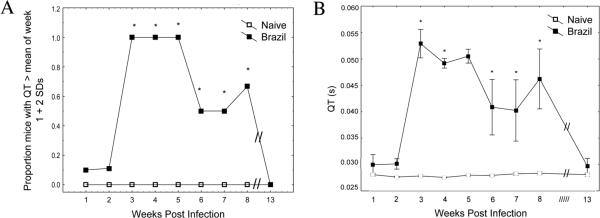
FIGURE 1.
Kinetics of QT elongation following Trypanosoma cruzi infection. BALB/c mice were infected i.p. with 5,000 Brazil strain TCT, then lead 2 ECG tracings recorded at various time points (wk 1–8 and wk 13). QT intervals from individual mice were analyzed from 100–200 beats using an automated software package. (A) Baseline recordings from all mice were used to define an elongated QT interval as any value > QT(mean) + 2 standard deviations (0.035s). Significantly higher proportions of T. cruzi infected animals displayed elongated QT intervals wk 3–8 as compared to uninfected controls (P<0.05, Fisher Exact test). (B) Actual QT intervals obtained from individual mice were also significantly higher in T. cruzi infected animals than controls during wk 3–8 PI (P<0.05, Mann-Whitney U-test).