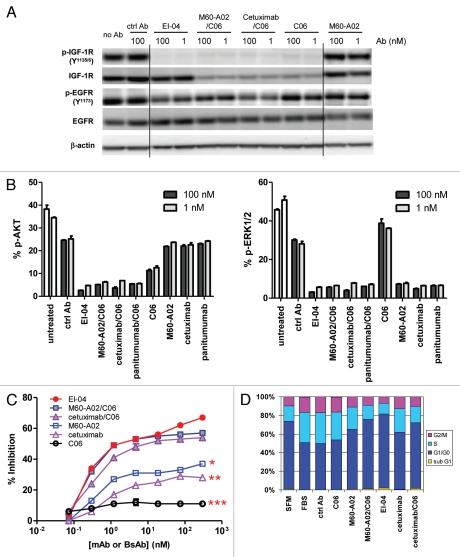
Figure 4.
Concurrent blockade of EGFR and IGF-1R signaling pathways and enhanced inhibition of tumor cell growth and cell cycle progression by EI-04. (A) Simultaneous inhibition of phosphorylation of EGFR and IGF-1R in HN11 tumor cells by EI-04. Cells grown in culture medium supplemented with 10% FBS were treated with the indicated antibodies against EGFR and IGF-1R or a control IgG (ctrl Ab) for 4 h. Phospho-EGFR, phospho-IGF-1R, total EGFR, total IGF-1R and β-actin in cell lysates were analyzed by western blot. (B) Simultaneous blockade of phosphorylation of Akt and ERK in HN11 cells by EI-04. Cells were treated as described in (A). Phospho-Akt (left part) and phospho-ERK (right part) levels were quantified using MSD. Data are means ± SD (n = 2), representative results from two similar experiments. (C) Improved inhibition of serum-driven HN11 cell growth by EI-04 compared to single mAbs. Tumor cells grown in culture medium supplemented with 10% FBS were treated with serially diluted antibodies starting from 300 nM for three days prior to cell viability determination. Percent growth inhibition was calculated relative to no antibody treatment control. Data are means ± SD (n = 3), representative results from two similar experiments. Significance of difference between mAbs and EI-04: *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, by one-way ANOVA. (D) Enhanced blockade of serum-driven HN11 cell cycle progression by EI-04 compared to single mAbs. Tumor cells were grown in serum-free medium (SFM) or in culture medium supplemented with 10% FBS and treated with 100 nM of the indicated antibodies against EGFR and IGF-1R or a control IgG (ctrl Ab) for two days. Percentage of cells in each cell cycle phases was determined by FACS analysis.