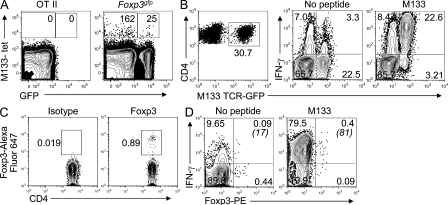
Figure 5.
Detection of M133-specific T reg cells in naive Foxp3gfp and M133 TCR Rg mice. (A) Lymphocytes were pooled from the spleens and LNs of three naive Foxp3gfp or two OT-II mice and analyzed for tetramer M133–positive T reg cells. Numbers of Foxp3− and Foxp3+ M133-specific CD4 T cells/3 mice are indicated. Representative data from one of three independent experiments are shown. (B–D) M133 TCR Rg mice were infected with rJ2.2 and sacrificed at 7 d after infection (B and D) or were not infected (C). (B) M133-specific (GFP+) CD4 T cells accumulated in the infected brain and expressed IFN-γ after M133 peptide stimulation. (C) GFP+ CD4 T cells from spleens of uninfected mice were analyzed for Foxp3 expression. (D) Lymphocytes from the brains of rJ2.2-infected mice were stimulated with peptide M133 and assayed for Foxp3 and IFN-γ expression after gating on GFP+ CD4 T cells. Numbers in parentheses represent percentage of IFN-γ+ T reg cells. Data shown in B–D are representative of two independent experiments containing three mice each.