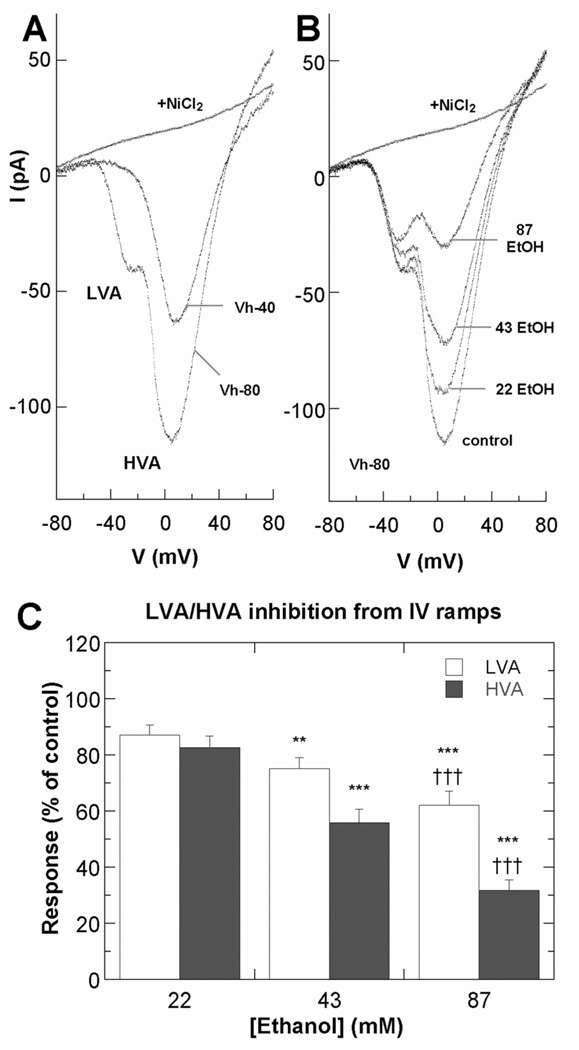
Figure 3. Ethanol inhibits VGCCs in hippocampal pyramidal neurons.
A–B. Representative IBa currents from voltage ramps from Stage 3 neurons 18–30 h after plating. A. Current voltage properties of LVA and HVA currents in a control neuron at Vhold −40 or −80 mV before and after exposure to 100 µM NiCl2. B. Current-voltage properties of LVA and HVA currents in an individual neuron at Vhold −80 mV before and after exposure to ethanol added by perfusion in the external solution. C. Summary of effects of ethanol on LVA and HVA currents, plotted as percent of peak amplitudes in the absence of ethanol. Asterisk indicates significant difference from the control group; *p < 0.005; **p < 0.0001 (n=15 neurons; repeated measures ANOVA with Dunnett posthoc test). Cross indicates significant difference from the 43 mM ethanol group; ††† p < 0.0001.