Figure 6. YY1 is an RNA-binding protein that bridges RNA and chromatin.
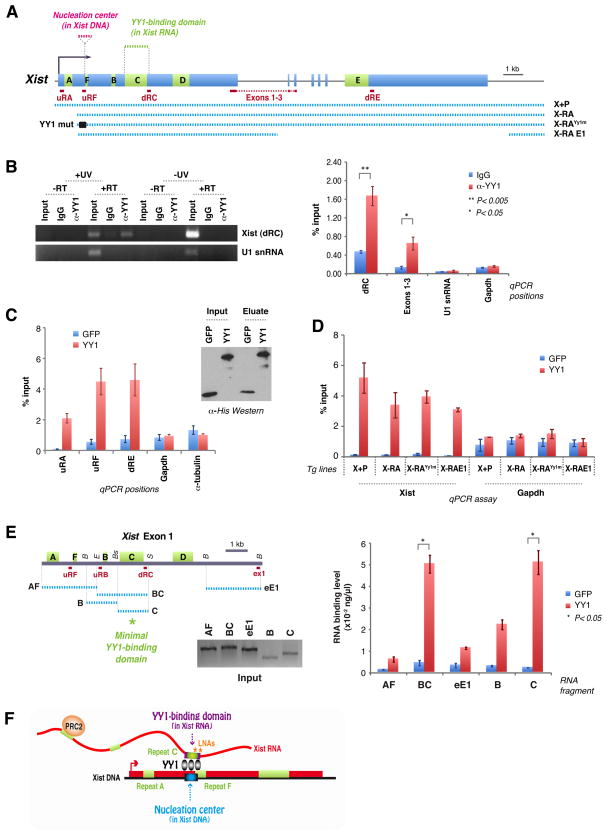
A. Map of Xist, transgenes, and RT-PCR amplicons.
B. UV-crosslink RIP of female MEFs, followed by qRT-PCR for Xist (dRC, Exons 1–3) or RNA controls (U1 snRNA, Gapdh). YY1 antibodies or IgG used. 1% input. -UV and -RT controls performed in parallel. Left panel, EtBr-stained gel. Right panel, RT-PCR quantitation. Averages ± SE of 3 independent experiments.
C. RNA pulldown assay using purified His-YY1 or His-GFP (Western blot) and WT female ES RNA. qRT-PCR at 3 different Xist positions (uRF, uRA, dRE) and two controls (Gadph, α-tubulin). Averages of 5 independent experiments ± SE.
D. RNA pulldown assay using RNAs from transgenic lines after dox induction. qRT-PCR performed at dRC. Averages ± SE for 3 independent experiments.
E. RNA pulldown assay using equal molar amounts of in vitro-transcribed RNA fragments AF (2.5kb), BC (2.5kb), eE1 (2.5kb), B (1.2kb), and C (1.8kb) as illustrated in the map. Quantitated by qRT-PCR. 20% of input shown on the gel. P calculated using t-test. B, BamHI; E, EcoRI; Bs, BstBI; S, ScaI. Averages of 2 independent experiments ± SE.
F. Bivalent function of YY1. YY1 contacts Xist RNA and DNA via different sequences. Asterisks, positions of blocking LNAs (Sarma et al., 2010).