Hz), 7.69 (d, 1H, J = 8.2 Hz), 7.52 (d, 1H, J = 7.1 Hz), 7.47-7.34 (m, 3H), 7.16-7.15 (m, 2H), 7.06 (d, 1H, J = 8.2 Hz), 5.93 (q, 1H, J = 6.8 Hz), 3.61 (s, 2H), 2.21 (s, 3H), 1.59 (d, 3H, J = 6.8 Hz); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3 plus a small amount of CD3OD): δ 172.0, 140.9, 140.3, 138.1, 135.5, 135.3, 132.4, 131.9, 129.9, 130.0, 129.0, 127.3, 127.1, 126.7, 126.5, 124.3, 123.7, 46.3, 46.0, 21.4, 19.3. MS (EI): m/z 318.30 [M]+; HRMS (EI), calcd for C21H22N2O 318.1732, found [M]+ 318.1734.
Computational Material and Methods
Docking
A genetic algorithm implemented in GOLD v3.225, was used to dock 46 inhibitors into the active site of the ligand bound form of the SARS-CoV PLpro crystal structure (PDB id: 3e9s)13. All ligand and water molecules except five, namely HOH2555, HOH2563 (conserved), HOH2590 (conserved), HOH2574, and HOH2595 (conserved) were deleted from the crystal structure of the ligand-bound form of the protease. Polar hydrogen atoms were added using the Sybyl package.26 The 46 ligands were drawn using Chem 3D-Ultra 9.0. These structures were minimized in Sybyl7.3 by molecular mechanics with the Tripos force field to a gradient of 0.005 kcal/(mol A), after addition of hydrogen atoms to the ligands. The crystal structure co-ordinates of the bound ligand, 24, were used as a reference molecule for docking the other 45 compounds in GOLDv3.2 which allows full ligand flexibility and automatic consideration of cavity bound water molecules. The genetic algorithm parameters were all set to default except the number of the operations were increased to 500000 and the population size was incremented to 500. If the top three conformations generated by the docking software for the ligands did not differ from each other by at least 1.5A, early termination was allowed, ensuring non-redundant ligand conformations. The five water molecules were explicitly defined in the docking configuration file and were integral to the docking procedure and results. The top three conformations were saved for further analysis. The best scoring ligand conformation was determined as the final docked conformation for each of the 46 ligands and was used for the alignment in the proceeding QSAR analysis.
CoMSIA
The final top scoring docked conformations of the 46 molecules were retrieved from the GOLDv3.2 run. Mulliken charges were calculated for these fully optimized structures based on the AM1 method in the Sybyl distribution of MOPAC. The resulting charged 46 molecules were aligned to each other for the CoMSIA analyses to explore the specific contributions of the effect of physicochemical properties on their bioactivities. By virtue of their similar docked conformations in the active site of SARS-PLpro, the overall alignment did not need much manual tuning. Using the QSAR module in Sybyl, a spreadsheet was created for the 46 aligned molecules. Five physicochemical properties namely, steric, electrostatic, hydrophobic fields, and hydrogen bond donor and acceptor were evaluated. Similarity indices were computed using a probe with a charge of +1, radius of 1 Å, a hydrophobicity of +1. The default value of 30 kcal/mol was set as the maximum cut-off for steric and electrostatic energies. With standard options for variable scaling, SAMPLE method, leave-one-out cross validations were performed to determine the optimal principal component number. The cross-validation runs were carried out for 20 groups and the 10 round bootstrap run followed. The final CoMSIA model was obtained with this optimal number of components and non-cross validated conventional correlations. The training set was further tuned to delete five outlier compounds; this improved the model’s q2 value considerably. Hence, the resulting CoMSIA model training set consisted of 41 molecules including compound 24.
SARS-CoV PLpro Purification and IC50 Value Determination
The SARS-CoV PLpro enzyme (residues 1541–1855) was expressed and purified from E. coli according to our previously reported proceedures.11d IC50 values for all inhibitors were determined using a 96-wellplate-based assay similar to our previously described methods.11 The substrate used in the assay was the fluorogeneic peptide Arg-Leu-Arg-Gly-Gly-AMC (RLRGG-AMC) which was purchased from Bachem Bioscience. Reactions were performed in a total volume of 50 μL which contained the following components: 50 mM HEPES, pH 7.5, 0.1 mg/mL BSA, 5 mM DTT, 50 μM RLRGG-AMC, 2% DMSO, and varying concentrations of inhibitor (0–200 μM). Reactions were initiated with the addition of PLpro to produce a final enzyme concentration of 125 nM. Reaction progress was monitored continuously on a Tecan Genios Pro microplate reader (λexcitation= 360 nm; λemission=460 nm; gain=40). Initial rate data were fit to the equation vi = vo/(1 + [ I ]/IC50) using the Enzyme Kinetics module of SigmaPlot (v. 9.01 Systat Software, Inc.) where vi is the reaction rate in the presence of inhibitor, vo is the reaction rate in the absence of inhibitor, and [ I ] is the inhibitor concentration.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Public Health Service Research Grant P01 AI060915 (“Development of Novel Protease Inhibitors as SARS Therapeutics”).
Abbreviations
- SARS
severe acute respiratory syndrome
- SARS-CoV
SARS-coronavirus 3CLpro, chymotrypsin-like protease
- PLpro
papain-like protease
- WHO
world health organization
- QSAR
quantitative structural activity relationship
- CoMSIA
comparative molecular similarity indices analysis
Footnotes
Supporting Information Available. HRMS and HPLC data of inhibitors and a stereoview of the X-ray structure of inhibitor 24-bound SARS-CoV PLpro. This material is available free of charge via the Internet at http://pubrs.acs.org.
References
- 1.World Health Organization. Communicable Disease Surveillance & Response, website. http://www.who.int/csr/sars/archive/2003_05_07a/en and http://www.who.int/csr/sars/country/en/coutry2003_08_15.pdf.
- 2.Drosten C, Gunther S, Preiser W, van der Werf S, Brodt HR, Becker S, Rabenau H, Panning M, Kolesnikova L, Fouchier RA, Berger A, Burguiere AM, Cinatl J, Eickmann M, Escriou N, Grywna K, Kramme S, Manuguerra JC, Muller S, Rickerts V, Sturmer M, Vieth S, Klenk HD, Osterhaus AD, Schmitz H, Doerr HW. Identification of a novel coronavirus in patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:1967–1976. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa030747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.(a) Ksiazek TG, Erdman D, Goldsmith CS, Zaki SR, Peret T, Emery S, Tong S, Urbani C, Comer JA, Lim W, Rollin PE, Dowell SF, Ling AE, Humphrey CD, Shieh WJ, Guarner J, Paddock CD, Rota P, Fields B, DeRisi J, Yang JY, Cox N, Hughes JM, LeDuc JW, Bellini WJ, Anderson LJ. A novel coronavirus associated with severe acute respiratory syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:1953–1966. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa030781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Peiris JS, Lai ST, Poon LL, Guan Y, Yam LYC, Lim W, Nicholls J, Yee WKS, Yan WW, Cheung MT, Cheng VC, Chan KH, Tsang DN, Yung RWH, Ng TK, Yuen KY. Coronavirus as a possible cause of severe acute respiratory syndrome. Lancet. 2003;361:1319–1325. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(03)13077-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Li W, Shi Z, Yu M, Ren W, Smith C, Epstein JH, Wang H, Crameri G, Hu Z, Zhang H, Zhang J, McEachern J, Field H, Daszak P, Eaton BT, Zhang S, Wang LF. Bats are natural reservoirs of SARS-like coronaviruses. Science. 2005;310:676–679. doi: 10.1126/science.1118391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Lau SKP, Woo PCY, Li KSM, Huang Y, Tsoi HW, Wong BHL, Wong SSY, Leung SY, Chan KH, Yuen KY. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-like virus in Chinese horseshoe bats. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005;102:14040–14045. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0506735102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.He JF, Peng GW, Min J, Yu DW, Liang WJ, Zhang SY, Xu RH, Zheng HY, Wu XW, Xu J, Wang ZH, Fang L, Zhang X, Li H, Yan XG, Lu JH, Hu ZH, Huang JC, Wan ZY, Hou JL, Lin JY, Song HD, Wang SY, Zhou XJ, Zhang GW, Gu BW, Zheng HJ, Zhang XL, He M, Zheng K, Wang BF, Fu G, Wang XN, Chen SJ, Chen Z, Hao P, Tang H, Ren SX, Zhong Y, Guo ZM, Liu Q, Miao YG, Kong XY, He WZ, Li YX, Wu CI, Zhao GP, Chiu RWK, Chim SSC, Tong YK, Chan PKS, Tam JS, Lo YMD. Molecular evolution of the SARS-coronavirus during the course of the SARS epidemic in China. Science. 2004;303:1666–1669. doi: 10.1126/science.1092002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Baker SC. Encyclopedia of Virology. 3. Vol. 1. 2008. Coronaviruses: Molecular Biology; pp. 554–562. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Ghosh AK, Xi K, Johnson ME, Baker SC, Mesecar AD. Progress in Anti-SARS Coronavirus Chemistry, Biology and Chemotherapy. Annual Reports in Med Chem. 2006;41:183–196. doi: 10.1016/S0065-7743(06)41011-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Yang H, Bartlam M, Rao Z. Drug Design Targeting the Main Protease, the Achilles’ Heel of Coronaviruses. Curr Pharm Des. 2006;12:4573–4590. doi: 10.2174/138161206779010369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.(a) Ghosh AK, Xi K, Grum-Tokars V, Xu X, Ratia K, Fu W, Houser KV, Baker SC, Johnson ME, Mesecar AD. Structure-based design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of peptidomimetic SARS-CoV 3CLpro inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2007;17:5876–5880. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2007.08.031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Jain RP, Pettersson HI, Zhang J, Aull KD, Fortin PD, Huitema C, Eltis LD, Parrish JC, James MNG, Wishart DS, Vederas JC. Synthesis and Evaluation of Keto-Glutamine Analogues as Potent Inhibitors of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome 3CLpro. J Med Chem. 2004;47:6113–6434. doi: 10.1021/jm0494873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Vederas JC, Jain RP. Structural variations in keto-glutamines for improved inhibition against hepatitis A virus 3C proteinase. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2004;14:3655. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2004.05.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.(a) Devaraj SG, Wang N, Chen Z, Chen Z, Tseng M, Barretto N, Lin R, Peters CJ, Tseng CTK, Baker SC, Li K. Regulation of IRF-3-dependent Innate Immunity by the Papain-like Protease Domain of the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:32208–32221. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M704870200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Ratia K, Saikatendu KS, Santarsiero BD, Barretto N, Baker SC, Stevens RC, Mesecar AD. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus papain-like protease: Structure of a viral deubiquitinating enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103:5717–5722. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0510851103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Barretto N, Jukneliene D, Ratia K, Chen Z, Mesecar AD, Baker SC. The Papain-Like Protease of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Has Deubiquitinating Activity. J Virol. 2005;79:15189–15198. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.24.15189-15198.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.(a) Lindner HA, Fotouhi-Ardakani N, Lytvyn V, Lachance P, Sulea T, Ménard R. The Papain-Like Protease from the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Is a Deubiquitinating Enzyme. J Virol. 2005;79:15199–15208. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.24.15199-15208.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Sulea T, Lindner HA, Purisima EO, Ménard R. Deubiquitination, a New Function of the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Papain-Like Protease? J Virol. 2005;79:4550–4551. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.7.4550-4551.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Ziebuhr J, Schelle B, Karl N, Minskaia E, Bayer S, Siddell SG, Gorbalenya AE, Thiel V. Human Coronavirus 229E Papain-Like Proteases Have Overlapping Specificities but Distinct Functions in Viral Replication. J Virol. 2007;81:3922–3932. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02091-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Ratia K, Pegan S, Takayama J, Sleeman K, Coughlin M, Chaudhuri R, Fu W, Prabhakar BS, Johnson ME, Baker SC, Ghosh AK, Mesecar AD. A noncovalent class of papain-like protease/deubiquitinase inhibitors blocks SARS virus replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105:16119–16124. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0805240105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Mu F, Coffing SL, Riese DJ, II, Geahlen RL, Verdier-Pinard P, Hamel E, Johnson J, Cushman M. Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of a Series of Lavendustin A Analogues That Inhibit EGFR and Syk Tyrosine Kinases, as Well as Tubulin Polymerization. J Med Chem. 2001;44:441–452. doi: 10.1021/jm000387g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Yokoyama N. Eur Pat Appl. 1988:EP284297. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Yang Q, Ney JE, Wolfe JP. Palladium-Catalyzed Tandem N-Arylation/Carboamination Reactions for the Stereoselective Synthesis of N-Aryl-2-benzyl Pyrrolidines. Org Lett. 2005;7:2575–2578. doi: 10.1021/ol050647u. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ciganek E. Tertiary carbinamines by addition of organocerium reagents to nitriles and ketimines. J Org Chem. 1992;57:4521–4527. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kraszkiewicz L, Sosnowski M, Skulski L. Oxidative Iodination of Deactivated Arenes in Concentrated Sulfuric Acid with I2/NaIO4 and KI/NaIO4 Iodinating Systems. Synthesis. 2006:1195–1199. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Wang L, Wang GT, Wang X, Tong Y, Sullivan G, Park D, Leonard NM, Li Q, Cohen J, Gu WZ, Zhang H, Bauch JL, Jakob CG, Hutchins CW, Stoll VS, Marsh K, Rosenberg SH, Sham HL, Lin NH. Design, Synthesis, and Biological Activity of 4-[(4-Cyano-2-arylbenzyloxy)-(3-methyl-3H-imidazol-4-yl)methyl]benzonitriles as Potent and Selective Farnesyltransferase Inhibitors. J Med Chem. 2004;47:612–626. doi: 10.1021/jm030434f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Sderberg BC, Chisnell AC, O’Nei SN, Shriver JA. Synthesis of Indoles Isolated from Tricholoma Species. J Org Chem. 1999;64:9731–9734. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Biasotti B, Dallavalle S, Merlini L, Farina C, Gagliardi S, Parini C, Belfiore P. Synthesis of photoactivable inhibitors of osteoclast vacuolar ATPase. Bioorg Med Chem. 2003;11:2247–2254. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0896(03)00106-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Caddick S, Judd DB, Lewis AK, de K, Reich MT, Williams MRV. A generic approach for the catalytic reduction of nitriles. Tetrahedron. 2003;59:5417–5423. [Google Scholar]
- 23.See supporting information
- 24.Klebe G, Abraham U, Mietzner T. Molecular Similarity Indices in a Comparative Analysis (CoMSIA) of Drug Molecules To Correlate and Predict Their Biological Activity. J Med Chem. 1994;37:4130–4146. doi: 10.1021/jm00050a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Jones G, Willett P, Glen RC, Leach AR, Taylor R. Development and validation of a genetic algorithm for flexible docking. J Mol Biol. 1997;267:727–748. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1996.0897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.SYBYL v.7.3 Tripos International, 1699 South Hanley Rd., St. Louis, Missouri, 63144, USA.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.