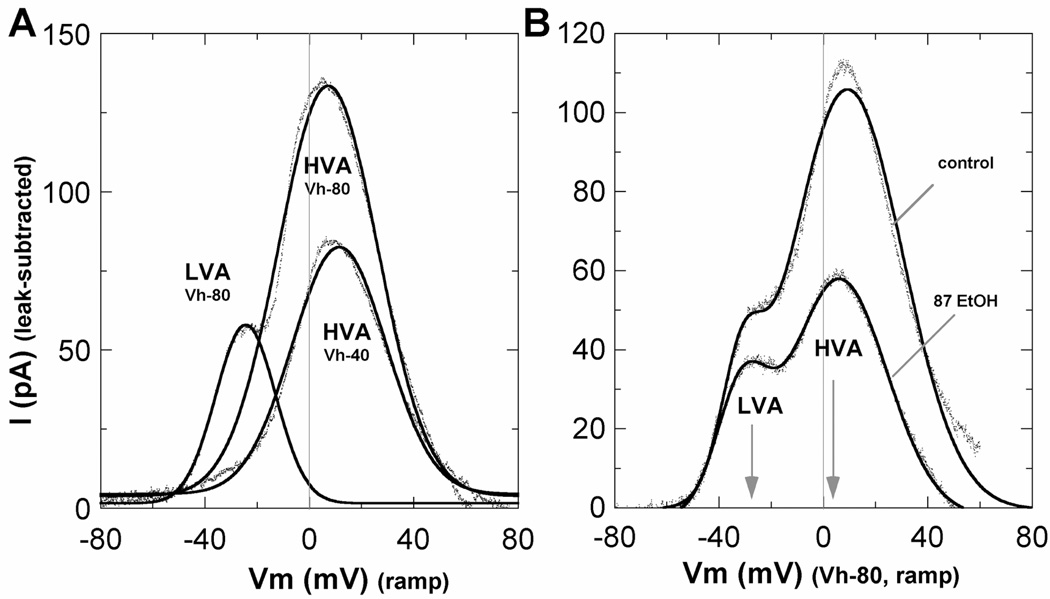
Figure 4. IBa components and ethanol inhibition after leak subtraction.
A. Absolute values of LVA and HVA current components after subtraction of the NiCl2-insensitive (leak) currents from voltage ramp data. Data from a representative Stage 3 neuron are shown as individual data points and fitted by one or two Gaussian distributions (solid lines). B. Leak-subtracted LVA and HVA current components in a representative neuron before and after exposure to 87 mM ethanol. In 6 cells compared before and after leak subtraction, inhibition of LVA current by 87 mM ethanol averaged 41% before and 30% after subtraction, whereas inhibition of HVA currents averaged 69% before and 61% after subtraction (not shown). Together, these results confirm greater sensitivity of HVA currents even though nearly half the measured peak of LVA current reflects the HVA component, and that ethanol effects are not related to altered leak currents.