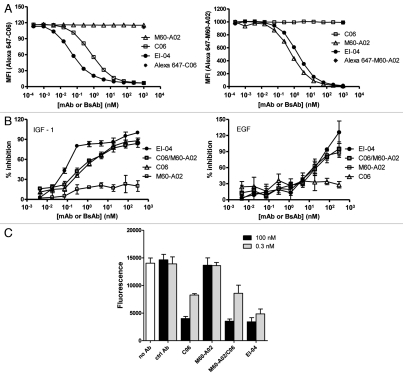
Figure 5.
High avidity binding and synergistic inhibitory effect of EI-04 on BxPC3 tumor cells. (A) Flow cytometric measurement of the abilities of EI-04, M60-A02 and C06 to compete with Alexa 647-labeled C06 (left part) and Alexa 647-labeled M60-A02 (right part) for binding to BxPC3 tumor cells. Mean fluorescence intensity was measured when cells were stained with Alexa 647-C06 or Alexa 647-M60-A02 in the presence of various serially diluted competitor antibodies. Data are representative results from two similar experiments. (B) Inhibition of IGF-1-stimulated (left part) or EGF-stimulated (right part) BxPC3 tumor cell growth by EI-04, M60-A02, C06 or the M60-A02/C06 combination. Cells grown in serum-free medium supplemented with 100 ng/ml of IGF-1 or EGF were treated with serially diluted antibodies for three days prior to cell viability determination. Percent growth inhibition was calculated relative to no antibody treatment controls. Data are means ± SD (n = 3), representative results from two similar experiments. (C) Inhibition of BxPC3 cell colony formation by EI-04, M60-A02, C06 or the M60-A02/C06 combination. BxPC3 cells plated in soft agar were treated with a single dose of 0.3 or 100 nM of the indicated antibodies and allowed to grow in complete medium supplemented with 100 ng/ml of EGF and IGF-1 each for two weeks. Fluorescence signals correlating with live colonies are shown. Data are means ± SD (n = 4), representative results from two similar experiments.