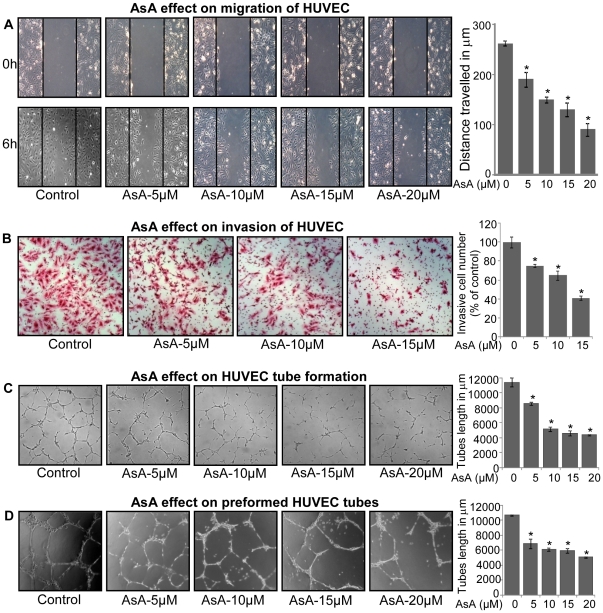
Figure 2. AsA inhibits motility and capillary-structure formation in HUVEC.
A. Effect of AsA treatment on the migratory potential of HUVEC was analyzed through wound healing assay. Representative photomicrographs of initial and final wounds are shown at 100x magnification and migration distance was measured as detailed in ‘Materials and Methods’. Cell migration distance data shown are mean ± standard deviation of three samples for each treatment. B. Effect of AsA treatment on the invasive potential of HUVEC was examined using invasion chambers as detailed in ‘Materials and Methods’. Cell invasion data shown are mean ± standard deviation of three samples for each treatment. C. Effect of AsA on the tube formation of HUVEC was examined by plating HUVEC on the matrigel. After 6 h, tubular structures were photographed at 100x magnification and tube length was measured as described in ‘Materials and Methods’. Tube length data is presented as mean ± standard deviation of three samples for each treatment. D. Effect of AsA on the pre-formed tubes in HUVEC was analyzed and tube length was measured as detailed in ‘Materials and Methods’. Tube length data shown are mean ± standard deviation of three samples for each treatment. These results (A–D) were similar in 2–3 independent experiments. *, p≤0.001.