Figure 1. PARP-1 gene deletion-associated inhibition of IL-5 occurs at the mRNA level without an effect on IL-4R activation.
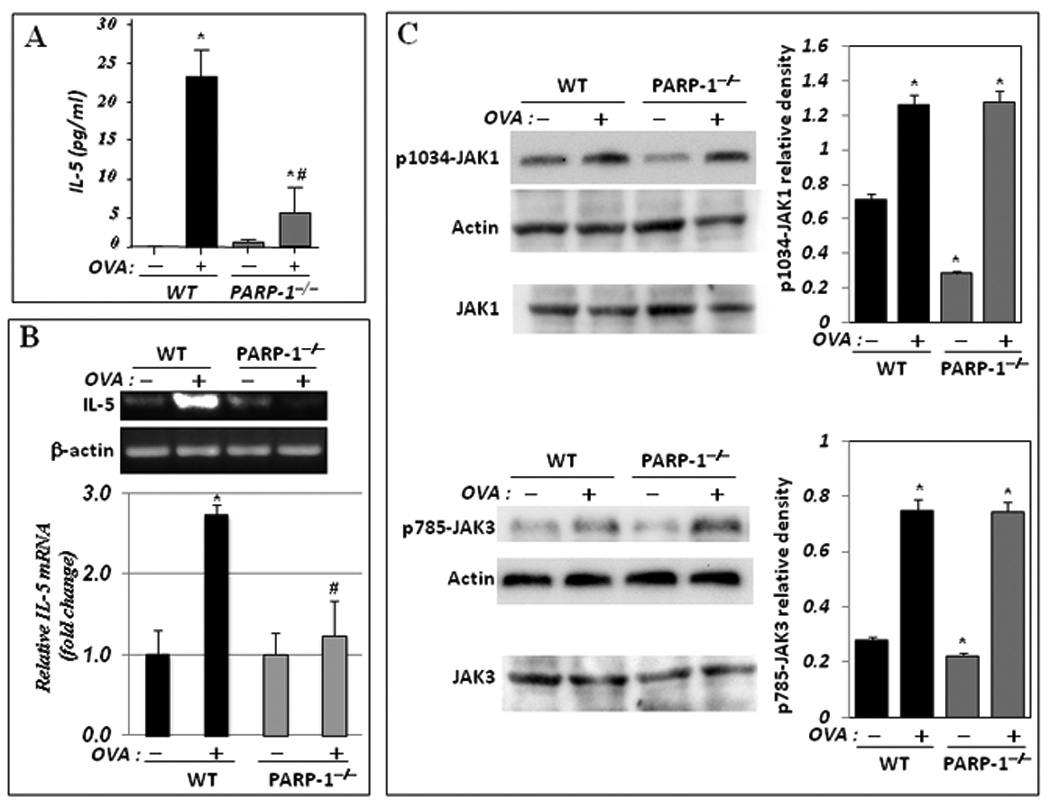
(A) WT and PARP-1−/− mice were sensitized to and challenged with OVA. Mice were then sacrificed and lungs were subjected to BAL and spleens were collected for RNA or protein extraction. (A) BAL fluids were assessed for IL-5 using a BioRad single-plex system. Data are given as means ± SEM of values obtained from at least six mice per group. *, difference from unchallenged mice, p < 0.01; #, difference from WT mice subjected to the OVA challenge, p < 0.01. (B) Total RNA, extracted from portions of the collected spleens, was subjected to cDNA generation followed by conventional (upper panels) or real-time (bottom panel) PCR with primers specific to murine IL-5 or β-actin. (C) Protein extracts were prepared from the remaining portions of the collected spleens and subjected to immunoblot analysis with antibodies to JAK1, JAK3, the phosphorylated form of JAK1 at tyrosine residue 1034 (p1034-JAK1), the phosphorylated form of JAK3 at tyrosine residue 785 (p785-JAK3), or actin. Note that JAK1 and JAK3 blots (C, bottom panels) are of the same samples used for p1034-JAK1 and p785-JAK3, respectively but were generated using a different gel. The immunoblots were quantified using Adobe Photoshop CS and data is expressed as relative density; *, Difference from untreated WT control, p< 0.01.
