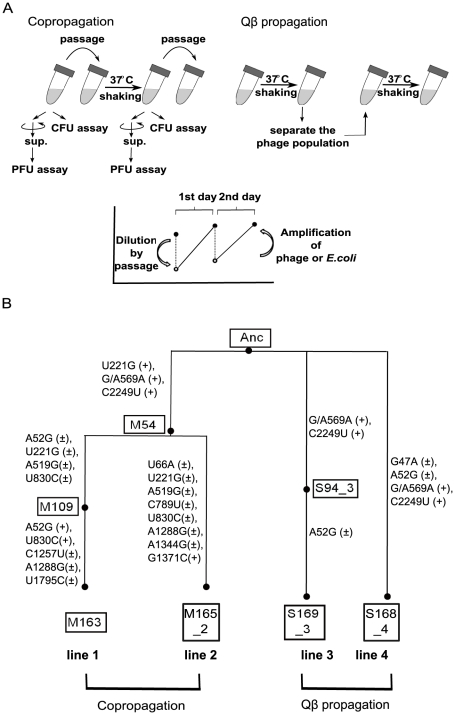
Figure 1. Model evolution system.
(A) In the copropagation regime, cultures including E. coli and Qβ were passaged into fresh medium every day. In the Qβ propagation regime, only Qβ was isolated and used to infect fresh growing Anc(C). The values of PFU/ml or CFU/ml of cultures incubated for about 24 h (copropagation regime) or about 6 h (Qβ propagation regime) were determined. The concentration of Qβ and/or E. coli decreased by dilution in passage and increased by amplification or growth. (B) Phylogeny and nomenclature of the experimental lineages used in this study. Copropagation was conducted in two lines designated as lines 1 and line 2. Qβ propagation was conducted independently in two lines: line 3 and line 4. The ancestral organisms were designated as Anc. The M and S represent the sample of copropagation and Qβ propagation lines, respectively. The numbers in the boxes represent the replication generation numbers of Qβ, and the numbers after the underbar represent the lineage line number. The mutations observed in the Qβ genome in both propagation experiments are shown in the order of the sequence of the ancestral Qβ genome, position on the genome, and the sequence of the evolved genome. The + and ± in parentheses represent monomorphic and polymorphic sequences, respectively. Position 569 of Anc was heterogeneous with G and A, although the Anc Qβ population was derived from cloned cDNA.