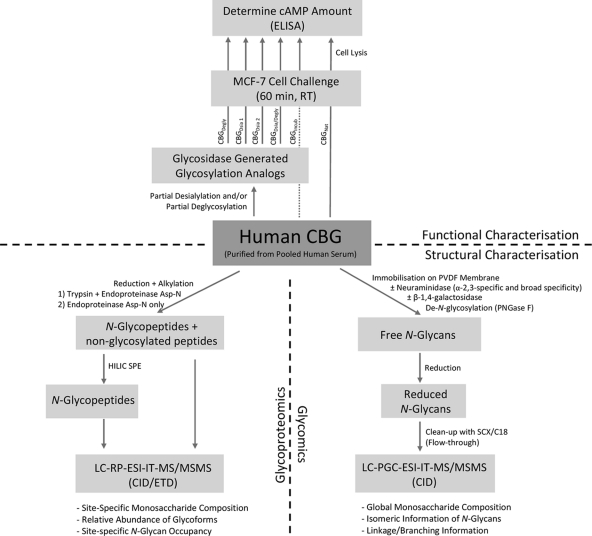
Fig. 1.
Workflow illustrating the experimental setup. The N-glycans of human CBG were structurally characterized (bottom half) using glycoproteomics (left) and glycomics (right). Functionally, the CBG N-glycan involvement in the CBG:receptor interaction was investigated (upper half) by challenging MCF7 cells with native/heat exposed CBG (CBGNat and CBGIncub) and glycosylation analogs (CBGDegly, CBGDesia 1, CBGDesia 2, CBGDesia/Degly) and monitoring the cAMP response, which has been shown to be an accurate measure to evaluate the CBG:receptor interaction.