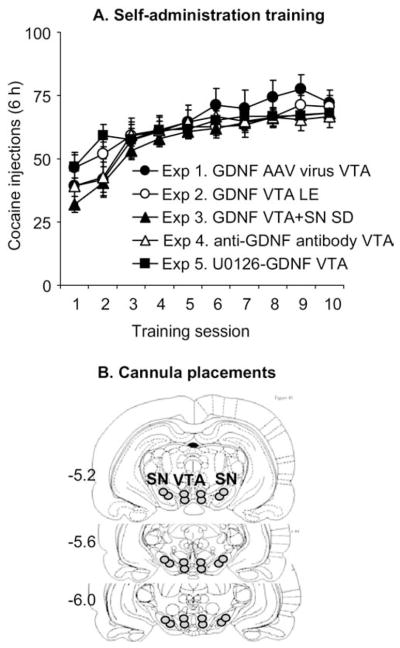
Figure 1.
Cocaine self-administration training in Experiments 1–5. (A) Mean ± SEM number of cocaine injections (.75 mg/kg/injection) over the 10 6-hour daily self-administration sessions. During training, lever presses or nose pokes were reinforced under a fixed-ratio-1 40-sec timeout reinforcement schedule; cocaine injections were paired with a 5-sec tone-light cue. Data are from rats that were subsequently tested for cue-induced cocaine seeking after ventral tegmental area (VTA) injections of an adeno-associated virus (AAV) viral vector containing glial cell line– derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) cDNA (AAV-GDNF) or red fluorescent protein cDNA (AAV-RFP) (Experiment 1, Long-Evans rats [LE], total n = 18), GDNF in VTA of LE rats (Experiment 2, total n = 28), GDNF in VTA or SN of Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats (Experiment 3, total n = 33), anti-GDNF monoclonal neutralizing antibodies or mouse immunoglobulin G (Experiment 4, SD rats, total n = 16), and U0126+ GDNF in VTA (Experiment 5, SD rats, total n = 34). (B) Schematic illustration of the approximate cannulae placements within the VTA (Experiments 1–5) and SN (Experiment 3) (This figure was published in The Rat Brain Stereotaxic Coordinates by Paxinos and Watson, pp. 18 – 83, copyright Elsevier 2005 [86]); numbers represent millimeters posterior from bregma. SN, substantia nigra.