Figure 1. HiSBE synthesis is facile and orthogonal to common biological nucleophiles.
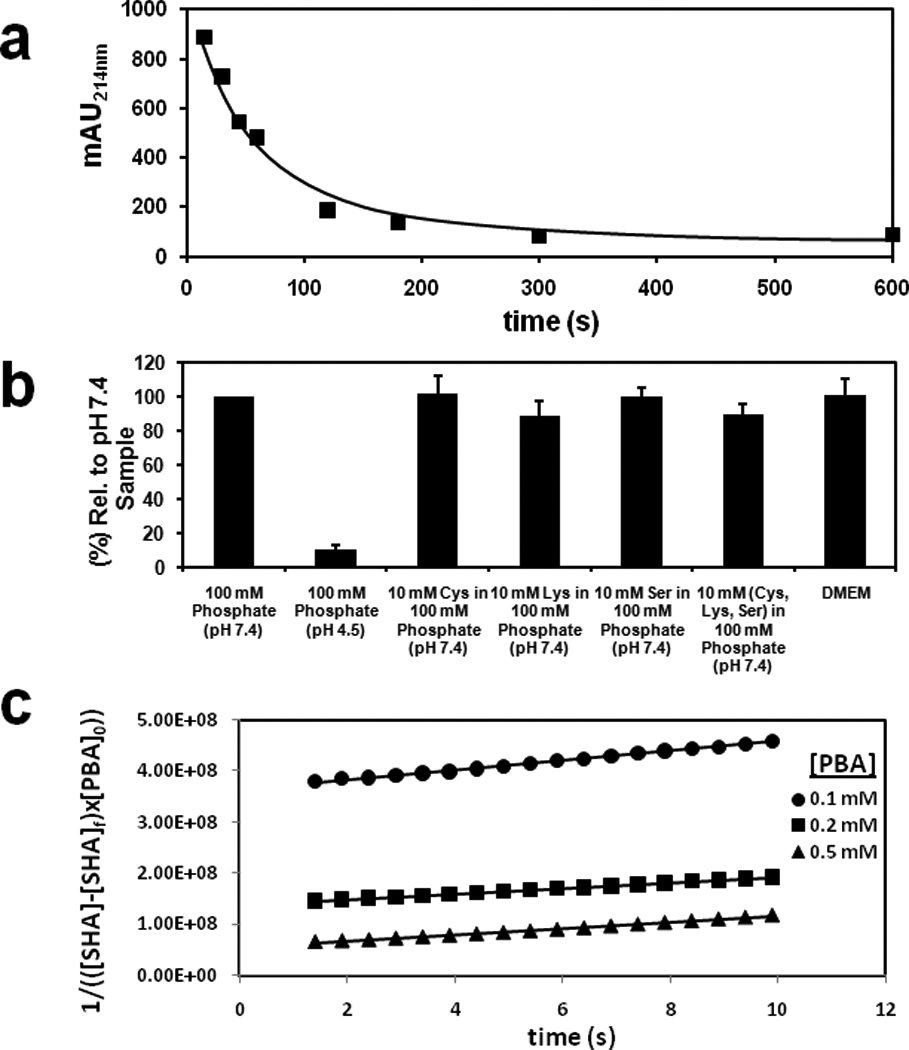
(a) Time dependent boronate ester formation between SHA and PBA immobilized on agarose in 100 mM phosphate buffer at pH 7.4. Reaction solutions containing 6 mM SHA (0.0036 mmoles, 0.6 mL) were incubated with PBA agarose (0.1 ml, 0.002 mmole of immobilized PBA). The SHA concentration in the supernatant was quantified by absorption spectrophotometry at 214 nm.
(b) The efficiency of HiSBE synthesis in the presence of common biological nucleophiles. Reaction solutions containing 6 mM SHA (0.0036 mmoles, 0.6 mL) in 6% DMEM/100 mM phosphate buffer at the indicated pH and with the indicated nucleophiles were incubated with PBA agarose (0.1 ml, 0.002 mmole of immobilized PBA) for 5 min. After incubation, the resin was washed to remove uncomplexed SHA, and the complexed SHA was eluted with 100 mM phosphate buffer at pH 4.5. Eluted SHA was quantified by absorption spectrophotometry at 214 nm.
(c) Kinetic measurement of 0.1 mM SHA with 0.1 mM, 0.2 mM and 0.5 mM PBA in 100 mM phosphate buffer at pH 7.4. The reaction rates were modeled after third-order reaction kinetics and were determined by plotting 1/(([SHA]-[SHA]f) × [PBA]0)) versus time. The slopes were used to approximate the rate constants. k = (7.01 ± 2.04) × 106 M−2s−1.
