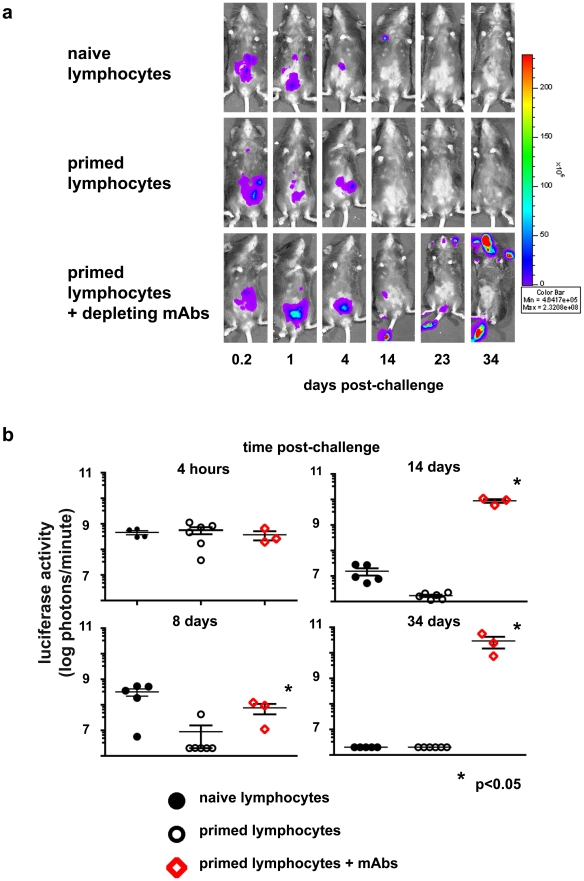
Figure 6. Protection conferred on naïve RAG1ko mice by adoptive transfer of primed lymphocytes is abrogated by simultaneous administration of T cell-depleting monoclonal antibody cocktail.
Groups of RAG1ko mice received 2×106 NK-depleted hepatic lymphocytes from naïve or vaccinia virus-primed mice; a third group received both the primed lymphocytes and T cell-depleting monoclonal antibody cocktail simultaneously. All groups were challenged with 1×105 pfu rVV-luc ip 5 days later. (a) IVIS images of representative mice from the indicated recipient groups are shown at various time points following challenge with rVV-luc. (b) The measurements of rVV-luc viral loads in each group over time are shown, with relative viral loads based on the number of photons emitted, normalized for a 1 minute exposure. The measurement for each individual mouse is plotted, and the mean is indicated by the centerline with error bars representing the SEM. Statistical analyses were performed using t tests and Mann-Whitney analysis comparing the primed lymphocyte transferred & T-depleted group and the isotype-treated groups at various time points to that of the naïve control group. Statistically significant differences between the depleted group and the isotype-treated groups post-challenge are indicated by asterisks (p<0.05). Results are representative of 3 independent experiments.