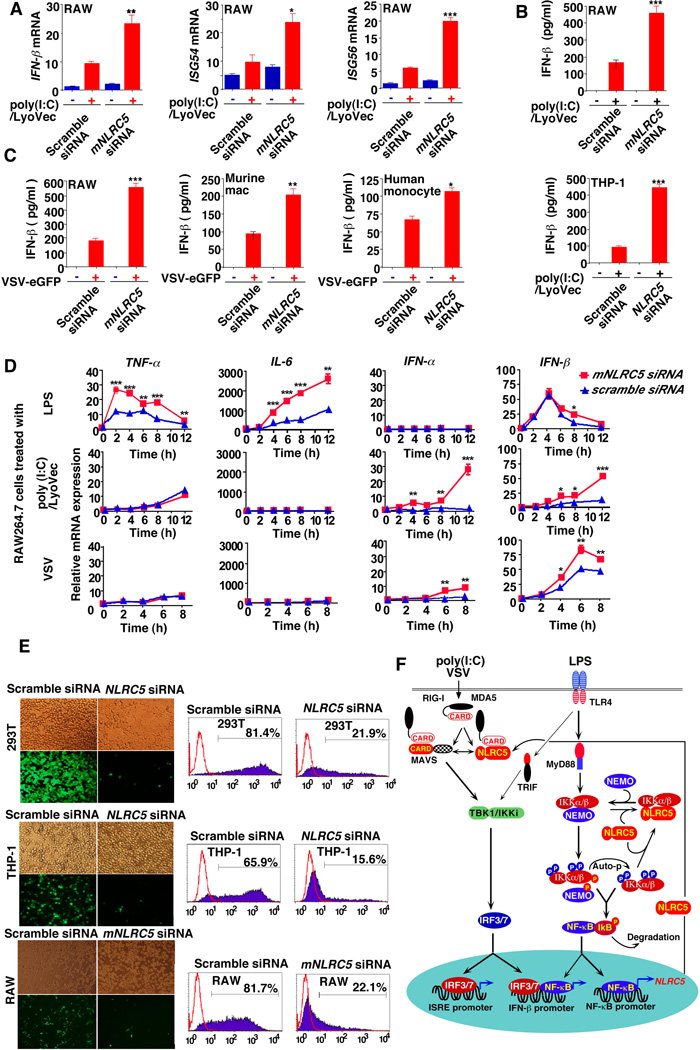
Figure 7. Knockdown of NLRC5 enhances cytokine response and antiviral immunity.
(A and B) RAW264.7 cells or THP-1 cells were transfected with mNLRC5/NLRC5-specific siRNA or scrambled siRNA, followed by poly(I:C)/Lyovec treatment. ISG-54, ISG-56, IFN-β mRNA and IFN-β protein were determined by real-time RT-PCR or ELISA.
(C) NLRC5 or mNLRC5 knockdown and control cells were infected with VSV-eGFP. Cell supernatants were used to measure IFN-β protein secretion by ELISA.
(D) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with mNLRC5 siRNA or scrambled siRNA for 36 h and then treated with LPS, poly (I:C)/LyoVec (1 µg/ml) or VSV-eGFP infection. Total RNAs from the treated cells were harvested at different time points and used for real-time PCR analysis to determine the expression of TNF-α, IL-6, IFN-α and IFN-β. The data in (A–D) are reported as means + SEM of three independent experiments. Asterisks indicate significant differences between groups (* P< 0.05, ** P<0.01, *** P<0.001 determined by t-test analysis).
(E) 293T cells, THP-1 cells and RAW264.7 cells were transfected with NLRC5-, mNLRC5-specific siRNA or scrambled siRNA, and then infected with VSV-eGFP. Viral infections were analyzed by fluorescence microscopy (with phase contrast as a control) as well as FACS analysis.
(F) Proposed model illustrating how NLRC5 negatively regulates both NF-κB and type I IFN signaling pathways. Auto-p, autophosphorylation.
See also Fig. S7.