Figure S1.
Generation of iRhom/rhomboid-5 Mutant Drosophila, Related to Figure 2
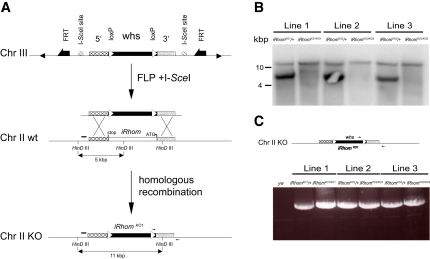
(A) At the top is the donor construct, as it would appear on the third chromosome (Chr III) when initially introduced by P-element transformation. FRT sites allow the FLP recombinase to free the DNA from its chromosomal integration site. This results in circular extra-chromosomal donor DNA, which is subsequently linearized by I-SceI. Homologous recombination can then occur between the donor construct comprising 5′ and 3′ homology arms either side of the mini-white marker gene (whs), which is flanked by loxP sites. Note that donor transformant lines carry the donor construct on the third chromosome and the iRhom/rhomboid-5 locus is on the second chromosome. Upon successful homologous recombination, the whs marker becomes genetically linked to the second chromosome, and the donor construct loses its FRT sites, which was exploited to enrich for correct targeting events as described in Experimental Procedures. The lower panels show the recombination event between the extra-chromosomal donor DNA (after FLP- mediated excision and I-SceI cutting) with the genomic locus containing iRhom/rhomboid-5. The black bar indicates the position of the DNA probe used to screen for correct site-specific integration by Southern blot. Note that the probe was generated against genomic sequence just outside the 5′ homology arm, to detect the wild-type 5kb genomic fragment after HinDIII digest upon site specific integration. Correct targeting replaces the iRhom genomic region with the whs marker, leading to the loss of a HinDIII site, which increases the predicted size of the genomic HinDIII DNA fragment to 11kb.
(B) Southern blot analyzing three independent mutant fly lines (KO1, KO2 and KO3) with the mini-white marker on chromosome II. All three homozygous mutant lines (KO1-3/KO1-3) showed the expected 11kb fragment predicted by the correct targeting, while a HinDIII digest of genomic DNA from heterozygous (+/KO1-3) lines resulted in a 5kb wild-type and 11kb mutant fragment.
(C) Genomic PCR strategy detecting a correct genomic targeting replacing the iRhom/rhomboid-5 locus with the mini-white gene. Note one primer was designed outside the 3′ homology arm, and the second within the mini-white gene; a PCR product can only be formed when correct targeting occurs. Correct integration was further confirmed by sequencing the PCR product covering the insertion region.