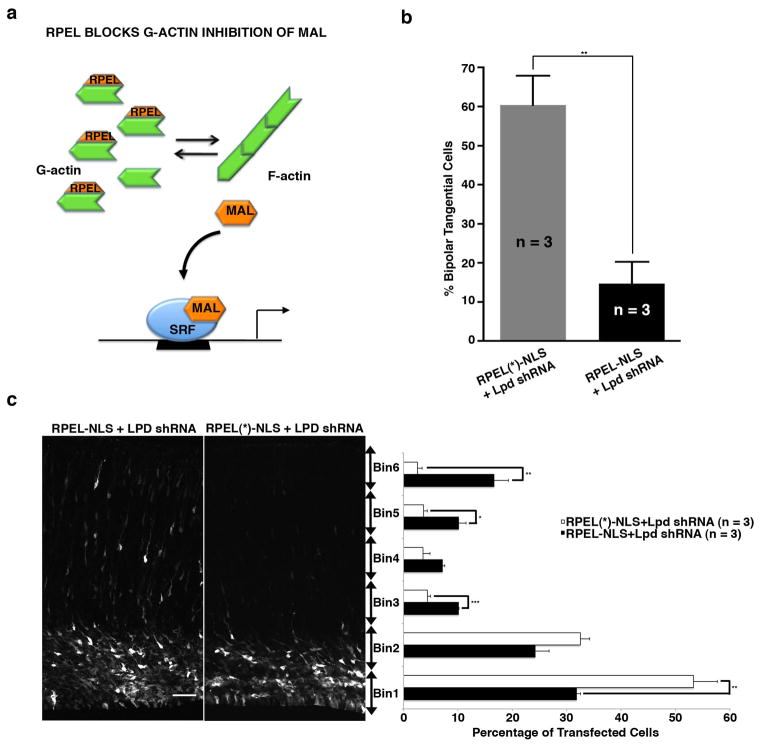
Figure 5. Expression of MAL G-actin binding motifs (RPEL) rescues the Lpd knockdown orientation and positioning defects of bipolar pyramidal neurons.
Mouse embryos were electroporated in utero at E14.5 and harvested at E18.5. (a) Schematic representation of SRF/MAL activity upon RPEL-NLS23 rescue of the Lpd knockdown. (b) Percentage of bipolar tangentially oriented cells in the IZ/SVZ of samples co-electroporated with Lpd knockdown vector and RPEL-NLS or RPEL(*)-NLS containing RPEL motif (mutations) ** p <0.01, Student’s t-test, n = 3 brains per condition). Bar graphs are plotted as mean ± SEM. (c) Quantification of cell distribution in cortical sections co-electroporated with Venus, Lpd shRNA and either RPEL-NLS or RPEL(*)-NLS containing mutations in the RPEL motif that disrupts G-actin binding. (* p <0.05, **p <0.01, *** p <0.001, Student’s t-test, n = 3 brains per condition). Scale bars: 50 μm. Bar graphs are plotted as mean ± SEM.