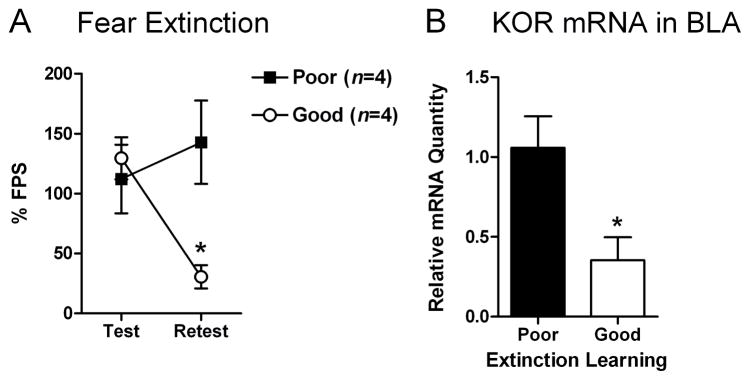
Figure 6. Effective fear extinction decreases the relative quantity of kappa opioid receptor (KOR) mRNA in the basolateral nucleus of the amygdala (BLA).
Rats were subjected to fear conditioning (10 light-shock pairings) and tested 24 hr later for fear-potentiated startle (FPS). One day later, rats were given extinction training (60 presentations of the light alone) and the next day they were retested for FPS. Rats with the lowest (“good” extinction; n=4) or highest (“poor” extinction; n=4) levels of FPS were killed immediately after testing by decapitation and gene expression in the BLA was analyzed using qPCR. (A) Rats that had good extinction learning had significantly less FPS during the retest than rats with poor extinction learning (mean ± S.E.M.). (B) Rats that had good extinction learning had 67% less KOR mRNA in the BLA than those that had poor extinction learning. *P<0.05.