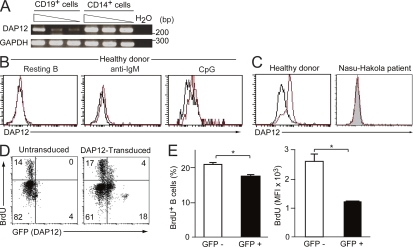
Figure 7.
DAP12 inhibits human B cell proliferation. (A) PBMCs derived from a healthy donor were stained with PE-conjugated anti-CD19 and FITC-conjugated anti-CD14 mAbs. CD19+ B cells or CD14+ monocytes were sorted to >99.9% purity by flow cytometry. The RNA was extracted from the purified cells and was subjected to semiquantitative RT-PCR for expression of DAP12 and GAPDH transcripts, according to template dose by dilution. (B and C) PBMCs derived from a healthy donor or a patient with Nasu-Hakola disease were stimulated (B) or not (C) with anti-IgM or CpG for 48 h and then stained with PE-conjugated anti-CD20 (B) or anti-CD14 (C). Cells were fixed and then stained with anti-DAP12 (red line) or control Ig (black line), followed by FITC-conjugated secondary antibody. Plots in B are gated on CD20+ cells and plots in C are gated on CD14+ cells. (D and E) PBMCs from a patient with Nasu-Hakola disease were transduced or not with the lentiviral vector encoding DAP12 and EGFP and then stimulated with CpG. BrdU was pulsed for the final 24 h in the culture. Cells were stained with PE-conjugated anti-CD19 mAb and then fixed, followed by staining with APC-conjugated anti-BrdU mAb and analyzed for B cell proliferation, as determined by BrdU incorporation, on the CD19+ gated cells by flow cytometry (D). The frequencies of BrdU+ cells in GFP− and GFP+ cells and mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of BrdU+ cells in GFP− and GFP+ cells were determined (E). The data represent two independent experiments (A–E). *, P < 0.05. Error bars show SD.