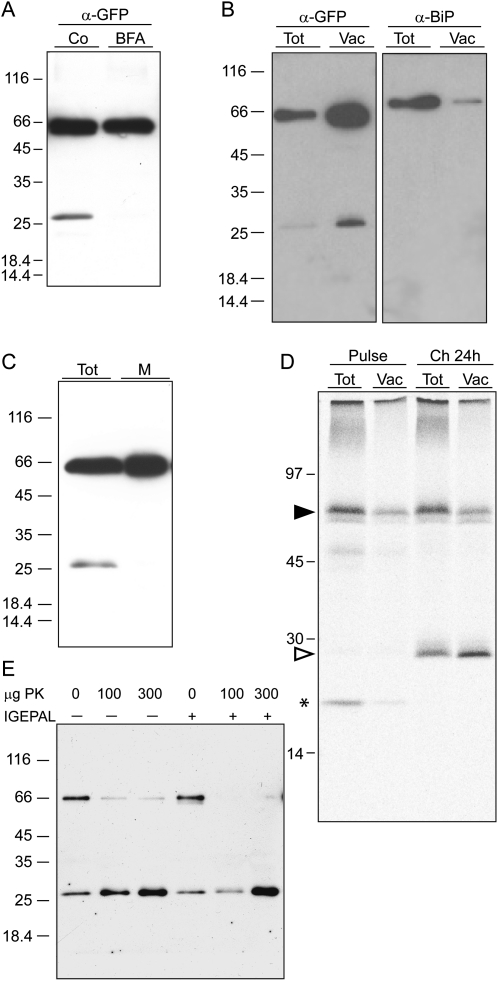
Figure 7.
Free GFP is released upon internalization of TPK1-GFP in the vacuole. A, Transgenic leaves were incubated for 24 h in the presence (BFA) or absence (Co) of brefeldin A. Proteins were extracted and equal volumes of homogenates were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and protein blot using anti-GFP antiserum. B, Vacuoles were isolated from protoplasts prepared from transgenic leaves. Protoplast (Tot) and vacuole (Vac) aliquots corresponding to equal α-mannosidase activity were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and protein blot using anti-GFP (α-GFP) or anti-BiP (α-BiP) antiserum. C, Transgenic leaf tissue was homogenized in the absence of detergent and microsomes were isolated. Equal aliquots of total homogenate (Tot) and microsomes (M) were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and protein blot using anti-GFP antiserum. D, Protoplasts prepared from transgenic leaves were pulse labeled for 1 h with 35S-Met/Cys and subjected to chase for 0 (Pulse) or 24 h (Ch 24 h). Equal aliquots of protoplast or vacuole homogenates were immunoprecipitated with anti-GFP antiserum and the selected proteins analyzed by SDS-PAGE and radiography scanning. The positions of TPK1-GFP (black arrowhead), free GFP (white arrowhead), and 20-kD polypeptide transiently associated to TPK1-GFP (asterisk) are indicated. E, Vacuoles were isolated as in B and the preparation was divided into six equal aliquots, which were treated with the indicated amount of proteinase K (PK) in the absence (−) or presence (+) of nonionic detergent (IGEPAL). Analysis was by SDS-PAGE and protein blot using anti-GFP antiserum. In each section, numbers at left indicate the positions of molecular mass markers, in kD.