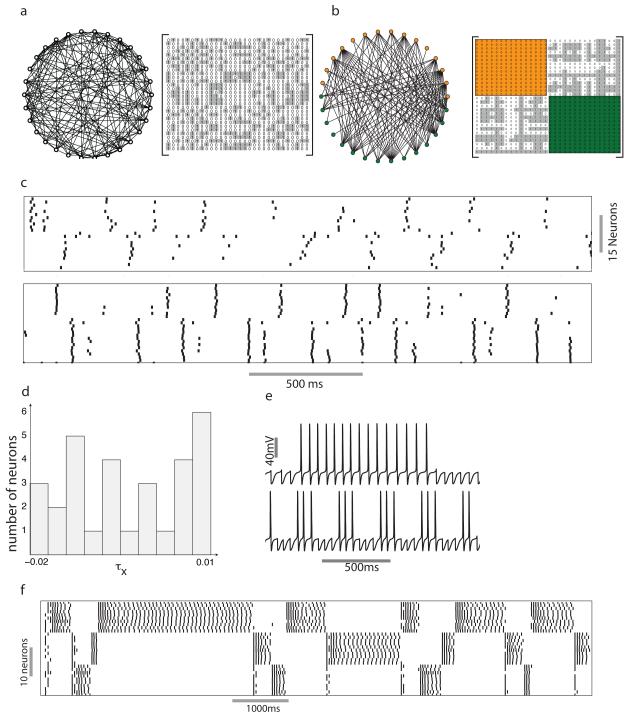
Figure 6.
Coloring–based dynamics in realistic neural networks. a) A random bipartite graph. Individual neurons receive between 1 and 14 inputs from LNs belonging to a different color and the corresponding adjacency matrix. b) The neurons were grouped into two groups based on the color. Adjacency matrix of the network shows off–diagonal blocks with ones (shaded gray) and zeros. c) Raster plot showing the response of the network to input in the absence (top panel) and the presence (bottom panel) of random excitatory input from PNs. d) Distribution of the parameter τx that perturbs the time scale of the Ca2+ dependent potassium current. e) Dynamics of inhibitory LNs as a function of τx. The top trace shows the response of a neuron belonging to a reciprocally inhibitory pair with τx = 0.01. The bottom trace shows the response of a neuron with τx = 0.02. f) Dynamics of a group of 30 LNs that form a three–color network. The value of τx for each LN in the network was picked from the distributions shown in (d).