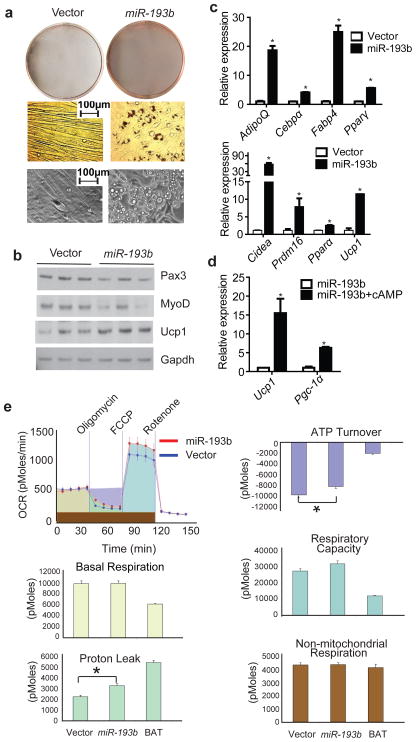
Figure 4. Ectopic expression of miR-193b induces C2C12 to form brown adipocytes under adipogenic differentiation conditions.
(a), C2C12 cells ectopically expressing miR-193b or control were exposed to pro-adipogenic conditions (described in Methods) for 5 days. ORO staining was used to assess lipid accumulation in cells. Representative micrographs of these cells are depicted (bottom row). (b). Western blot for myogenic markers Pax3, MyoD and brown fat marker Ucp1. n=3. (c), Real-time PCR analysis for expression of common adipogenesis markers (upper row) and brown fat selective markers (bottom row). n=3. (d), C2C12 cells expressing miR-193b (day 6) were stimulated with 500uM dibutyrul cAMP for 4h, and the expression of thermogenic markers, Pgc-1α and Ucp1 was examined by real-time PCR. n=3. (e), The metabolic profile of C2C12 cells expressing miR-193b (day 6) was assessed using the Seahorse XF24 Extracellular Flux Analyzer. A representative curve of the oxygen consumption rates (OCR) of control and miR-193b expressing cells at their basal states and upon treatment with drugs used to dissect the multiple components of the respiration process is plotted in the top-left panel. The parameters analyzed are represented by different colors in the upper panel and quantitated in other panels. In vitro differentiated primary brown adipocytes (BAT) were used as a reference. n=8. * P < 0.05, Student’s t-test; Means ± SEM.