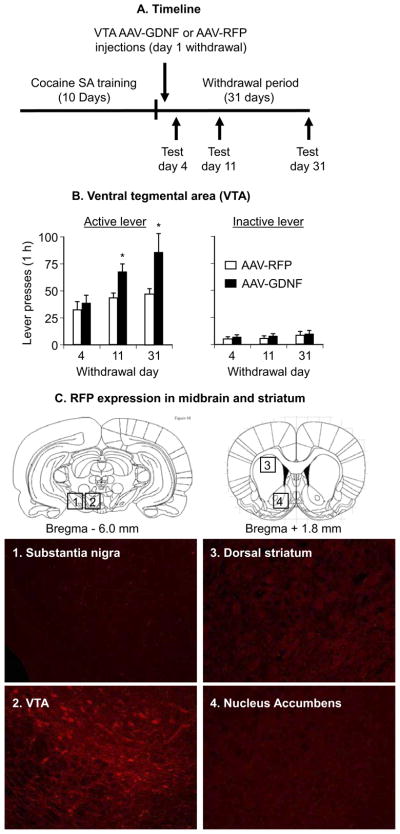
Figure 2.
Ventral tegmental area (VTA) injections of an adeno-associated virus (AAV) viral vector containing rat glial cell line– derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) cDNA potentiate cue-induced cocaine seeking. Data are mean ± SEM responses per 1 hour on the previously active lever (left column) and on the inactive lever (right column) during the extinction tests for cue-induced cocaine seeking performed on withdrawal days 4, 11, and 31. During the test sessions, cocaine was not available, and lever-presses resulted in the delivery of the tone-light cue previously paired with cocaine injections. AAV viral vector containing rat GDNF cDNA (AAV-GDNF) or red fluorescent protein cDNA (AAV-RFP) was injected bilaterally into the VTA on withdrawal day 1. (A) Timeline of the Experiment, (B) VTA injections and (C) RFP expression in midbrain and striatum (see Supplement 1 for details of the experimental procedures) (This figure was published in The Rat Brain Stereotaxic Coordinates by Paxinos and Watson, pp. 18 – 83, copyright Elsevier 2005 [86]). * Different from AAV-RFP, p <.05 (n = 8 –10, Long-Evans rats per experimental condition). SA, self-administration.