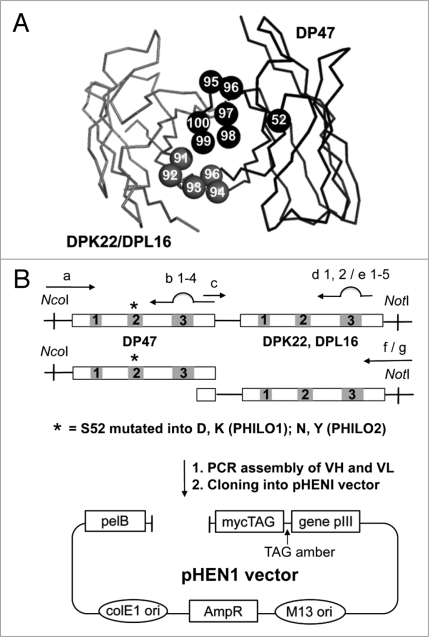
Figure 1.
Design and cloning strategy for the PHILO antibody library. (A) Three-dimensional structure of a scFv antibody fragment. Heavy chain and light chain backbone are represented in dark grey and light grey, respectively. Residues subject to random mutation are DP47 CDR3 position 95–100 (dark grey space-fill representation), light chain position 91 to 96 (light grey space-fill representation) (in more details, for DPK22 CDR3 residue 91–96, and for DPL16 CDR3 position 92–95 and 95b). The scFv structure was displayed using the program PyMol, based on the protein data base (Brookhaven Protein Data Bank) file 1igm. The residue numbers were defined as previously published in reference 23 and 63. (B) Library cloning strategy. A point mutation was introduced, converting residue S52 of VH to D, K, N or Y. Mutagenesis in the CDR3 regions was generated by PCR using partially degenerate primers. Genes are indicated as rectangles and CDRs as numbered boxes. The VH and VL segment were then assembled by PCR and cloned into the pHEN1 vector.64 Primers used in the amplification and assembly are listed in Table 1.