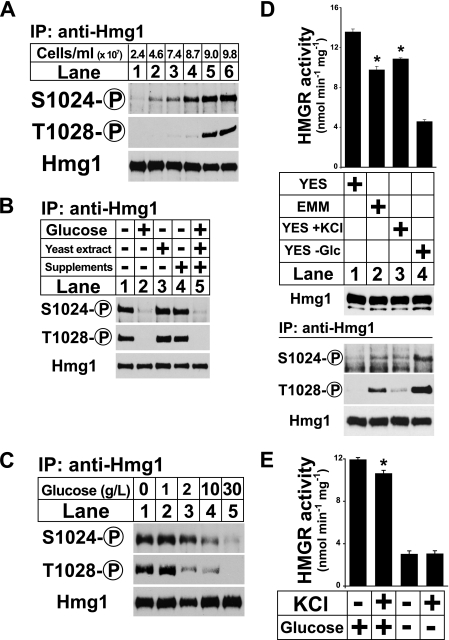
FIGURE 4.
Hmg1 is phosphorylated in stationary phase due to low glucose. A, wild-type cells were grown in YES medium and harvested by centrifugation at the indicated cell densities. Hmg1 immunoprecipitates were blotted using anti-Hmg1 IgG or Hmg1 phosphospecific antibodies. B, wild-type cells (1 × 108) grown in YES medium to early stationary phase were treated with 30 g/liter glucose, 5 g/liter yeast extract, and/or 1 × supplements (see “Experimental Procedures”) as indicated. Samples were harvested after 15 min and processed as in A. C, wild-type cells were grown in YES medium, harvested by centrifugation, and resuspended in medium containing different concentrations of glucose as indicated. Samples were harvested after 15 min and processed as in A. D, wild-type cells were grow in YES medium overnight to exponential phase, collected by centrifugation, and transferred to either YES medium, EMM minimal medium, YES medium containing 0.6 m KCl, or glucose-free medium for 30 min. Microsomes were prepared, assayed for Hmg1 activity, and immunoblotted with anti-Hmg1 IgG. Data are the average of three technical replicates; error bars show S.E. Asterisk indicates significant difference from YES plus glucose condition (p < 0.001). Whole cell lysates were also prepared, from which Hmg1 was immunoprecipitated and analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-Hmg1 IgG or Hmg1 phosphospecific antibodies. E, wild-type cells were grown overnight in YES to exponential phase, collected by centrifugation, and resuspended in YES medium, YES containing 0.6 m KCl, glucose-free medium, or glucose-free medium containing 0.6 m KCl for 30 min. Microsomes were prepared and assayed for Hmg1 activity. Data are the average of three technical replicates; error bars show S.E. Asterisk indicates significant difference from YES plus glucose condition (p < 0.01).