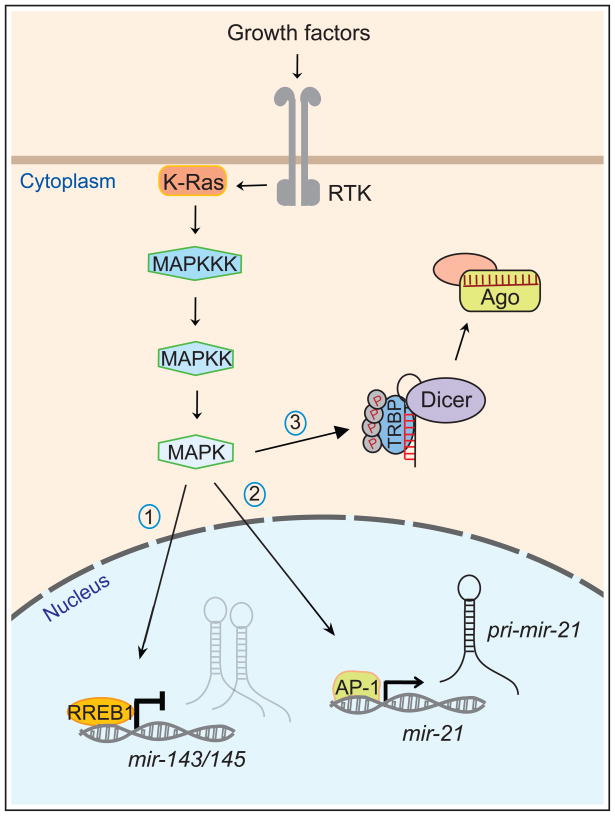
Figure 3.
Control of transcription and miRNA biogenesis by RTK/Ras signaling. Stimulation of receptor tyrosine kinases (RTK) by extracellular growth factors results in activation of the small GTPase Ras and a downstream kinase cascade including MAP kinase kinase kinase (MAPKKK), MAPKK and MAPK. Translocation of MAPK to the nucleus mediates the activity of downstream transcription factors, including (1) RREB1, a repressor of mir-143/145 and (2) AP-1, an activator of mir-21. Naturally, there are also many protein-coding genes whose transcription is regulated by RTK/Ras signaling. In addition, activation of MAPK results in phosphorylation of TRBP, a dsRBD cofactor of the Dicer RNase III enzyme. Phospho-TRBP mediates enhanced biogenesis of most miRNAs, including many growth-promoting miRNAs, although its activation is also associated with lower levels of the tumor suppressive miRNA let-7. For simplicity, Drosha cleavage of pri-mir-21 is not shown. Saj and Lai Highlights A set of fundamental cell signaling pathways controls most aspects of animal development. These pathways regulate expression of protein-coding genes and non-coding genes, including miRNAs. Several cell signaling pathways also directly regulate miRNA biogenesis at a post-transcriptional level.