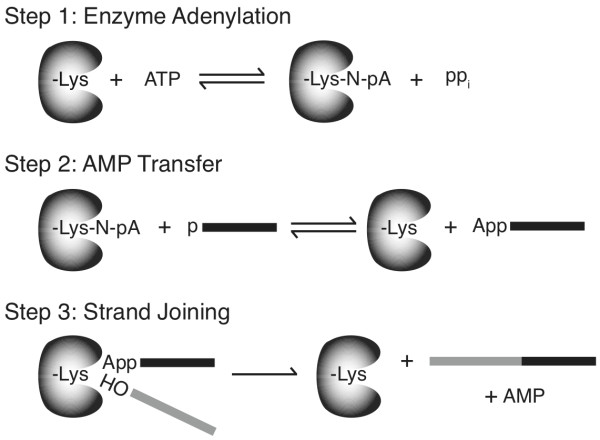
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of a nucleic acid ligation reaction. In step 1, the enzyme reacts with ATP and becomes adenylated on an active site lysine residue yielding adenylated enzyme and pyrophosphate. In step 2, the AMP is transferred from the active site lysine to a 5'-phosphorylated nucleic acid donor (black). In step 3, the enzyme promotes phosphodiester bond formation between the 5'-adenylated nucleic acid donor, and a polynucleotide acceptor molecule that is 3'-hydroxylated (grey). The reaction yields a ligated polynucleotide and AMP.