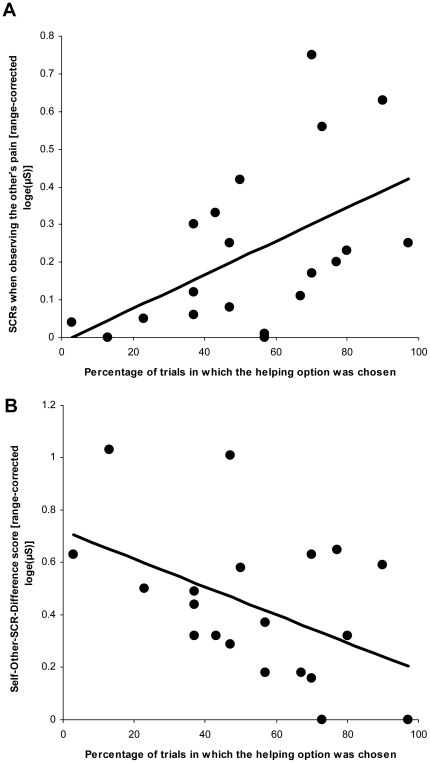
Figure 1. Main results of the correlation analyses.
A) Significant positive correlation between participants' skin conductance responses (SCRs) when seeing the other person in pain, and percentage of trials in which they chose the costly helping option (out of a total of 30 trials). B) Significant negative correlation between the score measuring the difference between the SCR to self pain and when observing the other's pain (|(SCR_self pain – SCR_other pain)|), and the percentage of trials in which they chose the costly helping option (out of a total of 30 trials).