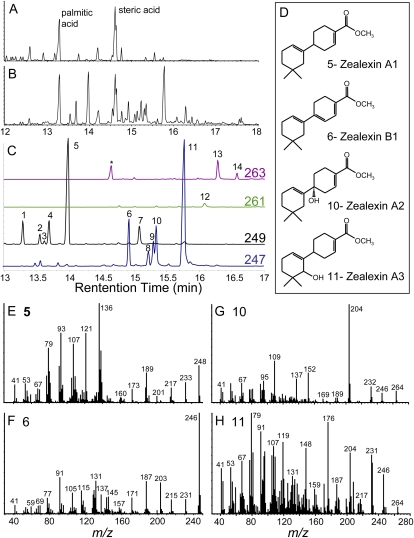
Figure 1.
Identity and GC/MS spectra of zealexin A1-A3 and B1 as methyl esters. A, Damage. B, Damage plus F. graminearum-inoculated (106 spores mL−1) maize stem samples after 48 h, analyzed as GC/(+)CI-MS total ion chromatograms (TIC). Predominant fatty acid methyl esters are labeled as palmitic and steric acid. C, Expanded GC/(+)CI-MS selected ion trace of predominant fungal-induced sesquiterpenoids as methyl esters. Analytes 1 to 5, denoted by [M+H]+ 249 ions, are unmodified sesquiterpene acids. For analyte 6, a partially unsaturated sesquiterpene acid, 247 is the parent [M+H]+ ion. As oxygenated acidic sesquiterpenoids, analytes 7 and 8 to 11 are denoted by 249 [M+H-H20]+ ions and 247 [M+H-H20]+ ions, respectively. Analytes 12 to 14 are denoted by 261 and 263 [M+H]+ ions, consistent with partially unsaturated, oxygenated acidic sesquiterpenoids. D, Zealexin structures deduced by NMR. EI spectra (mass-to-charge ratio) of: Zealexin A1 (E); analyte 5, Zealexin B1 (F); analyte 6, Zealexin A2 (G); analyte 10, and Zealexin A3 (H); analyte 11. In each section (A–C and E–H), the y axis denotes relative abundance of ions.