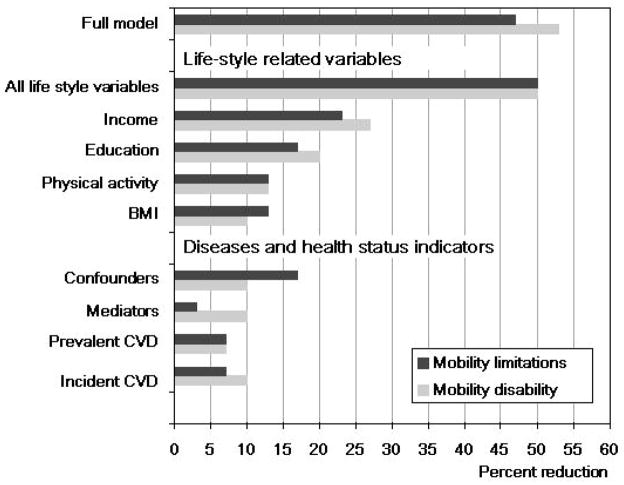
Figure 2.
Percent reduction of the protective effect of moderate alcohol intake (8–14 dr/wk in men; 4–7 dr/wk in women) on the risk of mobility limitations and mobility disability after adjustment of the basic model (age, gender, race, study site) for all potential confounders (full model), life-style related variables, diseases and health status indicators. Among these groups of variables, single variables with an effect greater than 5% were shown. Bars show the reduction in the protective effect of moderate alcohol intake obtained using the following formula: [(HR_basic − HR_adjusted)/HR_basic − 1] × 100