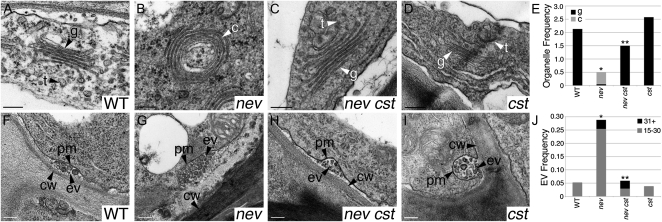
Figure 3.
Mutations in CST rescue the subcellular defects of nev mutant flowers. Transmission electron micrographs show cells in the sepal AZs of wild-type (WT) and mutant flowers (stage 17). A to D, The linear stacks of Golgi cisternae (g) and associated TGN (t) seen in wild-type (A) and cst-2 (D) flowers are replaced by circularized multilamellar structures (c) in nev-3 flowers (B). In nev-3 cst-2 flowers (C), the discrete structures of the Golgi and TGN are restored. E, Frequency of Golgi cisternae (black bars) and circularized structures (gray bars) per cell in sections of wild-type and mutant sepal AZs. Statistical differences between the type of multilamellar structure observed in nev and the wild type, and in nev cst and nev tissues are indicated by single and double asterisks, respectively (Fisher’s exact test; P = 0). A statistical difference was not detected between cst and wild-type tissues. n ≥ 26 cells per genotype. F to I, Extracellular vesicles are frequently observed in the apoplastic space of nev-3 AZ cells (G). In wild-type (F), nev-3 cst-2 (H), and cst-2 (I) AZs, the appearance of extracellular vesicles is significantly reduced. J, Frequency of extracellular vesicles (clusters of 15–30, gray bars; clusters of 31+, black bars) in wild-type and mutant sepal AZ cells. Statistical differences between nev and the wild type and between nev cst and nev tissues are indicated by single (Fisher’s exact test; P < 0.012) and double (P < 0.02) asterisks, respectively. A statistical difference was not detected between cst and wild-type tissues. n ≥ 26 cells per genotype. cw, Cell wall; ev/EV, extracellular vesicles; pm, plasma membrane; t, TGN. Bars = 200 nm.