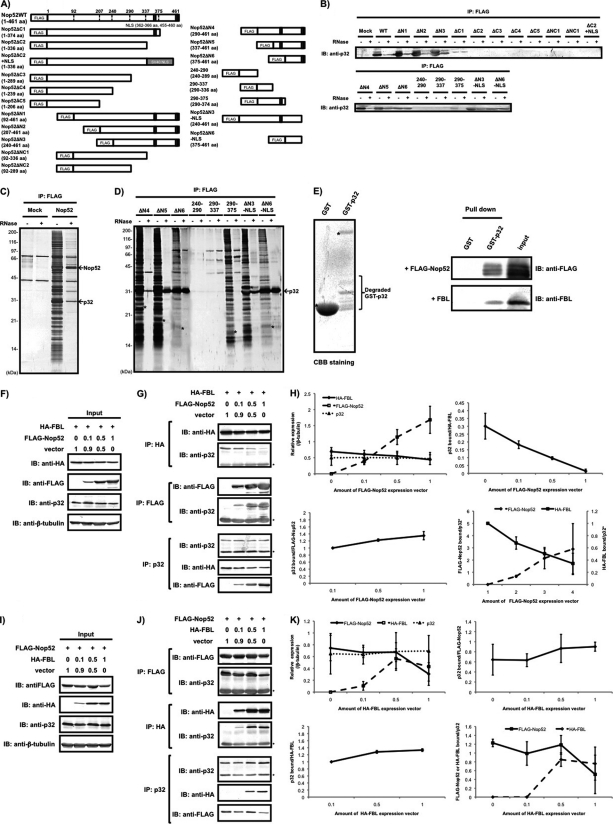
Fig. 6.
Competitive binding of FBL and Nop52 to p32. A, Schematic representation of FLAG-tagged wild-type Nop52 (WT) and its truncation mutants used in this study. Abbreviations used are indicated in the text. Proteins were immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-FLAG from whole-cell extracts of 293EBNA cells transfected with FLAG-Nop52 or its truncation mutants (see text for descriptions) and detected by immunoblotting (IB) with anti-p32 before (–) and after (+) treatment with RNase A (B) or by silver staining of a 12% SDS-PAGE gel (C, FLAG-Nop52; D, its truncation mutants). Asterisk indicates the position of its corresponding domain mutant migrated. The arrows indicate p32 and FLAG-Nop52 (Nop52). E,The isolated GST-p32 or GST was mixed with purified FLAG-Nop52 or FBL, pulled down with glutathione-fixed beads, and detected by immunoblotting with anti-FLAG antibody or anti-FBL antibody. The CBB-stained SDS-PAGE gel showed that the used-GST-p32 contained several degraded fragments that were detected by immunoblotting with anti-GST antibody (Degraded GST-p32). The isolated FLAG-Nop52 had several forms that were probably produced during thrombin cleavage (see Materials and Methods). (F, G) The expression vector encoding FLAG-Nop52 was mixed with pcDNA3.1(+) empty vector in the ratios indicated and then cotransfected with a constant amount of the HA-FBL expression vector. HA-FBL, FLAG-Nop52, p32 or β-tubulin was detected by immunoblotting with the corresponding antibodies in the cell extract (input) (F) or in the complex isolated by immunoprecipitation with anti-HA, anti-FLAG, or anti-p32 from the co-transfected cells (G). Asterisks in F and G indicate the light chain of the antibody detected by immunoblotting. (H) Statistical evaluation of the results obtained in Figs. 6F and 6G. The horizontal axis is shown as the amount of FLAG-Nop52 expression vector mixed. Vertical axis is shown as: each protein expression detected with the indicated antibody shown in Fig. 6F is normalized by that of β-tubulin in the same lane (upper left); p32 bound/HA-FBL, amount of p32 bound to HA-FBL shown in Fig. 6G (IP:HA) is divided by that of HA-FBL (upper right); p32 bound/FLAG-Nop52, amount of p32 bound to FLAG-Nop52 shown in Fig. 6G (IP:FLAG) is divided by that of FLAG-Nop52 (lower left); FLAG-Nop52 bound/p32, amount of FLAG-Nop52 bound to p32 shown in Fig. 6G (IP:p32) is divided by that of p32, vertical axis right-amount of HA-FBL bound to p32 is divided by that of p32 (IP:p32) (lower right). The values indicated in the graph are averages (±S.D.) of three independent experiments or two independent experiments (*). (I, J) Transfection and immunoprecipitation of the mixture of the HA-FBL expression vector and pcDNA3.1(+) empty vector in different ratios over a constant amount of the FLAG-Nop52 expression vector was also performed. Asterisks in I and J indicate the light chain of the antibody detected by immunoblotting. (K) Statistical evaluation of the results obtained in Figs. 6I and 6J. The horizontal axis is shown as the amount of HA-FBL expression vector mixed. Vertical axis is shown as: each protein expression detected with the indicated antibody shown in Fig. 6I is normalized by that of β-tubulin in the same lane (upper left); p32 bound/FLAG-Nop52, amount of p32 bound to FLAG-Nop52 shown in Fig. 6J (IP:FLAG) is divided by that of FLAG-Nop52 (upper right); p32 bound/HA-FBL, amount of p32 bound to HA-FBL shown in Fig. 6J (IP:HA) is divided by that of HA-FBL (lower left,); FLAG-Nop52 or HA-FBLbound/p32, amount of FLAG-Nop52 or HA-FBL bound to p32 shown in Fig. 6J (IP:p32) is divided by that of p32 (lower right). The values indicated in the graph are averages (±S.D.) of three independent experiments.