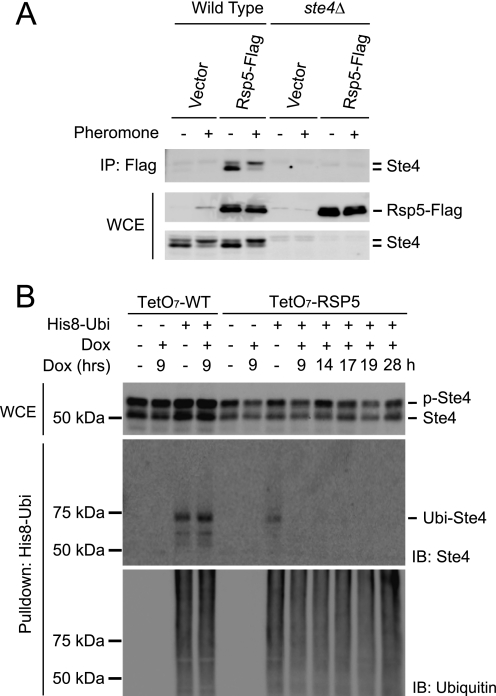
FIGURE 3.
Rsp5 is required for Ste4 ubiquitination in vivo. A, Ste4 coimmunoprecipitates with Rsp5. Wild-type or ste4Δ cells were transformed with either an empty vector or a plasmid expressing FLAG-tagged Rsp5 (Rsp5-FLAG). Early log phase cells were treated with 3 μm pheromone for 1 h. FLAG-tagged Rsp5 was immunoprecipitated (IP) using anti-FLAG M2 resin, and the copurified Ste4 was detected by immunoblotting of the immunoprecipitates (IP: Flag) using anti-Ste4 antibodies. The relative level of input Ste4 and Rsp5-FLAG in the whole cell extracts (WCE) prior to purification is shown in the lower panels. B, turning off RSP5 expression abolishes Ste4 ubiquitination. Wild-type (TetO7-WT) or TetO7-RSP5 (RSP5 under the control of doxcyclin-regulatable promoter) cells were transformed with either an empty vector or a plasmid expressing His-8-tagged ubiquitin (His8-Ubi). Early log phase cells were treated or not treated with 60 μg/ml doxycycline (Dox) for the indicated time (h), followed by treatment of 3 μm pheromone for 1 h. His-8-Ubi-conjugated proteins were purified from whole cell lysates under denaturing conditions. The level of Ste4 in the whole cell extracts (WCE) prior to purification was detected by immunoblotting (IB) with anti-Ste4 antibodies (top panel). The purified samples were analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-Ste4 antibodies (center panel) and anti-ubiquitin antibodies (bottom panel). p-Ste4, phosphorylated Ste4; Ubi-Ste4, ubiquitinated Ste4.